Author:
- Elena Vitalievna Naumova, otolaryngologist, leading doctor of the clinic
2.82 (Votes: 11)
Acute tonsillitis with purulent exudate is considered the most common infection.
The disease occurs in both adults and children due to the entry of pathogenic microbes and bacteria into the oral cavity. It is not difficult to get a purulent sore throat even in the absence of direct contact with a sick person. Bacteria are spread through contact and airborne transmission, such as by sneezing or coughing in a public place or sharing household items.
Forms of purulent sore throat
There are two varieties:
- Purulent sore throat, affecting the lacunae of the tonsils. The infection is localized in the upper part of the throat and does not penetrate deeper. Purulent deposits are easily separated with a spatula.
- Purulent tonsillitis affecting the lymph nodes. The infection penetrates deeper and affects the lymphoid apparatus. Purulent exudate cannot be separated manually. The condition is extremely serious and threatens the formation of a peritonsillar abscess. Urgent medical attention and hospitalization are required.
Using traditional methods
It is possible to cure purulent sore throat with folk remedies when it is not yet very advanced. This therapy also works well as an adjunct to drug treatment.
Compress recipes
Alcohol compress.
- Dilute medical alcohol (70%) in warm water in a 1:1 ratio.
- Add a few drops of orange and lavender essential oil.
- Soak the gauze in the prepared solution and use it as a compress to the throat (apply for 1–2 hours). People with sensitive skin need to hold the compress for no longer than 30 minutes.
Potato compress
- Boil a few potatoes with their skins.
- Mash the finished potatoes and add five drops of iodine and a tablespoon of vegetable oil.
- Place the finished mixture in a gauze bag.
- Apply the compress to your throat for 40 minutes.
Raw potato compress
- Grate four medium potatoes on a fine grater.
- Pour in a tablespoon of apple cider vinegar.
- Mix everything well and place in a gauze bag.
- Apply to the throat for 2 hours.
Cabbage compress
- Pour boiling water over a few raw cabbage leaves.
- Leave for a few minutes until the leaves soften.
- Remove the leaves from the water and wipe it dry.
- Lubricate with honey and apply to a sore throat.
- Wrap film on top.
- Leave for 2 hours, then remove the compress and wrap your throat with a warm wool towel.
Recipes for inhalations
- Boil a few potatoes. Cut and place in a deep bowl. Breathe hot steam from the potatoes, covering your head with a towel.
- Mix a spoonful of honey with five drops of orange essential oil. Inhale the aroma for at least 10 minutes.
- Brew cool black tea. Add a tablespoon of mint to it. Use for inhalation.
- Take sage, mint, thyme, pine buds and elecampane roots in equal proportions. Brew these herbs in a liter of water. Breathe the steam from the decoction.
Garlic remedies
- Peel two heads of garlic and chop the cloves. Add two tablespoons of apple cider vinegar to them. Leave for 12 hours. Then add a spoonful of honey to the product. Take half a teaspoon of this mixture daily.
- Squeeze juice from carrots. Add two chopped garlic cloves to it. Drink this remedy before meals, 2 times a day, a tablespoon.
- Squeeze the juice from peeled garlic. Drink a few drops of juice a day. The product will help cure purulent sore throat very quickly.
Rinse recipes
- Take two tablespoons of dry chamomile and one spoon of linden flowers. Pour boiling water (1 liter). Strain and gargle 5 times a day.
- Infuse five tablespoons of horsetail in 500 ml of boiling water for an hour. Then strain and gargle with it at least 3 times a day.
- Pour two tablespoons of raspberry leaves with a glass of boiling water. Leave for 20 minutes for the product to infuse and cool. Use for rinsing.
- Grate the red beets and squeeze the juice out of them. Add a teaspoon of vinegar to one glass of juice. Mix everything and use as a gargle twice a day.
- Pour four fresh plantain leaves into a glass of boiling water and leave for half an hour.
- Mix half a glass of lemon juice with 200 ml of warm water. Use for rinsing.
- Mix dry chamomile and calendula in a ratio of 1:3. Boil in a liter of water. Leave for 2 hours. Cool and gargle with the prepared product.
- Take calendula and chamomile flowers, wormwood and plantain in equal proportions. Boil the herbs in a liter of water. After this, let it brew for 2 hours. Strain and use for rinsing.
- Take a teaspoon of dry sage and a tablespoon of chamomile. Pour the mixture with 500 ml of boiling water and leave it for 24 hours. Strain. Gargle at least 3 times a day.
