Nobody likes going to the dentist, even though everyone knows how important oral health is and how strongly it relates to our overall health. But new technologies - from virtual reality to artificial intelligence (AI) - will soon revolutionize dentistry and our overall attitude to oral health.
In this review, we take a look at 9 new technologies that will change this area of healthcare in the near future.
Artificial intelligence
Already, dentists are using software to provide information to make clinical decisions. Soon such programs will work on the basis of AI algorithms, which will significantly facilitate the work of a doctor.
Such intelligent algorithms can be integrated into the healthcare system to analyze health data, research results and treatments to offer diagnostic and therapeutic recommendations for individual patients.
This will be possible thanks to the accumulation of information, in particular genetic data, which will allow a deeper understanding of the system of individual care for each patient. With AI tools that have access to such information, doctors will be able to select the best treatment options and increase the likelihood of success.
With ever-growing health data, AI algorithms can help professionals better manage dental problems. In 2022, researchers developed a machine learning method to accurately quantify immune cells near oral cancer cells. This gives a better idea of the cancer's spread and resistance, thereby helping to determine the chances of survival. Others are using neural networks to better detect tooth decay and periodontitis in X-rays. Such approaches may become standard practice in the near future.
How much does digital technology cost?
A good modern service provided by a digital dentistry clinic in Moscow, with modern equipment, cannot be cheap! There are many doctors offering crowns and veneers at a price that is not even half the cost of the work of doctors practicing in digital dentistry. The cost of restoration is not so high, and the price consists of the cost of the equipment itself - it is very expensive. There are a number of cases when digital technologies help to cope with a problem that cannot be solved without their use. For example, a patient’s tooth has chipped off, and he has an important event tomorrow.
Publisher: Expert magazine about dentistry Startsmile.ru
Teledentistry
Patients with special needs, elderly people in nursing homes and people living in rural areas have difficulty accessing a dentist and almost never have a choice. This may change significantly with the rise of teledentistry.
Telemedicine services, already offered in the US by companies such as Teledenists and MouthWatch, make it easier to access dental services. These services are significantly less expensive for patients, offer lower-cost prevention options, and allow patients to consult with otherwise unavailable health care providers. For example, MouthWatch's TeleDent service offers an all-in-one teledentistry platform that allows patients to take photos of their mouth or teeth, remotely send relevant information to the dentist, and conduct consultations in real time. The dentist can start a video chat with the patient and caregiver so that the provider can actually see and talk to the patient, establish rapport with them, and then bring them into the doctor's office (if necessary).
Candid, which provides teeth straighteners and treatment plans to patients, has tested a technology called Dental Monitoring that involves handing patients a connected ScanBox device. The device looks like a virtual reality headset. But instead of covering people's eyes, it looks into their mouths and controls how they use the aligners.
The ScanBox connects to the patient's smartphone, captures images and sends them to a remote orthodontist. The uploaded images are also scanned by an artificial intelligence algorithm which can track the patient's progress, assess oral hygiene and identify any potential health problems such as visible tooth decay or gum recession.
An orthodontist reviews each patient's case, determines whether they are eligible for treatment, and if so, creates a treatment plan. The aligners are then mailed to patients, who typically must be at least 16 years old and have mild to moderate alignment problems.
We also note that as the importance of remote care has increased during the pandemic, telemedicine is also gaining momentum, and authorities are responding accordingly.
Medical Internet conferences
Scientific supervisor:ass. Altynbaeva A.P.
Today we can state with absolute certainty that computer information technologies could not help but find application in dentistry, providing dentists with modern solutions in the treatment of traditional dental diseases.
The purpose of this work was a literature review of modern computer information technologies used in dentistry.
The task we set for ourselves was to familiarize the audience with computer technologies in dentistry with the aim of further striving to provide doctors with advanced types of treatment, which are carried out in a more effective, economical, informative and painless form.
