candidiasis in children is an infectious dental disease caused by fungal microflora (microorganisms belonging to the genus Candida). According to WHO statistics, manifestations of this pathology are observed in 5% of newborns and 10% of infants. Illness in pediatric dentistry can be chronic or acute. In this case, candidiasis can act as an independent dental pathology or be one of the signs of severe systemic diseases.
1.General information
In order not to be interrupted by terminological references in the future, we will stipulate the following as a kind of preamble.
Opportunistic is an infection that occurs, literally, “at an opportunity,” “if possible,” i.e. under a certain combination of conditions favorable for the opportunistic microorganism. In turn, conditional pathogenicity implies asymptomatic parasitism or commensalism (harmless coexistence) of any microculture in the host’s body - as long as the host is healthy and immunocompetent - and the ability of this culture to undergo rapid pathogenic activation with a weakening of the immune defense, a significant change in the structure of the microbiome and some other circumstances.
Mycosis is a systemic infection by fungal cultures. Candidiasis is an extremely widespread (in fact, the most common) variant of mycosis, caused by yeast-like opportunistic fungi of the numerous genus Candida, most often Candida ablicans (the causative agent, in particular, of urogenital “thrush”).
Thus, pharyngeal candidiasis is an opportunistic mycosis caused by the activation of Candida and predominantly localized in one of the ENT organs.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Prevention of candidiasis in childhood
Measures aimed at preventing the occurrence and development of the disease in childhood include:
- limiting contacts between children and carriers of this disease in preschool educational institutions, schools, sections and clubs;
- maintaining the baby’s personal hygiene;
- competent organization of the process of feeding the baby;
- maintaining a healthy diet;
- inclusion in the child’s diet of foods rich in all essential vitamins;
- sterilization of bottles, pacifiers and nipples;
- systematic visits to the pediatric dentist to assess the state of oral health.
It is important to understand that self-medication for oral candidiasis not only does not promote recovery, but can also lead to consequences dangerous to the health and life of the baby. That is why, if any symptoms indicating the development of this disease are detected, it is necessary to contact a dental clinic as soon as possible and undergo a course of treatment according to a regimen drawn up by an experienced dentist.
2. Reasons
In the clinic of infectious diseases, the main and universal cause, as well as a risk factor, is weakened immunity - no matter what causes the decrease in the body’s natural defenses. However, since the mid-twentieth century, another factor has appeared (and continues to gain strength), which is extremely “convenient” and favorable specifically for fungi. We are talking about antibiotics, which are often used as self-medication, in irrational doses, for too long a course, or in situations where antibacterial drugs are objectively not needed at all.
Suppression or destruction of bacterial microflora, including those that perform protective functions as a symbiont (it should be noted here that broad-spectrum antibiotics are not named this way by chance), disrupts the optimal balance in the microecological system of the human body, and fungi begin to occupy the vacated niche. According to modern estimates, fungal infections of the oral cavity and pharynx account for 40% of all mycoses of the mucous membranes. In the total volume of recorded oropharyngeal fungal invasion, candidiasis accounts for 90-95%. The remaining cases are caused by aspergillus, penicillium and other fungi, as well as their combinations (mixed pharyngomycosis).
The importance of risk factors such as diabetes mellitus, AIDS (every tenth patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome dies from fungal infections), smoking, allergic hypersensitivity, long-term use of hormone-containing anti-inflammatory drugs, oral sex with a carrier of genital candidiasis, as well as intestinal dysbiosis has been reported.
Visit our Otolaryngology (ENT) page
Signs of the disease
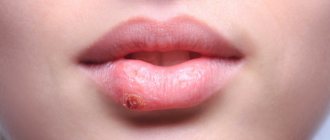
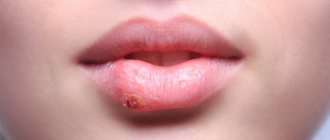
The key sign of the disease in childhood is the appearance of a whitish coating on the epithelial tissues, hiding eroded areas of tissue underneath. Lesions may appear on the tonsils, in the pharynx, on the tongue, in the corners of the mouth and on the edges of the lips.