It is also important to take enough fluid (at least 2 liters of water or compote per day). In addition, the patient must follow a diet. In order for the body to have enough strength to fight infection, it must receive the required amount of vitamins, minerals and trace elements every day
It is best to eat cereals, vegetable purees, broths and fermented milk products during this period. This food will not cause severe pain when swallowing and will be able to saturate the body well.
Causes of sore throat (acute tonsillitis)
The accumulation of purulent “sacs” in the tonsils occurs for various reasons. The main causative agents of tonsillitis are streptococci, but viral and fungal pathogens, staphylococci and pneumococci are also found. If the body is healthy, then the infection will not develop, but the following factors can aggravate the condition:
- Injuries to the tonsils and nasopharynx.
- Weak immunity.
- Chronic diseases of the ear, nose and throat, for example, stomatitis, caries, rhinitis, etc. foci of infection increase the proliferation of pathogens.
- Local and general hypothermia, for example, eating ice cream or drinking cold water.
- Autumn-spring vitamin deficiency.
The pathogenic factor penetrates deep into the tissues of the tonsils, forming a focus of infection.
Treatment of sore throat in children at home with folk remedies
Beet juice
Grate the beets on the finest grater, squeeze out the pulp well, add vinegar with a concentration of 6% to the resulting juice, in a ratio of 1 part vinegar to 10 parts juice, gargle with the solution every hour. A good anti-inflammatory effect will be provided, and the swelling of the tonsils will also decrease.
Chamomile
Add 1 teaspoon of pharmaceutical, dry chamomile to 300 milliliters of boiling water and leave for an hour. Store the finished infusion in the refrigerator, rinse the neck with the heated solution up to three times.
Sea buckthorn
Add a tablespoon of sea buckthorn oil to half a glass of boiled, cooled water or chamomile infusion; the rinsing process creates an enveloping and analgesic effect.
Milk with garlic
Mix 300 milliliters of milk with a large head of finely chopped garlic and put on fire until it boils. Strain, give 15-30 ml, several times a day. Improvements are observed after the first day of use.
Aloe honey
Cut 2 large aloe leaves into large pieces, place in a jar and pour half a liter of honey, close tightly with a lid and put in the refrigerator to infuse for three days. 10-15 minutes before each meal, give the child a teaspoon of treats. Course 3-7 days.
Medicines
Panadol, Viferon, Tantum Verde, Anaferon, Angin Hel, Bioparox, Faringosept. (Consult your doctor first)
Clinical picture
Once a pathogen enters the body, two hours are enough for it to spread. Streptococci settle on the tonsils, weakening local immunity. The incubation period varies from several hours to 5 days.
The main differences between purulent tonsillitis are symptoms:
- A sharp pain in the throat occurs, which causes discomfort even at rest. The next day she becomes unbearable when talking or eating.
- Within a few hours, the body temperature rises to 39-40°C. Against the background of high temperature, it throws you either hot or cold, sweating increases and chills are present.
- Swallowing saliva causes severe, sharp pain.
- There is not enough air when breathing due to swelling of the tonsils.
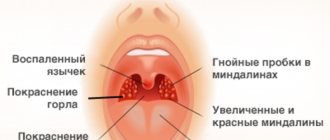
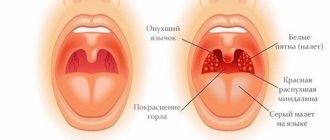
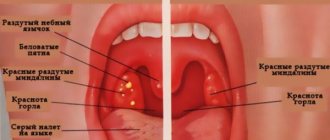
- When examined with the naked eye, swollen tonsils and severe hyperemia of the back wall of the throat are visible. The next day the tongue and palate swell.
- There is a sensation of a foreign body in the nasopharynx, which intensifies when saliva is swabbed.
- Due to the fact that the tonsils are well supplied with blood, a yellowish-white dot appears on them, the boundaries of which quickly expand. The next day, the throat may become covered with many white purulent dots, which gradually merge into large ulcers.
Purulent tonsillitis in children occurs in a more severe form. Due to the excessive pressure of the swollen lymphoid tissue of the adenoids on the Eustachian tubes, the ears become blocked and there is tinnitus. If treatment is not attempted, the infection can spread to the ears, complicated by otitis media.
Usually the acute period lasts no more than one week if treatment is prescribed on time.
Important to know and remember! Purulent tonsillitis is a dangerous infectious disease, so the patient should be immediately isolated from household members.
A sore throat
Roza Ismailovna Yagudina, Ph.D.
