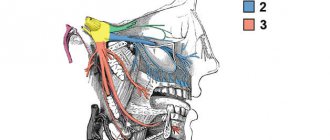
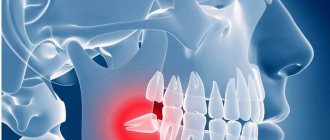
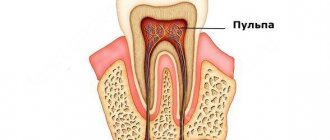
The dental nerve is one of the components of the soft tissues of the tooth, its central part (pulp). The pulp is located under the enamel and dentin layer and makes up the dental cavity. The pulp consists of three main elements - artery, vein and nerve. They penetrate into the dental cavity through the apical canals, which open at the tips of the roots. The number of canals is equal to the number of roots in the tooth. If a tooth has one root, then the number of canals is correspondingly equal to one, if there are two roots, then two, etc.
Painless removal of a nerve from a tooth: how it goes and consequences
Many people are familiar with the procedure of removing a nerve from a tooth, which was accompanied by the mandatory placement of arsenic. Previously, this method took several days, during which the substance killed the nerve, after which the doctor removed the pulp and installed a filling or crown. Modern methods make it possible not to resort to arsenic, using more effective and painless methods. The pulp or neurovascular bundle performs important functions; it nourishes and protects tooth tissue from infection. Without it, the enamel changes color, hard tissues are destroyed faster, but in some situations, removal of the nerve is necessary.
Stages of treatment
- Diagnostics . Before treatment, the doctor conducts an examination and takes an x-ray. It will show the structure of the root canals, their number, the depth of the carious cavity, and the condition of the tooth. Sometimes treatment is impossible and the tooth needs to be removed.
- Anesthesia . To numb the tooth and provide a comfortable treatment, local injection anesthesia (injection) is performed. In case of severe pain and severe inflammation, the gums are treated with an anesthetic gel or spray before the injection.
- Installation of insulation (cofferdam) . To isolate the canals from saliva and bacteria, a rubber dam is used - this is a latex scarf that is placed on the tooth being treated. Thanks to the rubber dam, sterile conditions are created for placing fillings and treating root canals.
- Treatment of hard dental tissues . All carious and destroyed tissues are removed, and access to the pulp chamber is created. A water-cooled drill is used to prevent surfaces from overheating. All fragile tooth walls are also removed in order to initially create good conditions for future restoration.
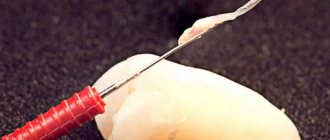
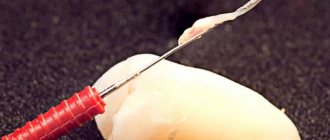
- Nerve removal . It is performed with small sterile instruments that look like needles. In some cases, a special apparatus is used: a tip with rotating instruments. This happens painlessly, since anesthesia was previously administered.
- Root canal treatment . The doctor cleans the canals, rinses them with antiseptic solutions, and measures their length. This is necessary in order to eliminate all infectious particles from the canals.
- Temporary filling . It is installed when it is impossible to fill the root canals immediately on the first visit. This also allows you to monitor the patient’s condition (after acute pain).
- Canal filling . Occurs on the first or next visit. A method for filling the canals is selected, then a permanent filling is placed in aesthetic dentistry.
- Control shot . After filling the canals, it is important to make sure that they are sealed tightly, to the top, and that there are no voids left. If the voids remain, re-inflammation will occur.
Causes of dental pulp damage
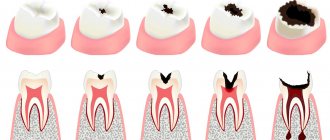
The dentist is often visited because of caries - damage and destruction of enamel, which at the initial stage causes aesthetic discomfort.
