A tumor of the upper lip in a child may appear for no apparent reason, that is, it was not preceded by a blow, and the presence of an abscess (boil) is not visually determined. The fact is that the mucous membranes in the oral cavity are characterized by increased sensitivity, especially in children (the immune system is not fully formed), which means that swelling can be caused by a variety of factors. A swollen upper lip in a child is a reason to visit a doctor, and first of all you need to see a dentist, since there are diseases of the oral cavity in which the first symptom will be severe swelling of the mucous membrane and, as a consequence, the phenomenon in question.
Symptoms of gum inflammation
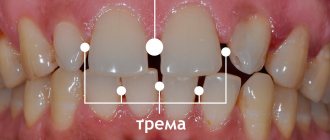
According to statistics, more than 70% of people have experienced inflammation of the gums between their front teeth at least once in their lives. The main signs of the problem include:
- redness of the gingival papilla,
- swelling of soft tissues,
- bleeding gums,
- bad breath,
- accumulation of pus in the interdental space,
- discomfort when brushing teeth and eating.
If you notice any of these signs, you should consult your doctor. These symptoms can indicate either injury to the gums from hard food or bones, or the development of serious diseases.
Why does my lip hurt?
Cheilitis
Cheilitis is a large group of inflammatory diseases of the mucous membrane and skin of the lips. They arise primarily or develop against the background of other pathologies. Typical signs include pain and burning in the lips when eating, opening the mouth, peeling, hyperemia, the appearance of cracks, crusts, and bleeding ulcers. The symptom can be provoked by the following types of cheilitis:
- Exfoliative.
It is formed against the background of neurotic disorders and is more often detected in women. It affects the red border without involving the mucous membrane, corners of the mouth, areas adjacent to the skin of the chin and nasolabial triangle. It manifests itself as a burning sensation, dry lips, and the formation of scales. The pain is more pronounced in the exudative form, also accompanied by swelling of the lips. - Glandular.
Diagnosed in people with developmental defects and acquired diseases of the minor salivary glands, caries, and periodontal diseases. The lower lip is most often affected. Initially, slight dryness is detected, which is subsequently replaced by painful erosions, deep bleeding and weeping cracks. - Contact allergic.
It is potentiated by cosmetics, formed by the habit of holding various objects in the mouth, and develops in people of certain professions (for example, musicians who play wind instruments). Severe itching, redness, and swelling of the lips prevail. The resulting blisters burst with the formation of painful erosions and cracks. - Meteorological.
Occurs under the influence of sunlight, less often - wind and cold. The exudative form is accompanied by burning, itching, and the appearance of small blisters, in place of which painful erosions remain. For the dry form, the presence of erosive defects is uncharacteristic; pain appears against the background of burning and dry lips. There is a danger of developing precancerous diseases and malignancy. - Atopic.
Diagnosed in patients with neurodermatitis and atopic dermatitis. Concerned about hyperemia, peeling, itching. Pain occurs when cracks form in the corners of the mouth. The listed manifestations are complemented by peeling and dryness of the face. - Hypovitaminosis.
It is provoked by a lack of B vitamins, especially B2. The skin of the lips is dry, hyperemic, covered with small vertical cracks that hurt and bleed. The mucous membrane is reddened, slightly swollen. The tongue is enlarged.
Herpes
The red border of the lips and the corners of the mouth are the favorite localizations of herpes simplex. The patient feels a burning sensation, tingling, and bloating. In the affected area, rashes form, which are a collection of small bubbles. As the changes progress, unpleasant symptoms increase, and pain is added to them. Then the bubbles open individually or after merging into one or more multi-chamber bubbles. In their place, erosions of irregular shape appear, painful when touched or when moving the lips.
Oral lichen planus
Involvement of the lip (mainly the upper lip) is characteristic of a rare atypical form of the disease. Papules, plaques or ulcers, erosive defects of irregular configuration, covered with fibrinous plaque, are found on the skin and mucous membrane. The pain syndrome is most pronounced in the presence of ulcers and is accompanied by a burning sensation. Several forms of lichen planus are often combined with each other or transformed into one another, so lesions can be present not only on the lips, but also on the gums, tongue, and oral mucosa.
Lip pain
Traumatic injuries
Acute damage to the mucous membrane or skin of the lip occurs as a result of injury from foreign objects or biting. It is quite rare. Manifested by the formation of a hematoma or erosive defect. The pain persists for 1-3 days. With secondary infection, erosion transforms into an ulcer, surrounding tissues swell, and pain intensifies.
