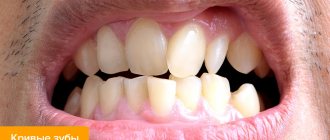
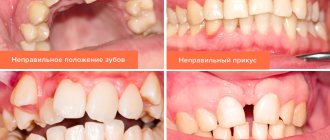
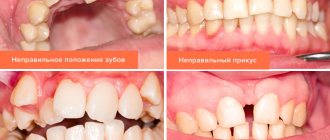
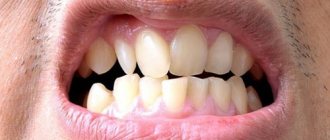
In case of complete or partial absence of teeth, one of the main treatment methods is the production of a complete or partial removable denture. At the same time, despite the fact that from an aesthetic point of view, at first it can completely satisfy the patient, from a physiological point of view there is a certain range of problems that it does not solve in any way and which are worth paying attention to.
Improving facial aesthetics is the only problem that a removable denture can solve. However, this effect is temporary; the patient must periodically reline it.
Let's consider the main consequences of tooth loss in patients. Spend 5-10 minutes reading this material, the information contained in it can be very useful.
Prices for treatment of caries of anterior teeth in Moscow
The price for treating caries of anterior teeth largely depends on the technique used. Standard therapy with the installation of a light filling will cost from 5,800 rubles. But prices for restoration start at 12,500 rubles. Treatment costs approximately the same without an Icon drill. Treatment of pulpitis on the front teeth involves cleaning the canals, which will add several thousand more to the total amount. If the tooth is seriously damaged and installing a filling is impossible, get ready for serious expenses. The average cost of a ceramic crown is from 25,000–30,000 rubles, and turnkey implantation will cost at least 55,000–100,000 rubles for the installation of one implant.
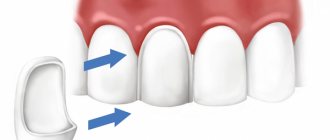
Installation of veneers
This is a highly effective correction method. Veneers are thin plates made of ceramic or porcelain. They are placed on top of natural teeth.
The main advantage of the method is that the plates cover and protect the enamel coating of the dental units. In other words, there is no need to grind or file down adjacent teeth.
Contraindications for installing veneers:
- Severe destruction of dental units from the tongue.
- The presence of large fillings.
- Grinding of teeth.
- Having a bad habit of opening bottles with your teeth, cracking nuts with them, etc.
In addition, veneers cannot be installed if six or more chewing units are missing from the mouth.
Installation of a bridge
The use of fixed orthodontic structures is a modern way to fill wide gaps in the dentition.
In order for the prosthesis to be securely fixed, it is necessary to have supporting dental units. It is on them that the entire structure is attached.
The best option is to make a bridge from metal ceramics. The service life of this design is 7 years or more. At the same time, the bridge retains its original shade and does not differ from adjacent natural teeth.
Contraindications to installing a prosthesis on rare teeth:
- Acute periodontitis.
- Parafunctions of the masticatory muscles.
- Insufficient height of supporting teeth.
If there are absolute contraindications, the doctor makes a decision regarding the advisability of using a different treatment method.
Causes of the anomaly
The reasons for “short” teeth can be many factors, both actually reducing the size of clinical crowns and creating a visual effect of their reduction:
- Heredity. “Short” teeth of parents are often genetically passed on to their children.
- Increased abrasion of occlusal surfaces , as a result of which clinical crowns become shorter. The reasons for increased abrasion can be different; this is a large independent topic.
- Inflammatory processes in the periodontium , directly or indirectly affecting the size of the clinical crown.
- Metabolic disorders in periodontal and dental tissues , including those caused by malnutrition of hard and soft tissues.
- Excessive thinness of the upper lip , in which the gums are exposed more than they should when smiling.
- Increased size of the lip frenulum , which “creeps” onto the crown.
- Gingival hyperplasia , leading to the closure of part of the crown.
- Underdevelopment of the alveolar process , leading to a lack of sufficient support for normal tooth growth.
- Radiation exposure.
- Early removal of milk jugs.
However, the most significant and common causes are still considered to be disturbances in the formation of teeth in the embryonic and childhood periods - both genetic and reactive (acquired) in nature.
For example, severe infections suffered in infancy or serious illnesses of the mother during pregnancy.
Installation of crowns
These are non-removable structures that can be used to eliminate dental defects. The installation of crowns is also indicated in case of severe destruction of dental units. The essence of the method is to insert an artificial tooth into the gum using a pin made of metal.
Installing crowns requires some preparation. The patient's natural teeth are prepared and, if necessary, pulp removal is performed. Crowns take several days to make. During this period, the patient is provided with temporary structures. The finished crowns are completely identical to the patient’s teeth. They differ only in width, which makes it possible to hide large gaps between chewing units.
The following conditions are contraindications: loose teeth, allergic reaction to the components used, periodontal pathologies. In addition, crowns are not placed on anyone under 16 years of age.