Digital technologies can be used in all areas of dentistry and at all stages of treatment. There are systems for automated completion and maintenance of various forms of medical documentation, for example Kodak EasyShare, Dental Base, ThumbsPlus, etc. In addition to automating work with documents, these programs may contain the function of modeling on the screen a specific clinical situation and a proposed patient treatment plan. Computer processing of information allows you to quickly and thoroughly examine the patient and show the results, if necessary, to other specialists. A variety of intraoral digital photo and video cameras have already been developed. Such devices easily connect to a personal computer and are easy to use. For X-ray examinations, computer radiovisiographs are increasingly used: GX-S HDI USB sensor, ImageRAY, etc. New technologies make it possible to minimize the harmful effects of X-rays. Programs and devices have been created that analyze the color parameters of dental tissue more objectively, for example, the Transcend and VITA Easyshade systems.
There are computer programs that allow the doctor to study the characteristics of the patient’s articulatory movements and occlusal contacts in an animated volumetric form on the monitor screen (3D articulators). Programs for functional diagnostics and analysis of the characteristics of occlusal contacts: MAYA, VIRA, ROSY, Dentcam, CEREC 3D, CAD (AX Compact).
Automated systems have also been created for use in the training process for students - dentists and dental technicians - dental simulators. Such complexes significantly accelerate the acquisition by students of manual skills in therapeutic, surgical and orthopedic treatment, as well as methods of providing emergency care within the framework of a phantom course.
Conclusions. Computer technologies can be used at all stages of dental care. Timely training of specialists who are fully proficient in such technologies is an important condition for the widespread introduction of modern information technologies in all areas of dentistry.
Smart toothbrushes
The “smart” toothbrushes that have appeared on the market, according to their manufacturers, make it much easier to maintain oral hygiene and prevent the formation of plaque or caries.
The Kolibree Electric Toothbrush provides proper teeth cleaning and offers children different games to maintain the habit of brushing regularly. The Philips Sonicare smart toothbrush comes with sensors in the handle. They provide real-time feedback through a companion app, warning you if you're using too much force when brushing your teeth and even coaching the user on how to brush properly. There are several such devices on the market, including from companies such as Colgate and Oral-B.
True, we must admit that these are technologies that are not particularly necessary. While having a personal trainer to optimize your daily oral hygiene routine may seem tempting, not everyone is enthusiastic about the technology. An app like this tells you to change your brushing, but doesn't improve that technique. Rather, this will be done by the dentist, who can demonstrate the correct technique at the next appointment.
Additionally, by purchasing smart toothbrushes from companies like Procter & Gamble and Philips Oral Healthcare, you agree to their privacy policies, which allow them to share your data with third parties. So you might want to consider getting a toothbrush like this only from a company that gives you more control over your data, or one that won't share it with third parties at all.
Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR) technology is already beginning to be used in dentistry for both educational and clinical purposes.
Image Navigation's DentSim Simulator system pairs this technology with a mannequin on which students can perform procedures, receiving immediate feedback as their movements are tracked. This helps them quickly identify where they need to improve and develop their skills. Today, the system is already used by 8,500 students at dental schools around the world.
In dental practice, this technology is more common in reconstructive and aesthetic procedures to help patients know what they will look like after treatment. For example, SmartTek and Kapanu have developed AR applications that use a phone or tablet camera to superimpose a virtual image of an improved set of teeth onto real teeth before the procedure. The application works by comparing a 3D scan of the patient's oral cavity (many doctors already perform such an operation in Europe) with pre-prepared sets of scans, which represent healthy teeth obtained during similar treatment procedures.
The program uses a camera to take pictures of the patient's mouth and teeth, then overlays an image of the corrected teeth, and that's where the fun begins. Then the user can correct his own smile by adjusting his teeth - the distance between the teeth, different shapes of teeth, etc. Moreover, all these changes are visible “live”.
After the patient has “customized his dentition” and carefully assessed it in the augmented reality “mirror,” the finished model is sent to production, wherever such tooth replacement is performed.
A virtual reality
Just like augmented reality technology, virtual reality (VR) can be used for training and advanced training of dentists. Typically, only a couple of students can peer over the surgeon's shoulder as he performs a complex operation, and this significantly complicates the learning process. But a VR camera allows you to broadcast an operation around the world and do it literally “through the eyes of a surgeon” if students use VR glasses. For example, back in 2015, Nobel Biocare organized a broadcast of dental surgery, which was accessible through virtual reality devices.