Chronic trauma is possible when carious anterior teeth are damaged by sharp edges. It occurs with swelling, slight pain, and a feeling of discomfort. With prolonged injury, an ulcer forms. It is possible to develop a local or widespread inflammatory process with increased pain, swelling, and the appearance of purulent discharge.
Lip bruises are usually the result of fights. Children often develop as a result of falls. They are characterized by rapidly growing swelling and may be accompanied by abrasions of the mucous membrane due to sudden contact with the teeth. Painful sensations are pronounced in the first minutes after the injury, and then gradually subside. Recovery occurs after 1-2 weeks. Lip wounds are often lacerated and manifest as acute, raw pain and bleeding.
Trigeminal neuralgia
Repeated shooting intense pain impulses, reminiscent of an electric shock, are observed when the 2nd branch of the trigeminal nerve is involved. The pain spreads to the upper lip, upper cheek, upper jaw. When the 3rd branch is affected, similar sensations occur in the area of the lower lip, chin, lower jaw, and lower cheek. The duration of an attack of neuralgia ranges from a few seconds to 2 minutes.
Lip cancer
At the initial stage of lip cancer, there is no symptom. A painless, sometimes itchy ulcer or area of compaction forms on the lip (usually the lower lip). Pain occurs when nearby tissues grow. Becomes constant, progresses, reaches significant intensity. Upon examination, an ulcer with uneven edges or a node in the form of a wart or cauliflower inflorescence, covered with cracks and ulcers, is revealed.
Possible reasons
In most cases, the gums become inflamed due to poor oral hygiene. Plaque accumulates on the teeth, which is a favorable environment for the proliferation of microbes. Soft deposits compact and transform into tartar, which is located along the edges of the gums. Inflammation between the front teeth can also be associated with smoking, mechanical damage to the gingival papilla, a burn to the oral cavity, or a lack of vitamins and minerals in the body.
This symptom is also characteristic of the clinical picture of the following diseases:
- gingivitis – inflammation of the mucous membrane due to the accumulation of plaque, accompanied by redness and swelling of the gums;
- periodontitis – develops with advanced gingivitis, leads to the formation of periodontal pockets, loosening of teeth and their loss;
- papillitis is inflammation of the interdental papilla; provoking factors include caries, thermal and mechanical effects, allergic reactions, endocrine diseases.
Diagnostics will help to establish the exact cause of the problem: visual and instrumental examinations, radiography.
Types of labial frenuloplasty
There are three main types of frenuloplasty. Each of them is indicated for different diseases or anomalies of attachment.
- Frenotomy
– involves cutting the frenulum if it is too narrow or short. This operation eliminates discomfort when chewing and corrects the patient’s bite. - Frenuloplasty
is an operation in which the edge of the frenulum is fixed in another place (usually higher). Y-shaped and Z-shaped frenuloplasty are performed (the difference is in the type of incision). - Frenectomy
– resection of the wide frenulum of the upper lip. The most radical type of plastic surgery, as a result of which the interdental papilla and mucous membrane tissue are partially or completely removed.
Operation on the labial frenulum is divided into types depending on the method of implementation. Today, such plastic surgery is performed with a laser or scalpel. The laser method is more modern, painless and comfortable for the patient. The entire procedure takes a few minutes and does not require long-term rehabilitation.
Treatment methods
Treatment of inflamed interdental papillae is aimed at eliminating increased sensitivity and pain. This may include:
- rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions and chamomile decoction,
- applications of anti-inflammatory gels and ointments,
- taking antibacterial drugs,
- professional teeth cleaning,
- coagulation of overgrown tissues.
The treatment regimen is chosen by the doctor taking into account the diagnosis, clinical picture, and individual characteristics of the patient’s oral cavity.
What to do if your child has a swollen upper lip
If parents know that the condition in question was caused by a blow or insect bite, or an allergy to an external irritant, then you should not consult a doctor. You can apply a cold compress to the area and give the baby one of the usual antihistamines - after 20–30 minutes the swelling will become much less.
But in the case of a tumor of unknown origin or the presence of other changes in the child’s health (weakness, complaints of pain and burning, increased general body temperature), you must immediately contact a pediatrician. The doctor will conduct an initial examination and find out the true cause of this condition. Only after this will he give a referral for examination by a dentist, if required.