Preparing for treatment
Elimination of the defect requires a comprehensive examination of the oral cavity and selection of optimal treatment. In particular, the doctor assesses the size of the pathological holes. An x-ray examination is also prescribed, which allows you to identify the presence of hidden injuries. Regardless of the chosen scheme, before starting treatment of rare teeth, therapy for caries and other pathologies of the oral cavity is prescribed.
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
The most difficult operation to correct a malocclusion is implantation. Before it is performed, a panoramic photograph of the jaw is taken, which allows you to select the appropriate pin size.
Implantation is contraindicated in many cases. It cannot be used in the presence of oncological pathologies, tuberculosis, a number of chronic diseases and allergies to anesthesia. Implantation takes several hours. During the procedure, tooth extension is carried out in three projections: width, height and length.
After the operation, the patient should follow certain procedures for several months to prevent the development of complications.
Formulas for calculating proportions
The normality of the crown part of the teeth is determined not by their size, but by the width and length of the dental arches, which are considered normal for a specific group of patients.
If the length and width of the arch correspond to the norm, and all the teeth on it are located without crowding or gaps, then their sizes are considered normal.
Many different techniques have been proposed to determine the normality of the jaw arches, taking into account the age, facial type and nationality of the patient. Three of them are discussed below - the Gerlach, Pon-Linder-Hart and Corkhouse methods.
Gerlach method
According to the Gerlach method, the dentition is divided into 3 segments:
- anterior, consisting of 4 incisors;
- two lateral ones, consisting of canines, premolars and the first molar.
Next, the calculation is made according to the following algorithm:
- The length of each segment is measured. In this case, the value of the length of the lower frontal segment is obtained by multiplying the length of the upper frontal segment by the Tone coefficient (1, 35).
- Compare the obtained lengths of the segments with each other and the tabular data compiled by Gerlach. With normal jaw sizes, they must be in certain proportions to each other.
If it turns out that the dimensions of the arches are normal, and there is no crowding or gaps, then the dimensions of the clinical crowns are normal.
Reference. All methods used involve measurements of dental arches at strictly defined points and according to certain methods. Because of their relative complexity and length, they are not included here. But they can be easily found in numerous sources.
Pon-Linder-Hart method
This technique is intended to determine the normal width of the dental arches in children with variable and permanent dentition. In this case, the formula developed by Pont is used and has the following form:
A ∶ 80 × 100 = distance between first premolars
A ∶ 64 × 100 = distance between first molars, where:
- A – total width of 4 incisors;
- 80 and 64 – Pon coefficients (indices).
Linder and Hart found that these coefficients for children of German nationality should be 85 and 65, respectively.
The algorithm for determining the parameters of the upper jaw according to Pon-Linder-Hart is as follows:
- The total width of all incisors along their cutting edge is measured.
- The obtained data is substituted into the Pon formula, and the distance between the first painters and premolars is calculated.
- The actual width of the dental arch between premolars and molars is measured.
- The measured value is compared with the results determined using the Pon formula.
- A conclusion is made about the compliance of the width of the arches and the size of the crowns with the norm.
Based on the data obtained, a treatment plan is developed. In particular, when the row in the area of premolars and molars is narrowed by more than 6 mm, it is recommended to remove some units or widen the jaw.
Corkhouse method
The Corkhouse method is based on the relationship that exists between the total width of the maxillary incisors and the length of the anterior segment of the jaw arch, measured according to a certain scheme.
The following algorithm of the Corkhouse technique is used:
- The total width of the 4 maxillary incisors is measured.
- The length of the anterior segment of the jaw arch is measured. This is done using a technique developed by Corkhouse by connecting certain points on the occlusal surface.
- The actual size of the arc segment is compared with the desired one.
Based on the data obtained, a conclusion is made that the size of the teeth and arches corresponds to the norm, and a treatment plan is developed.
Possible consequences
The main problem of microdentia with preserved functionality of the dentofacial apparatus is the psychological discomfort that the patient experiences when realizing his defect. This is not as harmless as it might seem at first glance.
A person’s psychological state can have a decisive impact on his quality of life, cause central nervous system disorders and even lead to physical illness.
If microdentia is accompanied by functional and organic disorders, somatic diseases are added to psychological problems. This may be a gastrointestinal disease due to poor chewing of food, asymmetry disorder and the effect of premature aging of the face when the lower third is reduced due to a low bite, etc.
Ultimately, the consequence of “short” teeth can be a general deterioration in health caused by both physical and psychological factors.
As for the influence of microdentia on the condition of the dentofacial apparatus, it can be expressed in the following:
- Displacement of the crowns distally , that is, backwards.
- Formation of tremata and diastemas , as a result of which the teeth lose stability in the mesial-distal direction and create an increased load when chewing on the periodontal ligament. It should be noted that normally all crowns have contact with each other in the proximal areas.
- Impaired diction due to the gap between the teeth and the low height of the clinical crown.
- Development of periodontitis and periodontal disease.
Summarizing all of the above, it is necessary to conclude that severe microdentia must be corrected.
How difficult and dangerous is it to remove an impacted tooth in modern dentistry?
In this publication, we will consider the features of treatment of dental anomalies - hyperdontia.
Here https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/zubov/kolichestva/gipodentiya.html all the most important things about hypodentia.