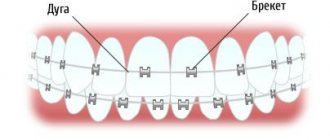
The position of the teeth with the jaws closed is called a bite in dentistry. Unfortunately, not every one of us can boast of perfectly straight teeth. Most people experience malocclusion. Most often, they are small and few people notice them, but there are situations when the malocclusion is pronounced and causes a lot of inconvenience. In these cases, it is customary to install braces. What to do if for some reason it is impossible to install braces? Dentistry has developed methods for correcting malocclusion using prosthetics, but doctors warn that they can only be used in specific clinical cases, strictly according to indications.
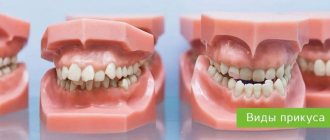
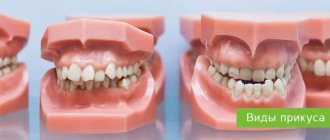
Types of bite
All babies are born with a malocclusion. Their lower jaw is moved back. Thanks to active sucking, it gradually moves forward. When bottle-feeding, you need to take this point into account and not give children a nipple with a large hole so that they train their muscles, ensuring their load.
By age 14
A permanent (adult) bite is formed, all milk teeth are replaced by permanent ones, the number of teeth reaches the physiological norm (28-32).
By this time, it becomes clear what type of bite has formed:
- Normal
It is also called physiological. A normal bite has variations: the lower teeth slightly overlap the upper teeth, the teeth meet rather than overlap, and some may be tilted forward. The main definition is that all teeth are closed, there is contact between them, the lateral teeth are closed without gaps.
- Deep
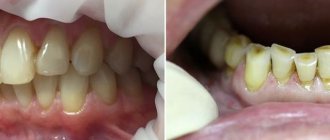
The upper teeth cover the lower ones by more than a third. Contact is broken. This pathology is called traumatic because it leads to injuries to the mucous membrane, abrasion of teeth, and disruption of the temporomandibular joint.
- Open
A gap remains between the teeth, resulting in food not being chewed completely. The defect affects the process of swallowing and even breathing. The mucous membranes dry out, saliva does not wash away plaque in time, hence frequent caries and other diseases of the oral cavity.
- Distal
The gap is formed as a result of the fact that the upper jaw is strongly pushed forward. Accompanied by dysfunctions of breathing, swallowing, and chewing. Pain in the joints often occurs.
- Mesial
With this defect, the lower jaw moves forward. With this pathology, two extremes can be observed: crowding of teeth or gaps between teeth (trema and diastema). When there is crowding, tartar accumulates very quickly and if it is not cleaned off in time, periodontal diseases (gingivitis, periodontitis) occur.
- Cross
The teeth overlap each other. Such a defect is difficult to treat and forces one to resort to surgical methods. Leads to facial deformation, disruption of the TMJ, and permanent injuries to the mucous membrane.
Other signs
There are indirect signs of malocclusion.
- Reduced height of tooth crowns.
Typically, the front teeth are rectangular in shape. If they become square, this may be due to thinning enamel. The thickness of the enamel on the cutting edges and chewing cusps of the tooth is about 2 mm. Due to an incorrect bite, the enamel wears off and the teeth become more square in shape. This is a clear sign of an “age-related” smile, but for young people it is not the norm (unless the teeth were square from the very beginning).
Worn teeth
- Increased tooth sensitivity.
The reason is the same - the enamel becomes fragile and thin. Teeth begin to ache from hot and cold, sometimes from sour and sweet.
- Pain or clicking in the jaw joints.
They are often unnoticeable because many people eat mostly soft foods and do not spend much effort chewing. Problems with the jaw joints usually appear when trying to chew solid food. Most often, the cause of dysfunction is malocclusion. The jaws are positioned incorrectly relative to each other, so the joint is loaded unevenly.
- Discomfort when chewing or biting.
The more complex the disorder, the more noticeable it is that when chewing the load is distributed incorrectly. With an open bite, for example, some of the teeth do not close together at all, so it is difficult to chew food well.