In children with unformed speech, acute candidiasis can manifest itself in the form of refusal to eat, irritability, tearfulness, somnological disorders, and bleeding from the gums. Older children may complain of pain in the mouth when eating, itching and burning of epithelial tissue in the affected area.
The main signs of chronic candidiasis are:
- swelling of the epithelium;
- the appearance of light brown plaque on epithelial tissues;
- dryness, pain in the mouth;
- systematic bleeding from gum tissue.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
As a rule, pharyngeal candidiasis occurs with few symptoms or with moderate severity of clinical manifestations. Typical symptoms include inflammation of the tonsils and mucous membranes, a dirty white coating, low-grade fever, mild malaise, discomfort or pain when swallowing.
Granulomatous, atrophic, hyperplastic, erosive-ulcerative forms are relatively less common, requiring differential diagnosis, in particular, with tuberculosis.
Candidiasis of the pharynx is easily chronic and occurs, as a rule, in waves.
The prognosis worsens when the mycotic infection spreads to adjacent and internal organs.
If oropharyngeal candidiasis is suspected, a smear is taken from the affected surface, then a culture is performed on a nutrient medium; Recently, genetic identification (PCR) and serological tests (detection of specific antibodies) have been increasingly used.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Causes of oral candidiasis
The main reason for the occurrence is a decrease in immune status, as a result of which the uncontrolled proliferation of microflora begins. Reduced immunity is observed in older people and infants, in patients suffering from HIV, AIDS and other diseases associated with immunodeficiency, in those who regularly expose the body to excessive stress, neglect the rules of a healthy diet and violate work and rest patterns. Risk factors include reasons such as:
- Use of medications.
Taking antibiotics, immunosuppressants (drugs that suppress the immune system) and some other medications leads to disruption of the immune system and the natural balance of microflora in the body. Oral contraceptives, which affect hormonal levels, have a similar effect. - Pregnancy.
During pregnancy, a sharp and significant change in hormonal levels occurs, which can lead to a surge in the activity of pathogenic and opportunistic microflora. - Radiation and chemotherapy.
Often occurs in patients undergoing drug and radiological treatment for cancer. - Injuries to mucous membranes.
Violation of the integrity of the mucous membranes leads to loss or deterioration of the barrier function, as a result of which the fungus enters deep into the tissues, causing inflammation and other symptoms. Small, but constantly recurring injuries are especially dangerous - for example, when wearing incorrectly fitted dentures or braces. - Overwork and stress.
Prolonged stress of physical and mental forces leads to a deterioration in the protective function of the body. Similar consequences are caused by hypothermia or overheating, regular lack of sleep, insufficient, excessive or simply unbalanced nutrition, abuse of alcohol, nicotine, and narcotic substances. - Hypo- and vitamin deficiency.
May be caused by a lack of nutrients, in particular vitamins B and C. - Somatic diseases.
Frequent companions of candidiasis include tuberculosis, dysbacteriosis and other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, diseases of the adrenal glands and other endocrine glands. Candidiasis is a contagious disease. A large number of pathogenic microorganisms are transmitted through kissing and sexual contact, through the use of shared dishes, towels and other household items. Infection can also occur during childbirth (vertical transmission from mother to fetus). In addition, there is a risk of infection through contact with infected pets.
Risk factors for development
The likelihood of infection increases with casual sexual intercourse, uncontrolled use of antibiotics and drugs that disrupt the natural microflora. Foods with large amounts of sugar and carbohydrates create a favorable environment for fungal growth. Excessive sweating also leads to an exacerbation of candidiasis, so it is necessary to wear cotton underwear that allows the skin to breathe and moisture to evaporate.
At the same time, excessive cleanliness can also cause harm. We are talking about douching. It should not be used as a method of contraception, since it is not effective, and also as a means of hygiene, because it leads to the leaching of the protective flora. If you experience discomfort, you should first consult a doctor.
Treatment of candidiasis
Treatment of candidiasis is aimed at eliminating factors that contribute to the occurrence of candidiasis. If the skin is affected, local treatment is carried out using an open method using antifungal ointments.