Virtual reality technology is also useful for patients. An experiment involving 69 patients showed that VR can be used as an effective distraction tool. Patients wore glasses that displayed calming natural scenes and then recalled the treatment more positively. One such VR tool for reducing dental anxiety is the OperaVR system.
Can the patient actively participate in the treatment process?
Yes, and this is another advantage of digital technology. If a patient is interested in 3D dentistry, what it is, he can visually observe in the clinic the entire process of planning and treatment: how his future teeth are recreated, the shape of the cusps, fissures, how the color is determined. This dramatically reduces the percentage of dissatisfaction with the final result and outcome of treatment. The patient first sees on the computer what his new teeth will be like, then he can evaluate the fitting restoration and make adjustments. The person is fully involved in this work, watches it with pleasure, films it, posts it on social networks - it turns out to be teamwork between the doctor and the patient.
Modeling and 3D printing
Computer modeling and manufacturing technologies using 3D printing are beginning to revolutionize dental laboratories. They are being transformed into significantly cheaper and more efficient digital laboratories.
With the help of new technologies, the manufacturing process, for example, of crowns, is significantly accelerated. The tooth is prepared for installation of the prosthesis, then a picture of it is taken, which is sent to the computer, which controls the machine, which produces a crown suitable for this particular patient right in the office and very quickly.
By using 3D printing, all intermediate stages that create a queue are eliminated, and the doctor’s work is significantly simplified. Such solutions for dentists are already offered by Stratasys, Envisiontech and FormLabs.
3D printers are also capable of faster and more accurate creation of orthodontic models, surgical guides, aligners, retainers, and more dental equipment. These are tasks that would take longer using traditional methods. This helps improve workflows, reduce errors and effort, ultimately saving time and money.
The importance of this technology has been further highlighted during the COVID-19 crisis as it can bypass traditional supply chains to meet hospital needs. Since the technology is expected to become an integral part of medical practice, it will also be introduced in dental laboratories.
CEREC technology. Dentistry today is at a new stage of technical development.
Today, it is impossible not to notice that many dental clinics and dental laboratories are increasingly opening their doors to all-ceramic restorations using computer technology. And it’s not easy for specialists to want to work with these technologies. Increasingly, patients are becoming the driving force stimulating doctors and technicians to change their routine. When faced with a choice, they give preference to all-ceramic restorations, arguing that the cost of this service is quite comparable to metal-ceramic restoration. And, of course, the fundamental factors in this case are the biocompatibility and natural appearance of restorations made from modern dental ceramic materials.
Thanks to CEREC technology, both clinics and laboratories have the opportunity to reach a new level of their professional activities. CEREC technology is the new inLab 3D V3 software. 01, providing users with even more options, and the improved inLab MC XL sander – more productive and less noisy. Despite the apparent evolution of these changes, users received an even more powerful tool for realizing their ideas in the field of metal-free structures.
The hardware and software are not everything, since the quality of manufactured all-ceramic structures depends to a very large extent on the initial blanks from which the restoration is machined. That is why, to this day, the production of high-quality metal-free bridges is still a difficult task. For a long time, there was no material that would have such qualities as high strength and wear resistance, and grinding such a material should take little time during the manufacturing process of the restoration.
Now confident steps towards the creation of such, without exaggeration, long-awaited material have been made by companies such as Vita, Ivoclar Vivadent, which are actively cooperating with Sirona.
Intraoral camera
One of the biggest inconveniences that we encounter in the dentist's chair is the inability to open our mouth even wider, which does not allow the doctor to clearly see what he needs to see, even with the help of his dental mirror. Such situations are not only inconvenient for both the patient and the doctor, but also painful. An intraoral camera solves this problem.
Various types of such devices are already offered by MouthWatch, Dürrdental and Carestream Dental. Recent developments in this area make it possible to create revolutionary devices with unique “liquid” lenses that work like the human eye, allowing you to easily obtain a clear, detailed image of all corners of the patient’s mouth.
For example, the MouthWatch mobile camera is a special medical tool for visualizing the condition of the inner surface of the mouth, which, unlike existing systems, is very inexpensive. The device connects to a computer or tablet via USB and includes special MouthWatch Home Monitoring software and an image capture program. The system integrates with popular imaging systems such as Dexis, Schick, Apteryx and many others. The camera does not need to be focused, and it is controlled with just one button.