- The symmetry of the smile is broken.
The easiest way to determine this is to look at the centers of the upper and lower jaw. They must match.
- Some teeth have a wavy edge.
The permanent teeth grow with wavy edges. And only then do they gradually grind down and become straight. This happens due to chewing. If one of the teeth is slanted or turned so that its edge is higher than all the others, it will remain wavy because it will not grind down.
Wavy edge of teeth
- The symmetry of the face is broken.
This sign needs to be assessed by looking not at the teeth, but at the face as a whole. Normally, the nasolabial folds are symmetrical. If only one of them appears, this indicates that the jaws are located asymmetrically.
- Obtuse angle between neck and chin.
If the lower jaw is too small or pushed back, a double chin may appear at a young age. This is due to the fact that due to the position of the lower jaw, the angle between the neck and chin is flattened.
Perhaps your chin looks small due to problems with your bite
If you have any doubts about the health of your teeth, consult a doctor - only an orthodontist can make a final diagnosis at an appointment, after which, if necessary, treatment can be planned.
Prosthetics for deep bite
The task of the orthopedist in this case is to eliminate damage to the mucous membranes, recreate occlusion (touching of teeth when closing), evenly distribute the chewing load and restore the height of the lower part of the face.
To do this, the occlusal surfaces of the teeth are leveled by grinding away the hard tissues. If a large number of units are missing, partial removable dentures with occlusal overlays are used. If the teeth are intact, the bite is corrected with crowns.
Basis of construction
The construction of the bite height is based on determining the distance between the two jaws in the position of maximum intercuspal closure of the teeth.
This indicator is of great importance in dental practice, since it allows one to determine the correct location of the elements of the dentofacial row.
A change in the physiological height of the bite as a result of the loss of some teeth or their displacement relative to the jaw line entails a change in the position of the main anatomical elements that surround the oral cavity.
In this situation, the patient is diagnosed with sunken lips, an increase in the depth of the nasolabial folds, a significant protrusion of the chin forward, and a decrease in the height of the lower sector of the face.
In addition to being aesthetically unattractive, this situation significantly complicates further orthodontic and orthopedic therapy.
Methods for correcting open bite
The teeth that prevent the jaw from closing are ground down. After a little grinding, the surface is polished and calcium and fluorine preparations are used for remineralization. When grinding off a significant thickness, the tooth is covered with a crown.
Teeth that lack height are augmented with crowns. In cases of insufficient height of the front teeth, veneers can be used. If all teeth are intact, then the main goal is to create occlusal contact. If a part is missing, then the task becomes more difficult. It is necessary to restore the dentition and occlusion at the same time. For this purpose, bridges and removable dentures (clasps) are used.
When will only a surgeon help?
If a person comes to an appointment not only with a greatly enlarged gap, but also with several missing molars or their strong inclination towards the throat, he is referred to a surgeon. In such situations, doctors have to disconnect part of the bone and move it to a physiological position. This is a complex operation that is performed under general anesthesia and recovery from it takes 6-8 months.
We told you what to do with non-physiological interdental distances. The main thing is to contact a competent orthodontist, be patient and set yourself up for a long journey to health. Before installing expensive structures and enrolling in surgical operations with a long rehabilitation period, it is important to undergo a full examination and start with gentle methods.
Prosthetics for crossbite
Intervention is possible only with the skeletal form of the anomaly, if the patient has refused other types of help. In a preserved dentition, crowns are installed on the lateral teeth. If there is a large overlap, the natural crown (the part of the tooth that is visible) is shortened, cutting off the excess. If there are missing teeth, bridges are used.
If the teeth are slightly tilted, preparation is limited. For large deviations, tabs are used, changing their axis relative to the axis of the root. Such dentures are used for malocclusion if the deviation does not exceed 15 degrees. A crown is placed on top of the stump with an inlay.
Consequences
If dental malocclusion is not corrected in a timely manner, irreversible consequences may occur, including:
- Dental pathologies.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- ENT pathologies.
- Speech disorders.
