Various strange and unusual tastes that appear in the mouth are alarming and make you wonder if everything is okay with the body. For example, what does the taste of salt in your mouth indicate? Doctors note that the feeling of excess salt cannot be considered normal.
Cardiologist, therapist, endocrinologist Tatyana Romanenko told AiF.ru about what diseases such a taste in the mouth indicates and what needs to be done .
When we talk about the taste of salt in the mouth, we must first of all exclude the most important, serious and dangerous causes of this pathological phenomenon.
Blood in the mouth
One of the most important and yet common causes of this phenomenon is bleeding. Naturally, since we are talking about the mouth, then most often it arises from the gums. But increased gum bleeding can be caused by a number of factors.
Question answer
What causes the bitter taste in the mouth? One of the most common problems is inflammatory infectious diseases of the oral cavity. The reason may be either untreated, not fully sanitized teeth, or inflammatory diseases of the gums and tonsils themselves. These could also be neoplasms. That is, the problem lies in all local processes.
Another fairly global problem that we should always remember is bleeding gums due to changes in blood clotting. These are various types of thrombophilia, for example. Of course, there will be not only a salty taste in the mouth, but also other symptoms of hemorrhagic syndrome.
Another rather serious reason is blood disease, in particular those that are accompanied by bleeding. This could be thrombocytopenia, anemia, etc. That is, in this case, salty in the mouth is the taste of blood, and such a condition always requires prompt differential diagnosis and initiation of treatment.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic methods are selected depending on the person’s concomitant health complaints. The symptoms listed above will help you understand which specialist to seek help.
To begin with, you should contact a therapist , who will suggest the further path of examination.
Important! If, during regular hygiene measures, an unpleasant odor persists in the mouth, and even more so if blood is found in the oral cavity, this is a good reason to visit the dentist.
It is necessary to exclude or confirm and treat gingivitis, periodontitis or other oral diseases.
You should also go to the dentist if your salivary glands are swollen to check whether the problem is inflammation.
Thrush that appears in the oral cavity is also diagnosed and treated by this specialist.
If you have a runny nose, cough and a constant desire to improve your throat, you should go to an ENT specialist . People turn to him for constant nasal congestion, which often indicates rhinitis.
Abdominal pain and other tastes in the mouth are a reason to consult a gastroenterologist. Most likely, gastroscopy and/or ultrasound of the abdominal organs will be prescribed.
If you have weakness, constant pallor, noise in the ears, or spots before your eyes, you need to check your blood and rule out anemia.
The doctor prescribes a general blood test and, depending on its results, additional tests to clarify the type of anemia.
Need to know! Constant headaches, vomiting, and lack of coordination accompany the occurrence of tumors and other diseases of the brain and nerves.
Therefore, in such a situation, it is better to consult a therapist, neurologist or oncologist.
The doctor will conduct tests of coordination and reflexes, and may prescribe an MRI or SCT.
Saltiness of the lips when taking medications can be prescribed in the instructions for the drug.
You can also ask the doctor who prescribed the medicine about this.
Oral hygiene
A common cause of a salty taste in the mouth is poor oral hygiene. If a person does not brush his teeth well enough, if plaque forms, all this contributes to the development of pathological microflora, the waste products of which will give this unpleasant salty taste.
Also, the appearance of taste is influenced by the presence of an infectious process in the oral cavity - the formation of tartar, fistulas, chronic tonsillitis.
Taste of illness. How to determine your diagnosis by the taste in your mouth Read more
Treatment
If nothing bothers you other than the taste of salt on your lips, you should try the following:
- brush your teeth regularly,
- use dental floss,
- use mouth rinses ,
- drink more water (from eight glasses a day if there are no contraindications),
- change your diet
- exclude or reduce fast food, snacks, fried, fatty, salty, spicy.
Remember! If this does not help or there are other symptoms that make you worry, you should see a doctor.
Excess salt on the menu
A similar symptom may appear when we eat excessively salty foods. For a long time now, scientists, doctors, as well as adherents of a healthy lifestyle have noted that salt in large quantities is dangerous for the human body. And its main danger is the load on the cardiovascular system, urinary system, and kidneys. It also increases blood pressure. Therefore, to some extent, modification of diets can lead to the fact that taste perception is restored and excess salt begins to be felt.
Why does my tongue sting?
Physiological reasons
In healthy people, a short-term tingling of the tongue is observed after eating certain foods: tomatoes, onions, garlic, herbs, spices, hot seasonings, pickles, marinades.
