Anesthesia methods in dentistry
All methods of anesthesia in dentistry are divided into general and local. General anesthesia is general anesthesia and intravenous sedation. That is, drugs are used that affect the entire body, and not just the oral cavity. This is a standard general anesthesia that is used not only in dentistry, but also in other branches of medicine. Local anesthesia is the familiar “freezing”, administered by injection. Xenon therapy can also be used in combination with general or local anesthesia.
Local anesthesia is most often used in dentistry. There are many indications for its use. These include:
- cleaning teeth from deposits;
- dental treatment of any complexity;
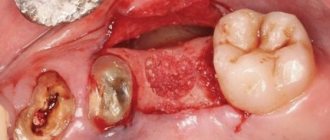
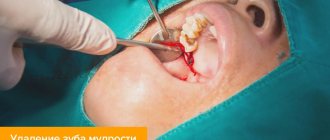
- removal of dental units;
- performing manipulations on the gums;
- surgical manipulations in the oral cavity;
- implantation or preparatory measures (but in some cases general anesthesia is recommended).
Local anesthesia has obvious advantages. The drugs are safe, they do not negatively affect the body, do not cause side effects and are eliminated quickly. At the same time, the techniques completely relieve pain of any nature.
Local application of anesthetics involves the use of special syringes with a very thin needle to avoid pain during injection. Main types of local anesthesia:
- Applique. It involves applying a pain-relieving anesthetic in the form of a gel. It is used primarily for oral hygiene and removal of deposits, especially if ultrasound is used for this. Its effect is short-lived.
- Infiltration. This is the standard injection “freezing”, which is carried out in almost all procedures. The injection can be injected into the mucosal tissue, bone or periosteum. In this case, the dentist must take into account the anatomy of the upper and lower jaw.
- Conductor. Used for long and complex surgical interventions. An anesthetic with a high content of the active component is selected. It is injected directly into the nerve, so the effects of anesthesia last longer and affect a larger area. Conductive anesthesia can be used during operations, tooth extraction, and when installing several implants at the same time.
Reasons why anesthesia does not take effect
A patient comes to me and says that anesthesia does not work on him and that the last time he had a tooth removed under anesthesia. And now we are supposed to work on tooth extraction. I honestly say that he may well go to the previous clinic, where he had general anesthesia, because... I don’t know the real reasons why the anesthetic didn’t work and why the doctors then switched to general anesthesia. Then the patient decided to remove the tooth from me without general anesthesia, with ordinary anesthesia. And it turned out that the anesthesia worked great and we removed the tooth painlessly.
I want to tell you in what cases anesthesia does not work. You can understand this, you can prepare for it and make sure everything goes well.
- It is not recommended to drink any alcohol in any quantity within 24 hours. Because the anesthesia will not work. How it works? The anesthetic reduces pain sensitivity by acting on the nerve endings going to the tooth. Alcohol also affects the nerves - it relaxes. And, in particular, it relaxes those small branches of nerves that innervate the teeth. And therefore, if you drink a glass of wine or a glass of beer, the nerves from the tooth will also be “relaxed” for about 24 hours: until the alcohol is transformed in the kidneys and liver and is eliminated from the body naturally. Usually, during anesthesia, pain sensitivity goes away immediately, that is, the anesthetic solution is perceived normally by the nerve fiber. And if it doesn’t work, one of the possible reasons is that there was alcohol in the blood, and it could even be one glass of wine!
- When there is a lot of swelling and inflammation inside. Inflammation is an acidic environment, the pH of which inactivates the injected anesthetic solution immediately. Those. the injected anesthetic solution, entering a place next to the tooth, cannot act on the nerve endings, because there is an acidic inflammatory environment there. When does this happen? When a visit to the dentist is postponed until the last minute, to such a state that it becomes more and more difficult to help.
- When your own adrenaline goes off scale from fear and general tension in the body, when the muscles of the neck, shoulder blades, back of the head, and upper shoulder girdle are so tense that the blood simply does not circulate due to tightness and muscle tension. All this does not help the anesthesia work; the substance simply does not reach the recipient. You need to take three deep, slow breaths, relax, relieve muscle tension in your shoulders and try not to concentrate on your images of fear, but to think about the good.
