Everyone experiences dental disease at some point. But more often, problems with teeth appear in pregnant women. The reasons are increased stress on the body, rapid consumption of calcium reserves necessary for the construction of the baby’s skeletal system. Many medications are prohibited during pregnancy. Doctors know what to do in such a situation. Dentists often prescribe Metrogyl denta to their patients, the instructions for pregnancy state that the drug can be used during the 2nd or 3rd trimester, but with caution.
Description of the drug
Metrogyl Denta is produced by an Indian pharmaceutical company that uses Ayurvedic knowledge when developing its drugs.
The release form of the medicine is a white gel with a faint menthol odor. The basic components of the product are chlorhexidine and metronidazole. Additional components:
- Sodium hydroxide
- Levomenthol
- Saccharin
- Carbopol
- Water
- E 1520.
Metrogyl Denta is an antimicrobial and antiseptic drug. When applied topically, the gel is almost not absorbed and does not penetrate into the general bloodstream.
The antibiotic effectively destroys gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms. However, the drug does not disrupt the microflora in the mouth. Therefore, the number of lactobacilli does not decrease.
Metrogyl denta is prescribed for the following diseases:
- Periodontitis is inflammation of the periodontium, leading to the appearance of a pocket in the gum and destruction of the bone process
- Gingivitis – occurs due to hormonal imbalance, lack of vitamins in pregnant women
- Aphthous stomatitis - the disease is characterized by the formation of aphthae, the ulcers hurt and take a long time to heal
- Cheilitis – characterized by the formation of ulcerations, crusts, and redness in the corners of the mouth
- Periodontitis – inflammation and suppuration of the periodontium
- Periodontal disease is a lesion of the tissues that fix the tooth, which exposes the neck of the tooth.
Doctors know whether Metrogyl denta gel can be used topically for dental diseases by pregnant women. But contraindications should be taken into account. These are intolerance to components, age under 18 years, diseases of the central nervous system or blood, 1st trimester of pregnancy.
Using Metrogyl may lead to side effects. Often, after using the gel, allergic manifestations and headaches appear.
Instructions for use of METROGYL DENTA® (METROGYL DENTA®)
A drug with antimicrobial action for topical use in dentistry.
In periodontitis, anaerobic bacteria are considered the predominant causative factor. Therefore, it is desirable to use pharmaceutical treatment specifically effective against periopathogenic anaerobic microflora instead of using broad-spectrum antibiotics with the associated risk of developing bacterial resistance and gastrointestinal complications. Metronidazole is a chemotherapeutic agent with activity against anaerobes such as Bacteroides species and spirochetes, which are widely believed to be the main pathogens associated with periodontitis.
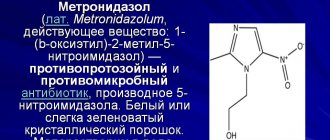
Metronidazole
Metronidazole is a 5-nitroimidazole derivative with activity against anaerobic protozoa and anaerobic bacteria.
Mechanism of action.
After metronidazole enters the body, it is reduced by intracellular electron transfer proteins. As a result of this change, a concentration gradient is maintained in the metronidazole molecule, which promotes intracellular transport of the drug. It is assumed that free radicals are formed, which in turn react with cellular components, and this leads to the death of the microorganism. Anaerobic bacteria associated with periodontal disease, such as Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedia, Fusobacterium nucleatum and Wolinella recta, are highly sensitive to metronidazole. The lowest concentration of metronidazole required to inhibit 50% of strains (MIC50) is below 1 μg/ml for the corresponding anaerobes. Topical metronidazole may produce higher subgingival concentrations than those achieved with systemic administration. Therefore, a lower dose of the drug will be required.
Microbiological analysis included determination of total anaerobically culturable bacteria and the relative proportions of anaerobes, aerobes, black pigmented anaerobic gram-negative rods, Actinobacillus actinimycetemcomitans, streptococci and spirochetes.
Both treatments resulted in a significant reduction in pocket depth. The decrease in GDC was statistically significant during treatment and during subsequent visits to the doctor (p < 0.00001). Metronidazole gel tended to be a better treatment than stone removal throughout the period. The reduction in bleeding on probing was statistically significant during treatment and during follow-up (p<0.02).
Chlorhexidine gluconate
Chlorhexidine is a disbiguanide antiseptic and disinfectant with bactericidal or bacteriostatic action against a wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
Mechanism of action.
At physiological pH, chlorhexidine salts dissociate, releasing a positively charged component. The bactericidal effect of chlorhexidine results from the binding of these cationic molecules to the negatively charged walls of bacterial cells and extramicrobial complexes. In low concentrations, chlorhexidine causes an imbalance in the osmotic balance of bacterial cells and the leakage of potassium and phosphorus, which gives a bacteriostatic effect. At high concentrations of chlorhexidine, the cytoplasmic contents of the bacterial cell are precipitated, which leads to its death.
Several hypotheses have been put forward regarding the mechanisms of action of chlorhexidine in relation to plaque inhibition.
1. Binds to bacteria that form oral plaque and affects their absorption by teeth.
2. Binding to glycoproteins in saliva and reducing pellicle formation and plaque colonization.
Chlorhexidine is poorly absorbed through intact skin or from the gastrointestinal tract. Does not accumulate in the body and is only minimally metabolized. If swallowed, chlorhexidine is primarily excreted in the feces. There are reports that extensive use of chlorhexidine for over 20 years has provided no evidence of absorption through intact skin.