The attending physician prescribes systemic and local medications for this disease. Local agents are not absorbed into the blood - they act only on the mucous membrane affected by the Candida fungus. They stop the reproduction and growth of fungi, relieve discomfort and restore affected tissue.
Interpretation of results
If there are clear signs of candidiasis (thrush), and during a laboratory test blastospores and pseudomycelia of the fungus were identified, the study ends here. A diagnosis is made and treatment begins.
If a microscopic examination gives a negative result, this does not indicate the absence of infection. The disease can occur in a latent chronic form. It is necessary to carry out a number of other tests, for example, microscopic examination of scrapings, determination of Candida DNA in scrapings, urine, and prostate secretions. Also prescribed:
- Clinical blood test.
- Test for HIV infection.
- Determination of trace element reserves in the body.
- Test for glucose and carbohydrate metabolism metabolites.
These laboratory tests can help identify conditions that may be causing the fungus to grow.
Symptoms of candidiasis
The disease is widespread. Pathogens of candidiasis have been found in the air, soil, vegetables, fruits, and confectionery products. Yeast-like fungi are found as saprophytes on healthy skin and mucous membranes.
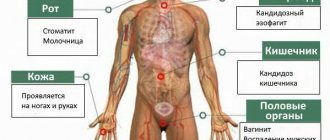
Manifestations of candidiasis, and therefore symptoms and signs, depend on the location of the source of the disease.
Candidiasis of the oral mucosa (oral candidiasis, infantile thrush) most often occurs in children; as a rule, they become infected from the mother through the birth canal. Symptoms:
- the mucous membranes of the cheeks, pharynx, tongue and gums become red,
- swelling appears,
- then pockets of white cheesy plaque appear on the oral mucosa.
With candidiasis of the skin and its appendages, the lesions are most often located in large folds:
- inguinal-femoral,
- intergluteal,
- armpits,
- under the mammary glands.
The skin in the interdigital folds may be affected, more often in children and adults suffering from serious illnesses - on the skin of the palms, feet, smooth skin of the torso and limbs. Lesions in large folds look like small 1-2 mm bubbles, which soon open to form erosions. Erosion increases in size and merges, forming large areas of damage.
Foci of candidiasis have an irregular shape, dark red color, and around the lesion there is a strip of exfoliating epidermis. Outside the folds, the lesions look like red spots with peeling in the center, and occasionally small blisters may appear around the lesion.
Vaginal candidiasis (candidiasis, thrush) is an infectious disease of the vaginal mucosa, which often spreads to the neck of the uterus and vulva. Almost every woman has encountered this disease, and some signs of candidiasis are constantly disturbing. Most often occurs in women of reproductive age, but can occur in girls
Intestinal candidiasis (dysbacteriosis) often accompanies vaginal candidiasis or develops in isolation. Typically, intestinal candidiasis appears after taking antibiotics or previous intestinal infections. Fungi of the genus Candida settle in the small intestine. Symptoms characteristic of this type of candidiasis: white curdled flakes are often found in the stool of a patient suffering from intestinal candidiasis.
Esophageal candidiasis is a disease that is very difficult to identify among all those available in the field of gastroenterology. The disease is characterized by a discrepancy between the severity of the disease, the level of damage and the condition of the patient himself.
Advantages of taking tests at JSC "SZDCM"
- Own laboratory with the latest diagnostic equipment.
- Convenient location of terminals within transport accessibility from anywhere in the city.
- Qualified laboratory technicians and friendly staff.
- Fast analysis and several options for obtaining results. Choose the one that is most convenient for you.
Medical centers and laboratory terminals of the North-Western Center for Evidence-Based Medicine are located in St. Petersburg, Leningrad region, Veliky Novgorod, Okulovka, Kaliningrad and Pskov.
Analyzes
- Bacteriological study for opportunistic pathogenic flora (OPF)
- NC yeasts of the genus Candida: C.albicans, C.krusei, C.glabrata
- Study of the biocenosis of the urogenital tract in women (“Femoflor 13 - screening”)
- Candida albicans
- Mycoses: identification of clinically significant fungi with determination of sensitivity to antimycotic drugs (only for fungi of the genus Candida and Cryptococcus neoformans)
- Specific immunoglobulin E - Candida albicans
go to analyzes