- Good anesthetics of the latest generation are effective. I use Ultracain DS forte in different dosages. I consider other, cheaper anesthetics not very effective. Although many doctors say that they are the same as Ultracain DS forte only one and a half times cheaper. I believe that you cannot skimp on anesthesia. It must be a priori good. No options. Good pain relief means job success and patient peace of mind.
Anesthesia does not work: what to do?
Situations where anesthesia does not work are extremely rare. Less than 1 percent of patients are sensitive to a particular drug, so choosing the right type of anesthesia is key. Frequent reasons for effectiveness are incorrectly selected dosage of the anesthetic or errors in its administration.
When using anesthesia, you must take into account the following health conditions:
- If you are prone to allergies, asthma or diabetes, medications without preservatives and with a low concentration of epinephrine are used. The funds are selected individually, taking into account the analysis.
- For heart pathologies and high blood pressure, medications with a minimum of epinephrine or without it are used. Also, they should not contain adrenaline. In these cases, xenon therapy or intravenous sedation may be used.
- For pregnant and lactating women, epinephrine dosages should be kept to a minimum. Then it cannot cross the placenta and enter breast milk.
Sedation and anesthesia are completely safe if performed by an experienced specialist. When carrying out long and complex interventions, such as implantation or prosthetics, sedation is even a recommended method, since the operation becomes more comfortable for the patient.
Our doctors select anesthesia individually. We offer all types of dental services: whitening, cleaning, surgical and therapeutic treatment for adults and children, installation of crowns, veneers and dentures. You can find out the clinic’s prices and make an appointment through the website or by phone.
Recommendations before visiting the dentist:
- The night before your appointment, drink lemon balm or chamomile tea before bed. These natural remedies have excellent calming effects.
- If you have constant strong feelings, before each dentist appointment, it is recommended to take a course of light sedatives a week before visiting the doctor. For example, “Afobazol” and “Tenoten”, they calm the nervous system, improving well-being and relieving anxiety before dental surgery. Drugs such as valerian and motherwort are best taken in tablets: tinctures are alcohol-based, which impairs the quality of pain relief.
- For the same reason, you should not drink alcoholic beverages at least 24 hours before your dentist appointment. Alcohol is eliminated from the body within 72 hours, but the products of its metabolism remain in the body for another week. To speed up the cleansing of the body from toxic substances, it is recommended to take sorbent preparations.
- Get a good night's sleep and eat before your appointment. This way you will save yourself from additional stress, and, consequently, from unnecessary problems during dental procedures.
- Be sure to tell your dentist about any medical conditions you have and the medications you are taking! This will help the doctor choose the right method of pain relief and anesthetic. In addition, taking certain medications can greatly reduce the quality of pain relief.
The main recommendation would be a careful approach to choosing a dental clinic and doctor. After all, a competent dentist, even if difficulties arise with administering anesthesia, will be able to find the right way out of the current situation.
Dentist advice
Osmanov Konstantin Gennadievich
Discuss concerns about the procedure with your dentist. Ask questions about medications used for pain and what to expect during and after treatment. Get a medical history from your physician, including information about allergies and other medications you take, including over-the-counter and prescription medications and dietary supplements.
Possible reasons
Note that ineffectiveness of the anesthetic drug is extremely rare. Typically the cause is the following factors:
- According to medical statistics, this list is topped by improperly stored injections or expired injections. This situation can often be encountered in little-known dentists.
- Many people know that the presence of alcohol in the blood can affect the effect of painkillers, or rather, provoke their inaction. If a patient came to the dentist for dental treatment while intoxicated or with a hangover, it is not at all surprising that the drug did not work.
- Insufficient experience of the doctor who uses the wrong drug, too low a dosage, too thin a needle, etc.
- Diseases of the mucous membrane accompanied by swelling. Thus, the medication may not reach the nerve endings. Again, this is only possible with low qualifications of the doctor. An experienced specialist knows all the nuances and anatomical features, so such an oversight is excluded.