Sc., prof., head. Department of Organization of Drug Supply and Pharmacoeconomics and Head. laboratory of pharmacoeconomic research of the First Moscow State Medical University named after. I. M. Sechenov. Evgenia Evgenievna Arinina, Ph.D., leading researcher at the laboratory of pharmacoeconomic studies of the First Moscow State Medical University named after. I. M. Sechenov.
One of the most common complaints in the autumn-winter and, oddly enough, in the summer periods is a sore throat. The causes of painful sensations can be various pathogenetic processes occurring in the human body, and in the summer - also a violation of the environmental situation (humid, dusty air, air conditioners). The most common types of throat lesions are laryngitis, pharyngitis and tonsillitis. The last of these diseases is inflammation of the tonsils. Tonsillitis is the most common cause of sore throat; moreover, the inflammation often has a chronic course.
Causes and mechanism of tonsillitis
Sore throat, according to patients themselves, is always associated with hypothermia. However, the etiology of the development of oropharyngeal lesions is very diverse: from bacteria to viruses. The occurrence of pain in these cases is almost always associated with damage to the palatine tonsils, located on the side walls of the oropharynx - the junction of the respiratory and digestive tracts. The tonsils have many lacunae into which crypts or sacs open, having a dichotomous division and immersed in the depths of the tonsils. This structure of the tonsils contributes to the accumulation of various exudates in them. The palatine tonsils do not have afferent lymphatic vessels, since they themselves actively produce lymphocytes. Also, the palatine tonsils take an active part in the formation of local and general immunity.
NB ! A sore throat should not be confused with chronic tonsillitis (more precisely, its exacerbation, which, with similar symptoms, requires different treatment).
Sore throat is a general infectious disease with acute inflammation of the components of the lymphadenoid pharyngeal ring (usually the palatine tonsils). Sore throats are divided into: primary, secondary and specific.
- Primary - ordinary, simple, or banal sore throats. They manifest themselves as acute inflammatory diseases that have signs of damage only to the lymphadenoid ring of the pharynx.
- Secondary - symptomatic tonsillitis. Damage to the tonsils with scarlet fever, diphtheria, infectious mononucleosis, etc., as well as with blood diseases - leukemia, agranulocytosis, acute infectious diseases.
- Specific - sore throats caused by specific infections (fungal tonsillitis, Simanovsky-Plaut-Vincent tonsillitis).
Chronic tonsillitis is a chronic inflammatory, periodically exacerbating focus of infection in the palatine tonsils with a general infectious-allergic reaction.
The mechanism of infection spread is airborne, mainly occurs when coughing, sneezing, kissing, sharing dishes, towels, etc. The most common cause of chronic tonsillitis is group A β-hemolytic streptococcus, other pathogens are St. Aureus, H. influenzae, M. Catarrhalis, N. Gonorrhoeae, C. haemolyticum, M. Pneumoniae, C. pneumoniae, Toxoplasma, anaerobes, adenoviruses, cytomegaloviruses, herpes viruses, etc. Chronic tonsillitis is not always a consequence of previous tonsillitis. In most cases, it develops unnoticed, masquerading as other diseases (ARVI, stomatitis, etc.). As tonsillitis progresses, the parenchyma of the tonsils is slowly replaced by connective tissue, encapsulated foci of necrosis are formed, and regional lymph nodes are involved in inflammation. There are several forms and types of chronic tonsillitis with different symptoms.
The presence of only local signs characterizes simple tonsillitis (initial stage)
- liquid pus or caseous-purulent plugs in the lacunae of the tonsils (sometimes with an odor);
- tonsils are small, sometimes smooth or with a loose surface;
- persistent hyperemia of the edges of the palatine arches (Gise's sign);
- swelling of the edges of the upper parts of the palatine arches (Zach's sign);
- thickened, roller-shaped edges of the anterior palatine arches (Preobrazhensky sign);
- fusion and adhesions of the tonsils with the arches and triangular fold;
- enlargement of individual regional lymph nodes, sometimes painful on palpation (in the absence of other foci of infection in this region).
Also at this stage, other diseases not related to tonsillitis may worsen, which can have serious consequences.
Toxic-allergic form I (TAF I ) - is caused by repeated previous sore throats. In addition to local symptoms (the same as at the initial stage), general toxic-allergic phenomena develop:
- low-grade body temperature (occasionally);
- weakness, malaise;
- increased fatigue, decreased ability to work;
- periodic joint pain;
- enlargement and pain on palpation of regional lymph nodes (in the absence of other foci of infection);
- functional disorders of cardiac activity (can manifest themselves during exercise and at rest, but only during exacerbation);
- Abnormalities in laboratory data are variable.