Such devices are very useful for launching teledentistry services.
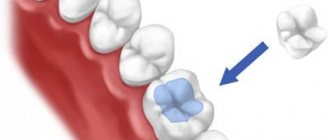
Application of 3D technologies in dentistry
There are main areas of application of 3D printers in dentistry: orthodontics, surgery, prosthetics.
Ready-made solutions for orthodontics
As you know, orthodontics is the correction of bite by any means. Previously, these were plates, then braces appeared, and now transparent aligners, new to Russia, have appeared, which are only gaining momentum.
Why are aligners interesting?
The first plus is that the enamel does not deteriorate. The bracket system element is not glued to the tooth, and after the course of treatment it is not dismantled. There is no stress on the enamel, it is simply absent.
Secondly, and most importantly, is the correct movement of the teeth. Because the teeth move inside the jaw and new bone tissue forms around them. When a patient is put on braces - rubber bands are put in, they are constantly tightened, and there is always movement of the jaws relative to each other, a change in the bite is possible, and what’s worst is that there may be constant clicking and discomfort from pain in the cervical spine, even headaches due to the fact that the patient once wore braces.
Clear aligners are a technology that allows teeth to move in all directions, i.e. and forward, and backward, and up, and down - it all depends on the clinical case.
The next important factor and advantage of this technology is that when using transparent aligners, the doctor, having given a set of aligners to the patient, can forget about it. In a month or three, the patient will come and have a check - if everything is in order, the treatment continues. There is no need for tightening or regular visits to the dentist.
And finally, an important factor - transparent aligners do not interfere with your personal life: they are not visible, food does not get stuck, etc., i.e. you are capable of doing whatever you want. From a meter away, transparent aligners are practically invisible, unlike braces.
There are two world-famous service centers that provide dentists with services for making trays for clear aligners.
Everything seems to be beautiful, but the truth is: for a doctor whose duties only include taking an impression or taking a scan of the teeth, this set of trays costs about $1,500. For the client, this price is $3,000.
How were aligners made in the past?
A plaster model of the initial position of the teeth was removed. It was cut and using wax, several blanks were created that imitate the step-by-step movement of the patient's teeth.
Next, these cut plaster models (a process absolutely identical to silicone casting) will be replicated. And from them, from these forms, polyurethane models were made for final vacuum molding.
Shipping to clients. Colored polyurethane forms are sent along with the aligner only to mark each stage of the treatment.
Production time is about 10 days. A lot of manual labor: cutting the plaster model, moving it by hand. There is no virtual modeling, none of this, it all happens manually - accordingly, about 10 days are spent in the laboratory on one clinical case. Manual labor - a lot of mistakes creep in.
How is this done today?
The first and most important stage is scanning the impression. This can be either a plaster cast or a cast made through two-component silicone.
After receiving a scan of the impression, the file is “entered” into the software, in which a virtual simulation of the movement of the dentition “from” and “to” takes place, i.e. from the initial crooked position of the teeth to the perfect smile.
Then the simulated course of treatment is sent to the printer and printed. The mouth guards are vacuum formed using printed modified models, and the mouth guard is issued to the client through the doctor.
Why use 3D printing to make aligners?
Firstly, high profitability.
The real cost of producing the same kit in your office is a maximum of 30,000 rubles. That is, at least about 60,000 rubles of profit remains with the business owner for the fact that his orthodontist will model the matrices directly in the program independently. Secondly, you can start treatment the very next day after the scans are taken. This means that you do not have to wait for the package to arrive, for the 30th set of caps to be printed and for it to be crimped. You can print one first starter tray, give it to the patient, and tomorrow he will leave happy for the course of treatment.
And another, important factor. During the treatment process, something can always go wrong, and in the case of working with service centers, we will have to send them a corrective scan, and they will start the treatment again from that moment. Yes, it’s free for the doctor, but it’s a waste of time: the patient’s treatment process is slowed down for at least 2 weeks, which can negatively affect the entire course of treatment with clear aligners.
Aligner software
"3Shape". An excellent and most advanced CAD CAM system to date, except that after purchase you pay annually to renew the license.