Types of local anesthesia
Application anesthesia
This method completely eliminates the use of a needle and syringe. A small amount of a special anesthetic (paste, gel or ointment) is applied to the selected area with a cotton swab or fingers, which penetrates 2-3 millimeters into the soft tissue and blocks the nerve endings.
Application anesthesia
Since “freezing” acts for a short period of time (no more than 20 minutes), this method is more often used when performing simple and quick operations where it is necessary to anesthetize only the oral mucosa.
Application anesthesia is often used before the subsequent use of injection, especially if the patient is very afraid of injections, or when treating children.
The drug in aerosol form can also be used as an anesthetic. However, due to the complexity of calculating the required amount of anesthetic substance, this type has not been widely used in dentistry. The use of an aerosol increases the risk of complications, as it can easily penetrate the patient's respiratory tract and bloodstream.
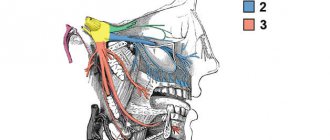
Conduction anesthesia
This type of anesthesia is the most effective method in which the active substance is injected in small doses (no more than 5 milliliters in volume) using a special needle into a place located in close proximity to the nerve that controls the site of the intended intervention.
Conduction anesthesia
With this method, using only one dose of injection, you can achieve “freezing” not only of one tooth, but of a much larger area. To improve the effectiveness of the injected substance, the injection is given at an angle of 90 degrees. 15-20 minutes after the injection, the drug begins to act, and the doctor can begin manipulation.
The main advantage of using conduction anesthesia is the long duration of action of the drug - from one and a half to three hours. During this time, the doctor can work with several molars and adjacent soft tissues, perform a complex tooth extraction, perform surgery for a jaw injury, and much more. The duration of action of the drug can be increased by adding a dose of anesthetic if for some reason the duration of the operation has increased. Due to the fact that complete anesthesia occurs, the patient’s salivation decreases, which greatly simplifies the doctor’s work.
Infiltration anesthesia
In modern dentistry, this is one of the most common types of local anesthesia, in which the drug is administered with a syringe into the gum tissue. With this method, the nerve endings are blocked directly at the site where the anesthetic is injected. Currently, two methods of infiltration anesthesia are used: direct and indirect.
Infiltration anesthesia
Direct anesthesia - the medicine is directly injected under the mucous membrane in the place where dental procedures will be performed and the sensitivity of which needs to be reduced.
Indirect anesthesia - the active substance is injected at a distance of 2 centimeters or more from the site of manipulation, penetrates into the tissue and numbs a larger area.
The advantage of infiltration anesthesia is that after the administration of the anesthetic, in just a couple of minutes the doctor can begin work and the “freezing” effect lasts about an hour. This time is enough to perform implantation surgery, remove a tooth, treat pathological conditions of the gums and teeth, remove various tumors on the oral mucosa and other manipulations.
Depending on the area where the injection is given, infiltration anesthesia is:
- intraosseous (spongy) - the injection is placed directly into the bone between the roots of the teeth. It is most often used in the area of lower molars, during the treatment or extraction of teeth, when conduction and infiltration anesthesia are ineffective. This method allows for high-quality pain relief using a small amount (1-1.5 milliliters) of a weak anesthetic.
- intraligamentary (intraligamentous) - the anesthetic is administered with a special syringe under high pressure not into the nerve itself, but into the gum and jaw tissue, that is, into the periodontal space. Anesthesia occurs within a minute from the time of injection and lasts from 20 to 40 minutes. This is enough to perform outpatient procedures. This method of pain relief is low-traumatic, the drug accumulates to a greater extent in the injection area, so there is no gums during and after the injection.
- intracanal - performed using a drill. First, a hole is made in the tooth that matches the diameter of the needle, and then the anesthetic is injected directly into the pulp or deeper into the canal itself. Intracanal anesthesia is used as an adjunct to intraligamentary anesthesia.