Often provoked by berries, sour fruits (lemon, kiwi, pineapple). Drinks that can cause the development of symptoms include kefir, some juices, strong tea, coffee, alcohol, primarily wine. Sometimes hot drinks or food cause superficial burns of the mucous membrane. In this case, the tingling is intense, complemented by tingling and burning. The sensation is also typical for heavy smokers and is associated with constant irritation of the tongue from tobacco smoke. Sometimes the disorder occurs while taking antidepressants, antibiotics, antiemetics, sedatives and hormonal drugs.
Glossalgia
It is a functional disorder, often develops against the background of gastrointestinal diseases, endocrine and neurological pathologies. Pinching, burning and rawness of the tongue during glossalgia can be periodic or constant, causing rapid fatigue when speaking, and is accompanied by dry mouth. Mostly it occurs in the area of the tip and side surfaces. The symptom intensifies against the background of excitement, disappears or weakens when eating. External changes, as a rule, are absent.
Glossodynia
Along with tingling and tingling, patients may complain of a hairy sensation or “crawling sensation.” The symptom is more pronounced in the tip area and can spread throughout the entire tongue. The root rarely suffers. Characteristic is the spread of the affected area and an increase in the duration of discomfort as glossodynia progresses. Manifestations increase in the evening, sometimes bother you all night, and disappear during meals. The disorder is observed in the following diseases:
- Lesions of the digestive system:
gastritis, gastric ulcer, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, colitis. - Endocrine pathologies:
diabetes mellitus, thyroid dysfunction. - Cardiovascular problems:
hypertension, atherosclerosis, ischemic heart disease. - Neurological dysfunction:
vegetative-vascular dystonia, functional disorders due to stress, neuroses, psycho-emotional exhaustion.
Tongue tingling
Desquamative glossitis
In most cases, the pathology is asymptomatic, however, some patients complain of changes in taste sensations, tingling, and pinching of the tongue. Diction problems are possible. Upon examination, multiple whitish areas are revealed, which, after peeling off the epidermis, turn into red spots. Desquamative glossitis can accompany the following conditions:
- Gastroenterological problems:
gastritis, enterocolitis, cholecystitis, hepatitis. - Autoimmune diseases:
rheumatism, systemic scleroderma, SLE. - Chronic dermatoses:
psoriasis, exudative diathesis. - Hypovitaminosis:
deficiency of vitamins B1, B2, B5, B6, B12.
Sometimes it develops during pregnancy and worries patients with pathologies of the hematopoietic system and autonomic disorders. Some patients have a hereditary predisposition.
Dental diseases
A common cause of tingling, pain and burning are dental diseases: caries, tartar deposits. The symptom occurs when the edge of the tongue is damaged by a tooth fragment, prosthesis or crown; the damage is local in nature. Sometimes the cause of development is an individual reaction to the prosthetic material. In such cases, itching, irritation and redness of the mucous membranes are observed.
Xerostomia
Due to an insufficient amount of saliva, the tongue dries out, and a feeling of tingling, tightness, and tingling occurs. The disorder is aggravated by eating hard, dry foods or talking for a long time. Over time, the changes progress, and the discomfort becomes permanent. To reduce the severity of symptoms, patients often drink water or rinse their mouth. Taste sensations are reduced or distorted. Xerostomia can be diagnosed in the following cases:
- Endocrine pathologies:
hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus. - Diseases of the salivary glands:
tumors, mumps, calculi. - Dehydration:
fever, increased sweating, repeated vomiting or diarrhea. - Infectious diseases:
HIV, some other viral infections. - Other reasons:
condition after radiation therapy, frequent or prolonged stress.
Oral candidiasis
Pinching, discomfort, tingling are detected in the chronic form of the disease. Acute candidiasis is often manifested by pain and burning. The unpleasant sensations are widespread, covering the tongue and oral mucosa. The affected areas are covered with a dense gray coating, which, when removed, reveals a bright red inflamed epithelium. With hyperplastic candidiasis, the mucous membranes become painful and rough. Atrophic candidiasis is localized, the lesions are located next to the dentures and are areas of erythema with clear boundaries.
Allergic reactions
The most common etiological factor for tingling is food allergy. The symptom can also be observed in a reaction to pollen, house dust, animal dander and other allergens. Severe itching predominates, which forces the patient to “scratch” the affected area with his teeth, may be supplemented by tingling of the tongue, and is accompanied by sneezing and lacrimation.