In turn, the dentist will visually assess the condition of the oral cavity, make a diagnosis and make medication prescriptions. They can be very different:
- antibacterial drugs;
- antiviral agents;
- antiseptic solutions for irrigating the oral cavity and rinsing it;
- antifungal drugs.
If a child has a swollen upper lip, the doctor will tell you what to do in this situation. Self-medication in this case can cause deterioration of the condition and rapid spread of the inflammatory process. If the cause of the swelling is a purulent focus, then the lack of qualified assistance can lead to serious consequences: damage to the soft tissues and periosteum of the jaw, and general blood poisoning.
Treatment of herpes in the mouth
Can herpes be in the mouth?
Maybe! Herpes in the mouth requires the same responsible approach and competent treatment as other diseases of the oral cavity. Despite the fact that the infection is often mild and goes away naturally, there are still risks of serious complications, and the possibility of infecting other people remains. Many factors influence the degree of development of the pathology and the presence of possible dangers for the patient. Complete diagnosis and comprehensive treatment can completely stop the manifestations of the infection, although complete elimination of the virus is considered impossible. Herpes, a viral disease known to many as a “cold sore,” is often perceived as a minor problem that does not require treatment. It is characterized by the appearance of a moderately painful blistering rash, but not many people know that this disease is not limited to appearing only on the lips , but can also develop on the oral mucosa . The disease is often accompanied by weakness, general malaise and severe itching, and in some cases can cause complications. During the active phase of the virus, a patient can easily infect others with it through household items, close contact or by airborne droplets.
At what age is the procedure performed for children?
In children, pathologies of the lower lip frenulum can cause various negative medical and aesthetic consequences. Therefore, if a doctor finds a defect during a routine examination and recommends plastic surgery, it is better to take his advice.
Dentists believe that the best age for frenulum correction in children is from 5 to 8 years. It is during this period that temporary teeth are replaced with permanent ones, so it is important that the frenulum does not disrupt the correct development of the molar units.
If there are indications, plastic surgery of the lower lip frenulum can be performed in adolescents or adults. For infants, this operation is prescribed only if there are serious problems, for example, the inability to fully feed on breast milk.
How is inflammation of the palate treated?
How to treat inflammation on the roof of the mouth, a specialist will tell you after determining the diagnosis. The following therapy methods can be used:
- If the cause of inflammation is minor damage to the mucous membrane, rinsing with decoctions of medicinal herbs is usually sufficient. Decoctions and infusions based on calendula, sage and chamomile have an antiseptic and healing effect. The herbal decoction for rinsing should be used warm.
- When the palate is affected by a fungus, patients are prescribed topical agents. The most effective are the solution and gel “Chlorhexidine”, “Rotokan” or “Stomatofit”.
- In case of severe pain symptoms, regardless of the cause of inflammation, drugs of combined action are prescribed. “Cholisal-gel” and “Kalgel” have proven themselves well.
- If a purulent inflammatory process is detected in the oral cavity, the patient is prescribed antibiotics. The minimum course of treatment is usually 7 days, but there are also stronger drugs that only need to be taken for 3 days. Along with local agents, antibacterial drugs for internal use - Sumamed, Flemoxin Solutab - can be prescribed.
- The inflammatory process of the palate is easily treatable. The earlier therapy is carried out, the less likely it is to develop complications.
Causes of oral herpes infection
Herpes that affects the oral cavity develops when infected with the herpes simplex virus type 1, which not only provokes the appearance of a blistering rash, but can also cause complications in 10% of cases. The second type of herpes virus (genital) also causes a rash in the mouth, but does not cause serious disruption to the body and differs in its mode of transmission (through sexual contact).
Most often, primary infection with a herpes virus occurs in childhood, after which it is introduced into the genome and remains in an inactive form for life.
The main routes of infection with a viral agent are close conversation, skin-to-skin contact, kissing, and the use of shared hygiene products or utensils. However, the entry of viral particles into the body does not guarantee that the disease will develop, since the immune system can suppress the action of the pathogen. In this case, situations that worsen the overall health of the body, on the contrary, provoke a clear manifestation of infection:
- surgical interventions;
- emotional and physical stress;
- lack of sleep, overwork;
- colds;
- chronic pathologies;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- periods of menstruation, pregnancy or lactation;
- vitamin deficiencies;
- AIDS;
- abuse of nicotine or alcohol;
- the appearance of microtraumas from excessive exposure to the sun or frost.