Tuberal anesthesia
Tuberal anesthesia
When using this method, the anesthetic is injected into the tubercles of the upper jaw, which are called tuber in Latin. The posterior alveolar nerve is located in this area, thanks to which most of the alveolar ridge is “frozen”. The tuberal anesthesia method is rarely used, as it is considered dangerous from the point of view of the occurrence of various complications due to the individual structure of the jaw in this area and the location of nerves and blood vessels in it.
Expert advice
So, now let’s look at the unique recommendations of doctors that will help prevent inaction of anesthesia:
- Alcohol should not be taken three days before visiting the doctor. If a trip to a medical facility was not planned, and you drank alcohol the day before, the situation can be resolved with the help of enterosorbents. Even regular activated carbon will do. You need to drink the appropriate dosage for your weight twice with an interval of 1-2 hours.
- If you do not want to take sedatives. Replace them with a soothing tea, mint tea, a warm bath with lavender, etc.
- To normalize your psychological mood, try to think about positive aspects. Good emotions will help you overcome your fear of the dentist and successfully undergo the necessary dental procedures without pain and discomfort.
Psychological factor
We should also talk about the moral state and psychological state of the patient. People who are very afraid of the dentist are called dentophobes. This category of people comes to the doctor only in advanced cases, when the pain can no longer be endured or it is a purulent process. As soon as the patient crosses the threshold of dentistry, the heart begins to beat faster, the body actively produces adrenaline, as a result of which spasm of the smallest blood vessels occurs. It is for this reason that the anesthetic is ineffective.
To eliminate this factor, dentists recommend starting to take sedatives at night 2-3 days before. A conversation with a doctor, a detailed description of the process, a cozy atmosphere and pleasant music are conducive factors that will help you relax as much as possible.
Anesthesia for children during dental treatment
In pediatric dentistry, the choice of anesthetic depends on the age of the child, the characteristics of his immunity and nervous system. Sedation through a breathing mask is often used - especially at a young age, when it is still difficult to explain to a child that he needs to sit still and endure an injection with a large and scary syringe in the gum. The dosage of the sedative is designed for approximately 10-15 minutes - this time is enough to calm the child and carry out all the necessary manipulations.
General anesthesia is also used in pediatric dentistry, although it is recommended in extreme cases.
In our dentists “As-Stom” for dental treatment for children
Injection anesthesia is carried out, and if the child is afraid of an injection, application anesthesia is first applied. If necessary, to exclude an allergic reaction to an anesthetic drug, a pediatric dentist can give a referral for allergy tests.
What type of anesthesia should I choose?
Choosing an anesthesia that will work specifically for you and will be most effective for a specific treatment is the task of the dentist. To prevent him from making a mistake, you definitely need to tell him about your allergy to one or another component of the drug (if you know about it), as well as about pregnancy or lactation, if you are currently going through this period. In the case of treating a child, the doctor will certainly consult with the parents first and select a safe drug.
You can make an appointment with a dentist by phone 597-05-05
or using
the online application form
on the website.
Don't forget about our promotions and discounts on dental treatment
, and be healthy!
Why might painkillers not work?
The effect of an anesthetic drug is always individual, and sometimes, even with the calculated dosage, the patient complains that the gums remain sensitive, and he is afraid to begin treatment. It may depend:
- From the specific location of the nerves in the gums and soft tissues;
- From the psychological mood of the patient (yes, the more we are afraid, the worse the drug can act);
- From the release of adrenaline during stress;
- From the body's immunity to a specific substance;
- From alcohol abuse.
Also, immunity to painkillers is possible in case of severe suppuration at the site of anesthesia: a large accumulation of pus blocks the effect of anesthesia.
Important!
At As-Stom dentistry, they always accommodate the patient halfway if he says that he still feels pain. The doctor will administer an additional dose of the drug, or change it in case of immunity, and in case of severe stress, he will offer the patient a sedative, turn on a distracting movie on the screen, and provide a comfortable blanket.
If you are seriously anxious, you may want to ask your dentist directly what anti-anxiety medication you can take before treatment to help reduce your anxiety levels.