"Maestro 3d Ortho Studio" is Italian software. The price for the kit is initially almost 2 times more expensive, but you get the software completely open and at the output you will always receive an stl file, one license is purchased for life. If any new modules are released, you can purchase them separately. But new modules do not affect old functions, i.e. It’s just some new functionality that appears, which you can purchase additionally if you wish.
And the third program is software from the Russian company Avantis. The license is inexpensive - 15,000 rubles, but as a result you do not receive any file. At the end, all files are sent directly to Avantis 3d and they print them on their equipment.
In this case, it is possible to purchase an additional module for .STL output from yourself, but this option is provided for an additional fee.
3D technologies when using bracket systems
Why braces anyway? They haven’t left the market, they exist, they are popular. And the advantages that you will hear about braces:
Firstly, this is the most widespread in the world at the moment. This remedy really works, i.e. There have been cases where many difficult clinical situations have actually been corrected. It works. Yes, it ruins the enamel. But the teeth become equal.
Another plus is the predicted result. If you are constantly monitored and go to the dental office once a week, then, in principle, you can predict the result.
The next plus for the doctor: the braces cannot be removed by the patient. A lot of orthodontists will talk about the disadvantages of transparent aligners on the side that the doctor cannot control the fact that the patient is guaranteed to wear them, and claims will then be presented to the doctor. The patient took off and forgot to put on the clear aligners. This will not happen with braces: if the doctor puts them on, the patient is desperately obliged to wear them.
And finally, the main advantage, which still prevails on the Russian market now, is brace systems of various price categories, for absolutely any budget. That is, you can install budget braces - metal, around 50,000 rubles, and you can install ceramics costing half a million and more. It all depends on the means, on the orientation.
But where to use a 3D printer? In order to have a predictable result. Braces can be installed, roughly speaking, by eye, or they can be installed according to a jig template. There is special software for this: the previously mentioned ones can do the same.
A tray is printed - a positioning tray, where the bracket system is then placed directly. All elements of the braces will be positioned and glued directly to the places where it will be required, where it will be necessary, without errors and predictably accurately. But, unfortunately, no one uses this system, because everything is done by eye.
Ready-made solutions for implantology: production of surgical templates
The next area of treatment is implantology. Accordingly, when the situation and the picture are critical, when the tooth is completely destroyed and nothing can be done with it, but you need to chew on something, you simply cannot install a crown, then an implant comes to the rescue.
Surgical templates. What are they needed for!? Pros of using templates
A 3D printer is needed to make a surgical template - this is a kind of conductor through which it will be quickly and accurately drilled at the desired angle without any negative consequences.
What is important is that the operation is planned in advance. These are two visits to the dentist: the first is to take an impression and a referral for a CT scan, the second is directly for implantation. Returning to the advantages, we repeat that the operation is planned in advance, no unplanned situations will arise, and correct positioning during drilling is guaranteed.
Surgical templates. Main problems
- Drilling to greater or lesser depth
- Drilling at the wrong angle
- Inaccurate positioning
The price of a mistake is waiting from 2 months to a year for bone tissue restoration.
Here you can see the pin has hit the nerve. Why did this happen? Due to the fact that there was deep drilling, uncontrolled. The doctor did not check the CT images at the time of drilling. He may not even have had a live 3D model to judge it from.
This happens, unfortunately, very often and situations like this will cause a lot of trouble later. Accordingly, the cost of a mistake, if the implant hits a nerve or goes in at the wrong angle, is from 2 months to almost a year of recovery. Because the implant is removed, the patient is sent for follow-up treatment, roughly speaking, but in fact, his bone tissue is simply overgrown - what this unfortunate surgeon did.
Incorrect angle when drilling, the implant came out of the bone.
Here is a picture collected from CT slices, which shows (the implant pin is shown in red) that when drilling they simply went right through the bone, and also drilled from the side. Accordingly, what does this threaten? The patient does not seem to be complaining, there is no pain and perhaps the implant has taken root, but if he starts gnawing nuts or simply bites off something hard, then he can instantly simply break off this piece of the jaw, and then the jaw will be used. facial surgeons. Rehabilitation will be very expensive and painful.