Important: if the disease is started, the process affects the deeper layers of the tooth and pulpitis develops, that is, the neurovascular bundle becomes inflamed.
Pathologies arise due to the rapid proliferation of microbes, but in addition, the pulp can be damaged for the following reasons:
- gum disease, in which the neck of the tooth is exposed, the bone tissue is destroyed and harmful bacteria penetrate inside;
- trauma, as a result of which part of the tooth can break off, and then microbes enter the resulting cavity;
- mistake by the dentist who installed the filling or crown. If some actions were incorrect, then the nerve will make itself felt after a while.
These are the main causes of pulp damage. The symptoms of this condition will be acute. The pulp will begin to react to cold, hot, too spicy, sweet foods. Removing the nerve in such situations is a necessity, despite the fact that minerals and nutrients will stop flowing to the tooth.
Symptoms of the lesion
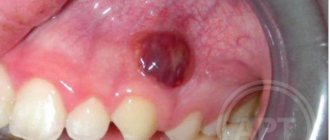
The cause of the formation of a pathological process can be carious lesions, inflammation of soft tissues, or mechanical damage to the teeth. The main symptoms include severe aching pain that can radiate to the temporal tissue. You may experience bad breath. The painful area may react acutely to hot and cold foods. With the development of the pathological process, swelling, inflammation of the pulp chamber, and the formation of pus may be observed over the course of several days.
Many patients often wonder whether the nerve in a tooth can die on its own. Yes, maybe, if the destructive process has gone far enough. The main symptom will be a sudden cessation of pain. However, without timely dental intervention, the infection can spread further and affect the trigeminal nerve, leading to trigeminal neuralgia. The consequence will be impaired facial expressions, facial distortion and other anomalies.
Why do you need to remove the pulp?
We talked about the main reasons why nerve inflammation occurs, but most often pulpitis becomes a consequence of advanced caries. Therefore, it is very important to visit a dentist, even if nothing bothers you. The decision to remove the pulp is made in the following situations:
- pulpitis has passed into the stage of periodontitis, when inflammation affects the whole complex of connective tissue in the tooth;
- large area of carious lesion;
- the infection spreads through the apex of the tooth root;
- the appearance of unbearable, prolonged pain;
- spread of infection under an artificial crown;
- consequences of improper treatment.
The nerve can be removed either completely or partially, it all depends on the degree of tissue damage. Depulpation will prevent the spread of the inflammatory process under the crown and preserve the natural tooth, which is a priority for endodontic therapy.
Indications for depulpation
When should a dental nerve be removed?
- Advanced caries;
- Pulpitis – including asymptomatic;
- Severe tooth trauma – partial destruction of the tooth and exposure of the nerve;
- Preparation for prosthetic crowns (at the discretion of the orthopedic dentist);
- Periodontitis;
- Consequences of unsuccessful treatment;
- Unbearable pain.
How does the pulp removal process work?
We mentioned the method using arsenic at the very beginning. Some dentists still use it. The disadvantages of this treatment include its duration and pain. Before administering arsenic, the doctor must widen the root canal and place the substance into it. He then seals the area with a temporary filling. After two days, the arsenic kills the nerve, then the dentist cleans the substance from the tooth cavity and removes the pulp.
Important! Arsenic should not remain longer than expected in the oral cavity, as it is a poison and can be destructive to tissue.
There are more modern ways of performing the procedure, which are both safer and more painless. Before any action, an x-ray is required, which shows the vitality of the pulp, the length of the canal and other features.
Pulp removal is carried out using the vital and devital method. The first option is used for patients of any age. Its stages are as follows:
- the tooth is exposed;
- the pulp is removed with a special tool - a pulp extractor;
- a filling is installed.
In some situations it may be temporary and after a few days it changes to permanent.
Note: all stages of treatment are performed under anesthesia, so they will not be painful or uncomfortable for the patient.