Fear of dentists in children
Under no circumstances should you postpone a visit to a pediatric dentist, since oral diseases in childhood progress very quickly and can lead to serious complications. Parents should understand that caries in children in the early stages can be treated painlessly without the use of a drill; Timely detection of malocclusion in a child will help to avoid aesthetic problems, difficulties with speech development and chewing food.
Kids are very inquisitive, and for the first time they can easily agree to come to the dentist because they are interested in everything new. But it happens that a child flatly refuses to go to the doctor. Usually the reasons are the following factors:
- The kid had a negative experience communicating with people in white coats. And it doesn’t matter what specialty the doctor caused trouble: the child will be afraid of everyone.
- Parents' stories about how bad doctors are and how painful it is to treat teeth. Even if adults talk to each other, children, like a sponge, absorb information and draw appropriate conclusions.
- Parents' experiences before visiting the dentist. If the mother is too worried and nervous, persuades the child to be patient and behave well, the baby begins to suspect that it will be painful. His mother's mood is transmitted to him, he also begins to worry and, most likely, refuses to go to the doctor.
- The indecisive nature of the child. Some children are so indecisive that they are afraid of everything unknown; If such a child is brought to an appointment without any explanation, he will burst into tears and flatly refuse to talk to the doctor.
- You can help your child overcome his fear of the dentist by following these recommendations:
- You need to start by choosing a clinic where doctors work who know how to communicate with young patients. Modern children's classrooms are equipped with toy corners and TVs for watching cartoons.
- You should start getting acquainted with doctors from the age of one: regular examinations at the dentist will turn a visit to the clinic into a habitual procedure; constant monitoring of the condition of the child’s teeth will help to detect diseases at the initial stages and avoid complex, painful treatment. Adults should set an example for children: undergo a medical examination with them, brush their teeth in the morning and evening.
- Before the appointment, parents should not be nervous or express pessimistic assumptions about the results of the examination.
- If the child is not in the mood to go to the doctor now, it is better to reschedule the visit to another time. It is necessary to avoid extremes: some parents, succumbing to their mood, may postpone dental examination for an indefinite period of time; others, realizing the importance of the procedure, begin to threaten the child with punishment.
- If serious procedures are to be carried out, you cannot tell your child that “the doctor will just take a look.” It’s better to tell the truth, but do it in a childish way: explain that insidious microbes have settled in the teeth, which bite and can hurt, and only a doctor can drive them out.
- Let the little patient know that after visiting the doctor, some pleasant surprise awaits him from the “tooth fairy”: at the end of the treatment, the parents or doctor will give it to the child.
People who have been familiar with two rules since childhood have no fear of the dental office:
- It is necessary to maintain oral hygiene daily.
- It is necessary to undergo a preventive examination at the dentist twice a year.
To stop being afraid of the dentist, start treating him as a friend and assistant who will get rid of the disease and restore health and beauty to your smile!
What is dentistry under anesthesia?
By the word “anesthesia” we are accustomed to understand a complete disconnection from reality, although in fact sedation also refers to anesthesia. When the procedure is performed under anesthesia, the central nervous system (CNS) is depressed, which allows you to “switch off” without feeling fear and pain.
Both sedation and general anesthesia are carried out under the supervision of an anesthesiologist, with constant cardiac monitoring, and have a certain list of contraindications.
Sedation
– another common type of dental anesthesia, but it affects the nervous system and control of the patient’s psycho-emotional state. A person under sedation remains conscious, but is in a state of a kind of half-sleep, relaxed and calm, his sensitivity is dulled, his emotional background increases, and the body does not react to dental operations as if it were severe stress. To immerse him in this state, a sedative is administered intravenously, and additional pain relief is performed with local anesthesia.
Interesting fact:
The first dental operation under general anesthesia was performed in 1846 by dentist T. Morton, and this was, in principle, the first operation under anesthetic. Local anesthesia began to be used in dentistry later, from 1881.
Important!
Dental procedures under general anesthesia are not carried out in all clinics: this requires additional equipment, an anesthesiologist, experience with such anesthetic drugs, and an appropriate license. At As-Stom dentistry, operations under general anesthesia are not performed!