Concomitant diseases in this case are the same as in the simple form, but they do not have a common infectious basis with chronic tonsillitis.
Toxic-allergic form II (TAF II ) - characterized by local symptoms inherent in the simple form and general toxic-allergic reactions:
- periodic functional disorders of cardiac activity (disturbances in heart rhythm are recorded on the ECG, pain in the heart area occurs both at the latent stage and at the acute stage);
- joint pain (both at the latent stage and at the acute stage);
- low-grade fever (may be prolonged);
- functional kidney disorders;
- deviations from laboratory data norms.
Concomitant diseases may be the same as in the simple form (not associated with infection). The course of this stage of chronic tonsillitis may be accompanied by the development of severe complications: peritonsillar abscess, tonsillogenic sepsis, etc.
Treatment of tonsillitis
How to get rid of tonsillitis? The palatine tonsils play a large role in the normal functioning of the immune system, so treatment of the disease should first of all include the restoration of the body's protective functions. Pharmacotherapy for chronic tonsillitis includes a set of measures aimed at eliminating the bacterial environment, relieving inflammation and eliminating purulent plugs from the pharyngeal mucosa. Treatment of chronic tonsillitis is carried out in accordance with the form and phase of the disease (acute tonsillitis, latent).
NB ! Conservative therapy is carried out at the initial stage of the disease and TAF I outside the period of exacerbation and not earlier than 1 month after it. Patients with TAF II are indicated for tonsillectomy!
Principles of pharmacotherapy of chronic tonsillitis:
- antibacterial drugs. To treat tonsillitis, various types of antibiotics are used: penicillins (mostly “protected”) or cephalosporins (2nd or 3rd generation), macrolides can be used, less often fluoroquinolones;
- desensitizing drugs that have an anti-edematous effect on tissues and help facilitate tolerance and improve the absorption of prescribed therapy;
- oral antiseptics: miramistin, octenisept at a dilution of 1:5, various gargles, etc. (how to gargle for tonsillitis is described below);
- homeopathic preparations that normalize and improve the trophism of the palatine tonsils;
- drugs that stimulate local immunity of the palatine tonsils.
Antibacterial therapy - what antibiotics are taken for tonsillitis
- Penicillins: preference in this group is given to amoxicillin in combination with clavulanic acid, since it is this combination that ensures the effectiveness of treatment in the event of penillinase-producing staphylococci joining the pathogenic flora. However, they are ineffective against methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus.
- Cephalosporins: cefepime (IV generation), ceftriaxone, cefoperazone, cefixime (III), cefuroxime (II). The first three drugs have only parenteral forms of release, while cefixime is produced only in oral form. Cefuroxime has both forms of release.
- Macrolides: azithromycin, clarithromycin, josamycin. The drugs are active against all pathogens, including penicillin-resistant strains.
- Aerosol forms of antibacterial drugs: fusafungine, active against hemolytic streptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans.
Immunomodulators
Immunomodulators are prescribed as part of complex therapy. Among vaccine-like immunomodulators that activate both specific and nonspecific local immunity, preparations containing lysates of thirteen microorganisms are used (including lysates of hemolytic streptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, Candida albicans). A similar mechanism of action (increased phagocytosis, increased lysozyme content, stimulation of immunoglobulin A production) is also characteristic of nasal sprays containing bacterial lysates: Streptococcus pneumoniae type I, II, III, V, VIII, XII, Staphylococcus aureus, Neisseria subflava, Neisseria perflava, Klebsiella Pneumoniae, Moraxella Catarrhalis, Haemophilus Influenzae Type B, Acinetobacter Calcoaceticus, Enterococcus Faecum, Enterococcus Faecalis, Streptococcus Pyogen ES Group A, Streptococcus Dysgalae Group C, Streptococcus Group G. Natural immunostimulating agents are also used: ginseng, leftze, echinacea, chamomile, garlic, garlic, garlic propolis, pantocrine. Peptides with immunoregulatory, detoxification, hepatoprotective, antioxidant effects are also used as an immunomodulator - arginyl-alpha-aspartyl-lysyl-valyl-tyrosyl-arginine, azoximer bromide, glucosaminyl muramyl dipeptide. Recently, herbal medicines such as tonsiral and tonsilgon have become widespread.