The role of Metrogyl Denta® gel
The effectiveness of the drug is due to the presence of two antibacterial components in its composition:
- Metronidazole has an antibacterial effect, is active against anaerobic bacteria
that cause periodontal diseases: Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedia, Fusobacterium fusiformis, Wolinella recta, Eikenella corrodens, Borrelia vincenti, Bacteroides melaninogenicus, Selenomonas spp. - chlorhexidine is an antiseptic and antimicrobial agent, active against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria
(Treponema spp., Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Trichomonas spp., Chlamydia spp., Ureaplasma spp., Bacteroides fragilis). Some strains of Pseudomonas spp., Proteus spp. are weakly sensitive to the drug, and acid-resistant forms of bacteria and bacterial spores are also resistant. Does not interfere with the functional activity of lactobacilli.
When applied topically, the active substances of Metrogyl Denta® gel are practically not absorbed.
Metrogyl Denta® gel includes a suspension of metronidazole benzoate with propylene glycol. When applied, the gel flows and fills the dental pocket. Upon contact with the aqueous portion of either gingival cavity fluid or saliva, which contains esterases, it hydrolyzes the microbiologically inactive metronidazole benzoate into free metronidazole and benzoic acid. Metronidazole has an aerobicidal effect on bacteria located in the periodontal area. Metronidazole also has anti-inflammatory activity, which targets inflammation associated with periodontal disease.
Chlorhexidine is an antiseptic and disinfectant and has a bactericidal and bacteriostatic effect on a wide range of bacteria.
Metrogyl Denta® is active against aerobic and anaerobic flora present in the oral cavity and, in particular, in the gum pockets.
Systemic metronidazole at doses of 750-1000 mg/day for 2 weeks is known to reduce the growth of anaerobic flora, including spirochetes, and reduce the clinical and histopathological signs of periodontitis. Metronidazole, when used in addition to thorough scaling and root planing, significantly reduces the need for surgery compared with mechanical scaling alone. Topical metronidazole in gel form reaches high concentrations locally around the gum tissue and is therefore very effective. The simultaneous use of topical metronidazole helps to avoid side effects with long-term use of metronidazole in the mouth.
Taking into account the fact that oral infections are mixed in nature and are usually caused by aerobic and anaerobic bacteria, and the disease is chronic, long-term use of oral antibacterial agents can lead to side effects and the risk of developing bacterial multidrug resistance. In such cases, topical treatment containing a combination of antibacterial agents acting on aerobic and anaerobic bacteria simultaneously (metronidazole benzoate 1% and chlorhexidine gluconate 0.25%) is of paramount importance.
Again considering the involvement of aerobic and anaerobic bacteria in periodontal disease, the combination of metronidazole benzoate and chlorhexidine gluconate would have an important therapeutic advantage over chlorhexidine gluconate alone.
Is it possible during pregnancy?
Doctors know whether pregnant women can use Metrogyl dent. The product contains an antibiotic, so doctors advise using it with caution.
Metrogyl denta should not be applied to the oral mucosa during pregnancy. But there are a number of cases prohibiting the use of the gel during this period:
- Intolerance to the components of the product
- The development of allergic reactions in the form of itching, nettle fever, headache and rashes.
Recommendations for use boil down to the fact that the medicine can be used topically, applied only to the affected areas of soft tissue. A little gel is squeezed onto a cotton swab and then smeared on the damaged areas.
The procedure is carried out twice a day. After applying the antiseptic, you should not eat for the next 30 minutes. Duration of therapy – 7 days.
If Metrogyl denta is used for periodontitis, then first you need to clean the diseased areas of the gums. The therapeutic effect of the gel lasts about half an hour.
For aphthous stomatitis, treatment lasts up to 10 days. For chronic dental problems, therapy is carried out every year for a course of 7-10 days. The gel can also be used to treat wounds formed after tooth extraction.
Treatment of catarrhal gingivitis
Treatment tactics depend on the stage of pregnancy. A course of therapy can only be prescribed by a doctor!
Removal of dental plaque.
Ultrasonic teeth cleaning is contraindicated for pregnant women, so hand tools are used to remove plaque. After the procedure, the teeth are polished.
Antimicrobial therapy.
The course may include rinsing with antiseptic mouth rinses, as well as the use of special medicinal gels and toothpastes.
Maintaining oral hygiene.
It is necessary to brush your teeth twice a day - in the morning and before bed, and after each meal. It is also necessary to use floss. Regular use of a mouthwash such as LISTERINE® is also important.
Up to contents
Reviews
Maria, Kursk: I will leave my positive review about Metrogil Denta. In the 3rd trimester of pregnancy, my gums began to swell and bleed. Rinsing the mouth with oak bark and chamomile did not help. But the gel quickly dealt with inflammation and swelling.
Elizaveta, Kislovodsk: In the second trimester of pregnancy, the dentist diagnosed acute gingivitis. I recommended using Metrogyl Denta 2 times a day. After the first application, I was able to eat without feeling pain or burning.
Is it possible to treat teeth during pregnancy?
Most likely, the tooth will decay during this time (the bulk of the minerals go to build the fetal body), damage neighboring ones, and also become a source of infection for the newborn. Let's add a change in the properties of saliva, which, due to its increased viscosity, cannot fully wash and protect teeth, and weak mineralization.
The answer is clear: treat. To do this, you need to choose the right time, place, specialist and materials. The specialists at SM-Dentistry treat their patients very carefully and choose only safe treatment methods.