The reason is tears
Another interesting reason may be related to the pathology of the tear ducts. It would seem, how are the eyes and the salty taste in the mouth connected? In fact, if there is a disruption in the functioning of the tear ducts, increased secretion of tears may occur; on the other hand, the normal passage of this tear content is also disrupted. As a result, the tear enters the nose, then it flows down the back wall of the throat, and a feeling of saltiness occurs in the mouth. Pathology of the lacrimal glands (ducts) can provoke a salty taste in the mouth.
Why does a metallic taste appear in the mouth? More details
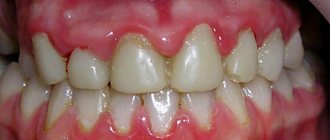
What should healthy lips look like?
Those who know how to moisturize their lips can boast of their naturally beautiful appearance. The natural red hue is due to the location of blood vessels near the surface.
Signs of healthy lips:
- smooth skin;
- smooth texture;
- pleasant natural shade;
- no peeling or cracking.
Healthy lips have even, uniform pigmentation without light or dark areas. Healthy skin looks elastic, it is not prone to irritation, peeling and allergies.
If a whitened area is detected, it means that the delicate skin does not receive enough hydration or there are not enough vitamins in the body:
- A,
- E,
- WITH.
First you need to learn how to use the right cosmetics. This applies to all people, because even if there are no problems with the lips, a careful attitude will not be superfluous.
You need to be able to choose the right cosmetics. And the first thing people pay attention to is the composition. Oil-based products should contain only natural ingredients:
- jojoba oil,
- cocoa,
- shi,
- nut oils.
It is best to buy products at a pharmacy or labeled “pharmacy product”. This means that cosmetics:
- passed dermatological tests,
- approved by experts
- considered safe.
In addition to moisturizers, there are small life hacks to improve the color and contour of your lips.
Shock freezing is often used: using ice to massage the lips. With prolonged exposure to cold, the appearance of the lips deteriorates, but short periods of exposure to shock cold cause the capillaries to expand sharply. Blood flows closer to the skin and provides:
- more active saturation with oxygen and nutrients,
- more saturated lip color.
The most common advice for lip care is the use of special lipstick. But there are several ways to moisturize your lips without chapstick.
Rare reason
Quite rarely, but it still happens, the reason lies in the pathology of the nervous system, when a change in taste perception is noted. In particular, such sensations can occur after suffering traumatic brain injuries, acute cerebrovascular accidents, chronic cerebral circulatory disorders and, of course, infectious diseases. Any viral infections can provoke a perversion of taste disturbance, and this can contribute to the appearance of such a salty taste in the mouth.
Disturbances in brain activity
With the development of pathologies in brain activity, disturbances occur in various organs and systems. If there are abnormalities in the brain, for example, tumor processes or epilepsy, such diseases may be accompanied by a salty taste on the lips and on the mucous membrane of the mouth.
But such a reason is very rare. Especially if there are no additional symptoms of possible pathologies. It is recommended to visit a doctor to find out the cause of the symptom, this will help to quickly eliminate it.
Chief author and editor-in-chief: Makarskaya S.E., 29 years of experience.
Last revision: 08/17/2017
Gastrointestinal tract and dehydration
A salty taste in the mouth often occurs with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Such a common pathology as gastroesophageal reflux disease causes a similar problem. First of all, of course, this is the appearance of a feeling of acidity, but some people may also complain of saltiness in the mouth.
Often, the taste of salt can be felt when the body is dehydrated, for example after some kind of infection. The effect is especially enhanced if, against the background of a lack of moisture, there is an excess of alcohol and caffeine-containing drinks. A characteristic aftertaste may arise here. Fluid imbalance causes more sodium chloride to appear in saliva. Hence the taste of salt in the mouth. Any loss of fluid and blood thickening are accompanied by this symptom.
Development of dehydration
Chronically dehydrated people experience a salty taste in their mouth. The salt is felt on the lips, they also become dry, and the person experiences constant thirst. Why does this happen to people? In this situation, such a feeling does not indicate the development of the disease. Such symptoms occur in those people who regularly abuse caffeine-containing drinks, for example, strong tea, coffee, and soft energy drinks.
Also included in the group of drinks that can cause dehydration is sweet soda. In this case, dry hands are additionally observed, the causes of which also lie in dehydration (the little finger may not only be dry, but also peel). In case of such a problem, it is recommended to exclude from life foods that negatively affect the body. This also includes alcoholic drinks, which absorb fluid in the body and retain salt.
Why does it occur in women?
If the specific taste in the mouth and lips in women does not cause a cough due to problems with the ENT organs or other listed problems, then the unpleasant symptoms are associated with the menstrual cycle or hormonal imbalance. Pregnant women especially often complain about this condition. Temporary restructuring of the body during childbearing followed by breastfeeding contributes to changes in taste buds.