Antiseptics
Rinse solutions
An important stage in the treatment of sore throat is the sanitation of the oropharynx using a variety of antiseptics. The best option for sanitation is systematic (up to 8-10 times a day) gargling for tonsillitis with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory solutions of furatsilin, tinctures of eucalyptus leaves (have an antimicrobial effect), calendula, propolis (have an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect), preparations containing the NSAID agent benzydamine and so on.
Sprays and lozenges
The above-mentioned benzydamine is available not only in the form of a solution, but also in the form of a spray, which provides the so-called “spot” sanitation of the oropharynx. Other sprays used for sore throats contain hexethidine, povidone-iodine, mixtures of camphor, levomenthol, chlorobutanol and eucalyptus oils.
Another convenient local form of throat sanitation is lozenges and lozenges based on the same antiseptics (a combination of dry sage extract with essential oil, ambazone, chlorhexidine in combination with tetracaine and vitamin C). As a rule, in addition to the analgesic effect, tablets and lozenges have a bactericidal, local anesthetic and immunomodulatory effect. The basis for local drugs for resorption can also be drugs from the PNVP group: flurbiprofen, acetylaminonitropropoxybenzene, benzydamine.
Antioxidants
Antioxidants in the treatment of sore throat are used to improve metabolism, restore the functioning of enzyme systems and reduce the destructive effects of free radicals and peroxide compounds, as well as to improve immunity (rutin-containing complexes, vitamins A, E, C, microelements Zn, Mg, Si, Fe , Ca, dietary supplements, etc.).
Criteria for treatment effectiveness
Indicators that the treatment is sufficiently effective are:
- disappearance of pus and pathological contents in the tonsils;
- reduction of hyperemia and infiltration of the palatine arches and palatine tonsils;
- reduction or disappearance of regional lymph nodes.
But even in this case, it is better to carry out courses of treatment at least three times a year, especially during the off-season.
However, if a patient has a relapse even with a simple form of chronic tonsillitis or TAF I, then after the first course of treatment, pus remains in the palatine tonsils and caseous masses form, so it is necessary to discuss with the patient the possibility of tonsillectomy.
Thus, conservative treatment of chronic tonsillitis should to some extent be considered as a stage in preparing the patient for tonsillectomy for chronic tonsillitis TAF I, and in a simple form (if there is a positive result of treatment), the patient must be taught to maintain the tonsils in a satisfactory condition - that is, to carry out prevention chronic tonsillitis. Many people are interested in how to cure chronic tonsillitis once and for all. Unfortunately, there are no universal recipes for the treatment of chronic tonsillitis, since it is a focal infection that constantly reduces immunity and can at any time cause an exacerbation of the patient’s condition.
Table 1. List of drugs for the treatment of chronic tonsillitis in adults and children (group Rx)
Drugs for the treatment of chronic tonsillitis (exacerbation stage). Prescription group (Rx-drugs)*
| INN | TN |
| Penicillin series | |
| Amoxicillin + clavulanic acid | Panclave 2X, Panclave, Augmentin®, Augmentin EC, Augmentin® SR, Amovycombe®, Arlet®, Amoxiclav® Quiktab, Amoxiclav®, Ecoclave®, Flemoklav Solutab, Fibell, Rapiclav, Ranclave®, Medoclav, Liclave, Klamosar, Verclave, Bactoclav , Amoxicillin + clavulanic acid-Vial, Amoxicillin + clavulanic acid, Amoxicillin + clavulanic acid Pfizer |
| Cephalosporins II generation | |
| Cefuroxime | Cefurus®, Cefuroxime Kabi, Cefuroxime, Cefurabol®, Cefuroxime J, Cetyl Lupine, Super, Proxim, Xorim, Kefstar, Ketocef, Zinoximor, Zinacef®, Zinnat®, Acenoveriz®, Antibioxime, Axosef®, Aksetin® |
| III generation | |
| Cefoperazone+[Sulbactam], | Tsefpar SV, Cefoperazone and Sulbactam Spencer, Cefoperazone and Sulbactam Jodas, Cebanex, Sulcefazone, Sulcef, Sulperacef®, Sulperazone, Sulmover®, Sulzoncef®, Pactocef |
| Cefoperazone | Cefpar, Cefoperus®, Cefoperazone-Vial, Cefoperazone-Agio, Cefoperazone, Cefoperabol®, Cefobid®, Ceperon J, Operaz, Movoperiz, Medocef, Dardum |