The devital method is similar to what was used ten or more years ago, only instead of arsenic, a non-toxic substance is installed in the tooth cavity. The main method of pulp removal in modern dentistry is the vital method, when in just 1 visit to the doctor you can undergo complete painless dental treatment.
Important: temporary pain after a dental procedure is considered normal, as tissue intervention has occurred. If severe pain does not go away within 3 days, you should consult a doctor.
Modern method of depulpation
Today, depulpation is carried out using a pulp extractor - a thin metal rod with teeth that can penetrate even remote areas of the root canals. The apex locator device helps determine the depth of the canal to reduce the risk of injury. After the procedure, a temporary filling is usually installed, but a permanent one can also be installed if the doctor does not see the risks of complications and has high-precision instruments on hand, for example, a dental microscope.
In what situations should a nerve not be removed?
We are talking not only about contraindications, but also about cases in which the pulp can be preserved. The procedure is not performed if the patient has:
- any infectious disease;
- one of the forms of stomatitis;
- psychoemotional disorders;
- acute pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
- unsatisfactory condition of the oral cavity with suppuration and inflammation.
The nerve is preserved if it is not subject to inflammation due to caries or other pathologies and injuries. The dentist’s task is to save the pulp and remove it only in case of emergency.
Important: you cannot endure a toothache and hope that the pain in your nerve will stop. Inflammation can become chronic and show almost no effect, but any provoking factor will affect the development of a purulent abscess. In this case, the minimal consequence will be tooth loss, and the possible consequence will be the spread of infection to other tissues.
Contraindications
Before treatment, the doctor must collect medical history data, that is, all information about the patient’s health status. Contraindications to nerve removal may include:
- pregnancy (first and last trimesters);
- hepatitis, HIV infection;
- open form of tuberculosis;
- acute inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa.
It is worth noting that in case of acute pain, some contraindications can be considered relative: the decision is made by the dentist.
Consequences of nerve removal
If the treatment was carried out by a professional and experienced dentist, then apart from slight pain the patient will not be bothered by anything. Otherwise, there may be such complications:
- a fragment of the instrument remains in the dental canal;
- the nerve was partially removed;
- incorrect or poor-quality filling of the canal;
- mechanical damage to the root or wall;
- rapid darkening of the enamel;
- suppuration due to poor disinfection.
Important! Depulpation at the Crystal clinic is carried out with the minimum possible complications, since all procedures are carried out by certified doctors with extensive experience using high-tech equipment and tools.
After depulpation, it is recommended not to eat for 2-3 hours, not to eat cold, hot, hard or other foods that irritate the mucous membrane. Your doctor will tell you in more detail about the necessary actions after removing the nerve.
Pain Management Options
The duration of action of a standard anesthetic injection is 45 minutes. Patients who are afraid of injections are offered treatment of the depulpation site with a special paste-like composition of a similar effect. Tablet analgesics may reduce the effectiveness of anesthesia, so dentists do not recommend their use.
The dentist chooses the painkiller, as well as the dosage. Since everyone's pain threshold is different, the dose of anesthetic is often doubled or tripled. If the doctor has administered anesthesia according to the protocol, the patient will not feel any pain or discomfort.
What is pulpitis?
Pulpitis is an inflammatory process in the pulp (neurovascular bundle) and root canals of the tooth. The dental crown contains a cavity pulp chamber, where there is a plexus of blood vessels, connective tissue and nerve endings. All this together makes up the pulp, the main function of which is to nourish the coronal and root parts.
Under the influence of provoking factors, hyperemia of the pulp occurs. Most often, this is caused by caries in an advanced stage. Due to damage to the crown, soft tissues are exposed and primary serous inflammation occurs (the so-called initial type). In the absence of timely treatment, the disease develops into more severe forms and can lead to irreversible consequences.
Pulpitis of primary and permanent teeth has many similarities with other pathologies, so self-diagnosis is ineffective in most cases. However, there are a number of signs that are characteristic exclusively of pulp inflammation.