Salinity also occurs due to dehydration caused by toxicosis. A woman may complain of constant nausea, vomiting, weakness, dry mouth, and dizziness. In this case, it is advisable to eat natural food with a minimum amount of dyes, drink drinks that alleviate the condition, and eat sour fruits that smooth out the symptoms of nausea and strange taste in the mouth.
Dysgeusia often develops in pregnant women. This is a taste disorder under the influence of hormones. This phenomenon is temporary and disappears without a trace after delivery.
Salt in the mouth of women can appear as a result of sudden mood swings, crying, or tears. In older representatives of the fairer sex, a salty taste appears during menopause, when hormonal changes occur intensively. It is often accompanied by dry mouth, inability to swallow food, burning, and itching.
Related posts:
- The whole truth about real depression Depression is not just a bad mood, but serious changes...
- Benefits of Stress Stress is a normal defense mechanism that the human body needs...
- Constant fear and anxiety in children It is common for every person to experience fear, anxiety, and anxiety. But, unlike...
- Mysophobia is a pathological fear of dirt and germs. Mysophobia is a mental illness, the symptom of which is a strong, irresistible fear...
Diseases of the ENT organs and respiratory tract
A taste of salt in the mouth sometimes occurs with the development of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the upper and lower respiratory tract. When the paranasal sinuses become inflamed, mucus is actively secreted. It flows down the back of the throat, constantly causing a cough. When it enters the mouth, a salty taste is felt.
Runny nose
A runny nose due to a cold or allergy causes excess mucus in the nasal passages to flow from the back of the nose down the throat. The presence of this mucus can cause your saliva to be saltier than normal. Runny nose remedies can help clear your nasal passages and thus eliminate the salty taste in your mouth.
Bacterial sinusitis, sinusitis, allergic rhinitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis can occur in both acute and chronic forms. Regardless of the nature of the disease, mucus appears. It constantly bothers you when it gets into your mouth, changing your taste sensations.
Bleeding gums
There is a taste of salt and you don’t know what could be causing it? The cause of this phenomenon could be bleeding gums. It could arise against the background of trauma to the mucous membrane or as a result of the development of gingivitis or periodontitis.
Blood is close in its ionic composition to sea water. It contains sodium and chloride ions, due to which people with a similar pathology experience a salty taste.
Your mouth may also feel salty due to the fact that you recently had a tooth removed. After all, after this procedure, a wound has formed, which first bleeds, and then ichor is released from it for a long time. Damaged tissues need time to heal, after which the unpleasant symptom will no longer bother you.
Allergy
An allergic reaction is accompanied by the release of a whole cascade of substances. There are several mechanisms due to which salty taste develops. It is caused by mucus and tear fluid entering the mouth during allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, a decrease in the concentration of fluid in saliva, and the ingress of substances involved in the development of an allergic reaction. This is not the most striking symptom of an allergy, and there is no need to specifically fight it - the salty taste in the mouth will go away on its own after the allergic reaction is over.
Diseases of the salivary glands
A salty taste in the mouth that is not associated with food intake may be one of the signs of diseases of the salivary glands.
When the salivary gland becomes inflamed, its function is disrupted, resulting in changes not only in the amount of saliva produced, but also in its composition. Against the background of inflammatory processes of the salivary glands, the patient may complain of a persistent salty taste in the mouth. Associated symptoms of inflammatory processes are:
- increased salivation;
- pain in the lower jaw;
- enlargement and tenderness of the cervical lymph nodes.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
GERD occurs when the esophageal sphincter weakens, allowing bile or hydrochloric acid to back up into the esophagus. This leads to a burning sensation behind the breastbone, along with other symptoms. GERD can also cause an unusual taste in the mouth, often described as bitter, sour, or salty.
Taking medications
All medications affect metabolism to one degree or another. This may manifest itself as foreign tastes in the mouth - this side effect is safe, but sometimes irritating to the patient. This feature is usually indicated in the instructions if you carefully read the section on side effects. Most often, a salty taste is caused by: Unflavored lozenges; Sprays and solutions for rinsing the mouth and throat; Antibiotics; Antihistamines (antiallergic) drugs; Some hormonal medications; Chemotherapy drugs used in oncology; Antidepressants. Particular attention should be paid to diuretics. The salty taste may be due to the characteristics of the active substance or to incipient dehydration. When treating with them, you cannot change your drinking regimen without permission; this will reduce the effectiveness of therapy, so you need to consult a doctor and pay attention to the presence or absence of other signs of dehydration.