| Ceftriaxone | Ceftriaxone-Promed, Ceftriaxone-LEKSVM®, Ceftriaxone-KMP, Ceftriaxone-Jodas, Ceftriaxone-Darnitsa, Ceftriaxone-Vial, Ceftriaxone Elfa, Ceftriaxone Protech, Ceftriaxone Kabi, Ceftriaxone DS, Ceftriaxone Danson, Ceftriaxone, Ceftria bol®, Cefson, Cefogram, Cefatrin , Cefaxon, Hizon, Triaxone, Torocef®, Tercef®, Stericef, Rocephin®, Oframax®, Movigip, Medaxone, Loraxone, Lifaxone, Lendacin®, Ifitzer®, Biotraxon, Betasporina, Axone, Azaran |
| Cefixime | Ceforal Solutab, Cemidexor®, Suprax®, Pancef, Pancef®, Ixim Lupin |
| IV generation | |
| Cefepime | Epipim, Cefomax, Cefepim-Jodas, Cefepim-Vial, Cefepim-Agio, Cefepim, Movisar, Maxicef®, Maxipim®, Ladef, Cefsepim, |
| Macrolides | |
| Azithromycin | Ecomed®, Hemomycin, Tremac-Sanovel, Sumatrolide solutab, Sumamox, Sumametcin, Sumamed® forte, Sumamed®, Sumaclid, Safocid, Zi-factor®, Zitrocin, Zitrolide® forte, Zitrolide®, Zitnob®, Zetamax retard, Azicide, AzitRus forte, AzitRus, Azithromycin-McLeodz, Azithromycin-BI, Azithromycin-OBL, Azithromycin Forte, Azithromycin, Azitrox®, Azitral, Azimicin, Azivok |
| Clarithromycin | Ecositrin, Helitrix®, Fromilid Uno, Fromilid, SR-Klaren, Seydon-sanovel, Lekoklar, Coater, Clerimed, Klacid® SR, Klacid®, Klasine, Claromin, Claricite, Claricin, Clarithrosin, Clarithromycin-Teva, Clarithromycin-Verte, Clarithromycin retard-OBL, Clarithromycin Pfizer, Clarithromycin Protech, Clarithromycin Zentiva, Clarithromycin, Clarbact, Klabax®, Klabax OD, Kispar® Zimbactar |
| Josamycin | Vilprafen, Vilprafen solutab |
* State register of medicines
The more appropriate form of release of the drug in this case is determined by the doctor.
Table 2. List of drugs for chronic tonsillitis at the acute stage (tablets, solutions, sprays)
| INN | TN | Release forms |
| Fusafungin | Bioparox® | dosed aerosol for inhalation |
| Lysates of microorganisms | Kameton-MHFP Kameton | aerosol for topical use topical spray |
| Salvia officinalis leaf extract + Salvia officinalis leaf oil | Sage | lozenges |
| Ambazon | Faringosept | lozenges |
| Flurbiprofen | Strepfen, Strepsils® Intensive Rakstan-Sanovel | lozenges [honey-lemon] film-coated tablets |
| Benzydamine | Tantum verde forte Tantum verde | dosed topical spray dosed spray for topical use, solution for topical use, lozenges |
* State register of medicines
Treatment of purulent sore throat
Purulent tonsillitis threatens serious complications from the heart, kidneys, joints and soft tissues of the neck if therapy is chosen incorrectly or treatment is started late. It is for this reason that it is important to immediately consult a doctor when the first signs of a sore throat appear.
The basic treatment regimen for acute tonsillitis with purulent exudate:
- Taking antibiotics of the penicillin group or the macrolide group. You can't do without them. General and local remedies are prescribed. Antibiotics kill pathogenic microflora and after a few days the production of pus stops, blood circulation in the tonsils is restored.
- Taking anti-inflammatory lozenges, lozenges, lozenges.
- Gargling and irrigating the throat with different solutions every hour.
- Use of local antiseptics in the form of a spray.
- Taking antipyretic drugs.
- Vitamin therapy and taking immunomodulators.
The principle of treatment of acute tonsillitis in children is similar, the only differences are in the dosage of medications. The patient needs to observe strict bed rest, talk less and gargle more often.
If the prescribed drug therapy does not have positive dynamics within several days, the patient continues treatment in the hospital.
Due to the presence of purulent plaque on the palatine tonsils, eating is difficult or completely impossible, so you can eat only pureed and liquid food, and also drink a lot of warm water to relieve symptoms of intoxication.
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis.
When treating this disease, the rule applies: exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis should be treated in combination with the treatment of concomitant diseases of the nose and nasopharynx. Inflammation of the glands can be treated, but, for example, mucus constantly flowing down the wall of the pharynx due to constant inflammation of the inferior turbinates will provoke new inflammation.