- Central nervous system disorders, headaches and joint pains, development of psychological problems.
- Violation of facial symmetry, aesthetic defects.
This is a short list of the dangers of malocclusion. Each item has a number of medical diagnoses of varying severity.
Therefore, if you suspect the formation of a pathological bite, you should consult an orthodontist as soon as possible, who will conduct a thorough diagnosis and give recommendations for further treatment.
Minor defects
If there are anomalies in the size and shape of the front teeth, the position can be corrected without the intervention of an orthodontist. Veneers and crowns change the shape, close diastemas (gaps between the front teeth), tremata (gaps between other teeth), and visually increase the size of the teeth. Increasing the height of the bite has a positive effect: the lower jaw that has moved back returns, this reduces the load on the temporomandibular joint. The pain and clicking go away. Facial proportions are restored and posture is straightened.
general information
In medical terminology, occlusion refers to the relationship of teeth. The dentist analyzes the state of the chewing muscles and the temporomandibular joint at the moment when the jaws are clenched.
Bite is the position of the teeth in relation to each other when the jaws are fully closed.
There are physiological and pathological or, respectively, correct and incorrect bites.
A physiological bite in humans ensures high-quality functioning of the dental system (chewing food), clear diction, free breathing and an attractive smile.
With a correct bite, the face is harmonious, the lower and upper jaws are formed proportionally, the load on all teeth is carried out evenly, the vertical axis of symmetry of the face crosses the junction between the front incisors. This allows a person to chew food thoroughly without injuring soft tissue or periodontium and without overloading the temporomandibular joint.
Stage III - treatment and preparation of teeth for prosthetics
Before dental prosthetics, it is necessary to prepare the teeth so that they do not disturb the patient some time after the installation of expensive structures. To do this, Dial-Dent conducts a thorough diagnosis of the condition of previously treated canals and, if necessary, treats the canals of the teeth under a microscope, guaranteeing maximum service life of the teeth. To create a zone of attached gum, the surgeon performed periodontal manipulation. The hygienist performed gentle teeth cleaning and applied a special product to the front teeth to eliminate hypersensitivity. All these procedures were performed gradually, at a time convenient for the patient, while the dental implant was healing.
Initial consultation with an orthodontist
During the consultation, the following problems were identified: the absence of the 35th tooth (there is no place for its prosthetics), pathologically deep bite, bruxism, severely worn teeth in the lateral regions, minor chips on the front teeth, displacement of the jaw when opening the mouth, clicking in the TMJ on the left.
Bruxism, deep bite, increased tooth wear, TMJ dysfunction - all these problems, which are of the same nature, will only get worse without proper treatment. Treatment should be carried out comprehensively with the participation of several specialists: an orthodontist, an orthopedist, a neuromuscular dentist, an osteopath.
Reasons for the development of the anomaly
There are many reasons that influence the height of a person’s bite. Dentists name the following factors that contribute to reducing the distance between the jaws in occlusion:
- pathological abrasion of the tooth surface , accompanied by loss of its density and subsequent destruction of incisors and molars;
- bruxism or teeth grinding , which entails enamel deformation, subsidence of teeth and a decrease in central occlusion;
- uneven chewing load in certain areas of the jaw row, which often occurs when restoring teeth using a prosthetic bridge;
- loss of molars on one or both jaws;
- destruction and extraction of several teeth in combination with displacement of the remaining elements of the row relative to the central jaw line;
- metabolic disorders in the body , which entails a deficiency of calcium and phosphorus, which affects the strength of bone tissue and contributes to its atrophy;
- improperly manufactured prosthetic structures.
In order for prosthetic structures to be manufactured correctly, it is necessary to carry out a considerable number of measurements, one of which is considered to be carrying out all studies in a state of physiological rest of the patient’s maxillofacial apparatus.
How dental impressions are taken for prosthetics and orthodontic treatment.
Read here about the purpose of teeth filing.
At this address https://orto-info.ru/ortodonticheskoe-lechenie/podgotovitelnyiy-period/separatsiya-zubov.html all the most important things about teeth separation when wearing braces.