Tonsillitis treatment clinics offer two treatment options: conservative and surgical. For compensated and subcompensated forms, conservative therapy is prescribed. In the decompensated form, when all conservative methods of therapy have been tried and they have not brought results, they resort to removing the tonsils. But by losing them, a person loses his natural protective barrier, so the surgical method should be considered as a last resort.
Drug therapy for the chronic form of the disease includes:
- treatment with antibiotics prescribed by an otolaryngologist;
- use of antiseptics (“Miramistin”, “Octenisept”);
- antihistamines to relieve swelling of the tonsils;
- immunomodulators to stimulate weakened immunity (for example, Imudon);
- homeopathic remedies (“Tonsilgon”, “Tonsillotren”)
- herbal decoctions: chamomile, sage, string;
- if necessary, prescribe painkillers;
- adherence to a diet (no solid food, very cold or hot, alcohol, coffee and carbonated drinks are excluded).
Prohibited methods of treatment for purulent sore throat
Unfortunately, patients often make independent treatment attempts, which only worsen the clinical picture. The following actions are prohibited:
- Pierce the ulcers with sharp objects.
- Push out, tear off or squeeze out ulcers.
- Treat tonsils with hydrogen peroxide, Lugol's solution, iodine.
- Warm your throat and gargle with hot water.
- Rinse with vinegar and concentrated alcohol solution.
- Apply compresses of vodka and alcohol to the throat.
Important to remember! It is very dangerous to try to remove purulent deposits on your own.
At the ENT CLINIC in Chertanovo, otolaryngologists immediately help patients. They carry out non-contact removal of purulent plaque using ultrasound on the CAVITAR device (USOL therapy). Pharyngoscopy and smear analysis are performed to determine sensitivity to antibiotics in order to prescribe an effective medicine. Specialists use modern drugs of the latest generation to improve the patient’s condition. Based on the severity of the disease, individual characteristics, and age of the patient, the clinic’s ENT doctor prescribes medications and gives recommendations for treating purulent tonsillitis at home.
Treatment with folk remedies
Folk remedies help relieve sore throat. They don't require many ingredients to make them.
Teas and decoctions
- Boil seven to eight figs in a glass of milk for seven minutes. Cool the broth and drink warm three to four times a day before going to bed.
- Dissolve one tablespoon of butter in a glass of warm milk, add one tablespoon of honey. Drink the drink warm four to six times a day.
- Pour one tablespoon of dried linden flowers into a glass of boiling water and brew. Cool and strain the broth, then drink fifty milliliters three or four times a day.
- Teas with raspberries or rose hips are good for relieving sore throats. They can be drunk in any quantity, but warm.
- Mix one part of anise fruit with the same amount of mullein flowers and coltsfoot leaves, add two parts of thyme flowers, the same amount of mallow flowers, marshmallow root and five parts of licorice root. Take a tablespoon of the resulting mixture, pour a glass of cold water and leave for two hours. After this, bring the infusion to a boil and simmer for another five minutes. Strain and drink a quarter glass four times a day.
- Brew three to four tablespoons of elderberry in a glass of boiling water, simmer for five minutes over low heat. Strain the broth, cool, and use to gargle.
Washing
purulent forms of sore throat
The drugs used as medications are Rivanol, Furacilin, Streptocide, boric acid, and antibiotic solution. You will also need a syringe for rinsing. It needs to be filled with medicine, herbal decoction, saline or saline solution.
If salt is used, it is better that it be sea salt. The solution is prepared at the rate of one teaspoon per glass of water.
Rinse
Treatment of sore throat is very effective if you supplement teas, decoctions and gargling. Let's look at a few folk recipes:
- Pour two teaspoons of onion peel into two glasses of water. Cook for three minutes. Leave the broth for three to four hours, then strain and gargle three to four times a day.
- Add one teaspoon of salt, three drops of iodine and half a teaspoon of soda to a glass of warm water.
- Brew one teaspoon of chamomile flowers in one glass of water, strain, cool and gargle.
- Add one teaspoon of lemon juice to one glass of water. Gargle three to four times a day.
Compresses on the throat
Compresses on the throat can be considered one of the most effective and safest ways to treat sore throat. This procedure can be carried out for quite a long time.
To carry out the procedure, it is necessary to prepare soft tissue that absorbs liquid well. It needs to be dipped in the compress solution, squeezed out and applied to the throat.
For compresses, you can use beekeeping products, for example, honey, beeswax, propolis. Such compresses activate blood circulation in the capillaries, remove toxins and normalize metabolism in cells. The cabbage leaf is poured with boiling water to soften it. When it cools down, take it out and wipe it, and then spread it with honey. This compress is applied to a sore throat. The top is also insulated with polyethylene and a scarf.
Another option for compresses is compresses with homemade cottage cheese. Take two hundred and fifty grams of cottage cheese and rub it through a sieve. Add a couple of grated onions or two tablespoons of honey. This compress is applied to the throat and insulated.
Essential oils
Essential oils contain substances that, when evaporated, enter the respiratory tract and are deposited on the walls. The result is a therapeutic effect.
- Cypress essential oil. It is an antiseptic. Used for inhalation and massage. For massage, apply a few drops of oil to the chest and neck and rub into the skin. After the procedure, wrap yourself up and lie down for half an hour.
- Essential oil of menthol. It contains substances that fight many pathogenic microorganisms and clear the nasopharynx of secretions. Used for rubbing the bridge of the nose and dry and wet inhalations.
- Orange essential oil. It is used for the treatment of viral infections of the nasopharynx and throat in the form of inhalation, massage, and rubbing. It is recommended to use dry inhalations on fabric and porcelain and wet ones.
- Tangerine essential oil. Used as an adjuvant for the treatment of sore throat. Suitable for inhalations, massages, compresses, foot baths.
- Eucalyptus essential oil. Used for inhalations, baths, massage, rubbing.
Prevention and precautions when communicating with a patient
- Clothes must be worn appropriately for the weather conditions to completely prevent hypothermia.
- Regularly scheduled visits to the dentist will prevent large-scale development of caries and neutralize small foci of infection.
- Quitting nicotine, drug addiction and alcohol will restore the body's defenses.
- Sports activities will strengthen the immune system.
- Having proper rest and healthy food significantly improves metabolic processes.
- During seasonal epidemics, it is advisable to avoid attending public events.
When communicating with a patient with purulent tonsillitis, you should wear a cotton-gauze bandage, and also practice preventive gargling, using nasal ointments.
If therapy is carried out at home, it is important to clean the room every day using disinfectant solutions and periodically ventilate the room
Prevention of sore throat in pictures
Reception features
Each antibacterial drug is taken differently. The dosage, regimen, and duration of therapy are selected by the ENT doctor individually for each patient. Penicillins are usually eliminated from the body quickly, so treatment with drugs of this group involves frequent taking of tablets. Cephalosporins in tablet form are taken every 6-12 hours.
Uncontrolled use of antibiotics entails a decrease in the sensitivity of bacteria to the drug and a lack of treatment effect, and subsequently to the development of persistent resistance of the patient's microflora to antibacterial drugs.
Antimicrobial agents are taken one hour before meals or two hours after meals. Thus, the absorption of the active substance is higher.
Definition of disease
Sore throat or acute tonsillitis is an inflammatory disease of the tonsils. In rare cases, the focus of inflammation is localized on other lymphoid formations.
Sore throat can be either unilateral or bilateral.
Other causes of acute tonsillitis are other sites of chronic infections, such as caries or chronic diseases of the nasal cavity. This disease most often affects children aged five to fifteen years, and it is of bacterial origin. Depending on the stage of inflammation and the appearance of the tonsils, the following main types of tonsillitis are distinguished:
- Catarrhal sore throat. The tonsils are red and enlarged. There is no plaque.
- Follicular tonsillitis. There are spots of purulent plaque on the tonsils.
- Lacunar tonsillitis. There are accumulations of pus in the lacunae of the tonsils. The most severe form of the disease.
Without proper treatment, serious complications of tonsillitis can develop, for example, sepsis, pyelonephritis, abscess, bleeding from the tonsils, and so on.
In some cases, sore throat is confused with ARVI. To accurately diagnose the disease, an examination by a doctor is necessary. To do this, the doctor palpates the lymph nodes located under the lower jaw. In the case of a sore throat, they are swollen and painful. A urine test will also show the presence of blood and protein.
Important!
A deadly disease called “diphtheria” at the initial stage can masquerade as a sore throat. Therefore, it is better to play it safe and take a throat swab, which will determine the presence of Loeffler’s bacillus (diphtheria bacillus). This must be done even if you are vaccinated against diphtheria - the vaccine does not provide 100% protection, although it significantly reduces the likelihood of developing a severe form of the disease. A smear helps not only to remove the diagnosis of diphtheria, but also to identify the causative agent of sore throat.