Getting implants into the sinuses
The implants went into the maxillary sinuses. Accordingly, all treatment is stopped, and for six months the patient will walk, roughly speaking, with a false jaw, and in the evening put it in a glass. It is obvious that people come to implantologists not for this, but to get high-quality teeth and not have problems with dentistry later.
Template requirements
The main requirements for the template are that:
- It must be a transparent solid material.
- The material must be sterilized and withstand high temperatures.
- Accordingly, surgical templates are shown in live photographs.
Surgical templates. Implant Assistant
Software. There are a lot of programs on the market. Dentists, they are adherents of one system or another. Accordingly, the software of many systems is tailored only to work with certain implants.
An interesting program is Implant Assistant. The program has a low price, the buyer receives Russian support: on-line assistance via Skype almost 24 hours.
Dental models
In general, any dental work is not complete without a real fitting on a model.
Today, 99% of dentists make dental models using the traditional method - using plaster casts, which is long, dirty and again requires manual labor. But with the development of applications of 3D scanners, a natural question arises: why not print them. They took it, printed it based on the results of the intraoral scanner, and immediately you have a ready-made impression.
Here are some great inexpensive 3D printers capable of growing similar models:
» Formlabs Form 2 3D printer. Price: 419,900 rubles
» Russian DLP 3D printer. 343,900 rubles
Direct production. Production of dental products from CHS and Titanium
Direct production. Advantages
How does this happen and why, in fact, does it need to be printed?
Traditionally obtained by the following methods:
— The first is casting, which is already becoming obsolete. — The second method is milling. — And a completely new method is printing.
Russia is such a unique market where we are skipping certain stages of global development. Casting has been known to everyone for a long time. Then milling began to appear. Laboratories that could afford a milling cutter for 10 million and that wanted to move with the times purchased it. And literally 5-7 years later, a completely new topic appears - 3D printing. Those clinics that could not afford to purchase a milling cutter at that moment, they earned money, were already ready to purchase something new - printing entered the market.
Accordingly, what advantages do we get from printing? Firstly, it's speed. Secondly, this is the production of complex and precise structures. In the photo here you can see clasp dentures, and today they can be obtained only in two ways: the first method is casting, the second method is printing. It is impossible to mill such thin parts. Plus, at the time of casting, we may not shed some elements; they will be less elastic and will not meet the requirements that dentists place on them.
Direct production. Material
Printing occurs in layers. Of what? The raw material is a fine spherical powder with a fraction of 10-40 microns.
Waste no more than 15%. That is, during the printing process, during the process of laser melting of metal, you will definitely have a conglomerate of fused particles, and during the screening process, this rejection does not exceed 15-20%.
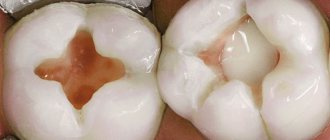
Printed parts are monolithic and homogeneous, which is very important. There are no pores. This is always important because if there are pores in the crown, then the ceramic will bounce off in this place. In a year, in two, maybe in a month, but it will definitely bounce back.
Direct production. Production process
Firstly, this is the creation of a digital model in a CAD program. There are a great many of them. The most popular are “Dental CAD”. What does it allow? It allows you to generate a crown, a bridge, and even a clasp prosthesis based on a scan. Place support on it and position it on the printing table.
Also another very important point. To work with metal printers, even though these are industrial systems, you must first cut the model into layers. The main dental programs, they are all slicers, i.e., ultimately, after forming the model, after generating the supports, you cut them in the same program.
Here in the picture, there are support pillars, below the platform and many, many units printed from cobalt chrome.
Any printing on metal printers must take place in a protective environment. This may be nitrogen or argon. If it is nitrogen, then it is possible to fill the chambers through a nitrogen generator. If it is argon, then, accordingly, cylinders are needed that will be supplied and connected to the machine.
The average dental printer platform holds about 80 units. A little further we will compare it with traditional methods and show how effective it is.
Everything is clear with the printing process, no questions arise. They printed it and removed the platform. After printing, it is necessary to anneal in order for the microstructure to stabilize, internal stress to be relieved and subsequent cracking of the ceramic to be avoided. Because ceramics are applied and fixed at a temperature of about 800 degrees.
After the part has been fired and released in the kiln, it is necessary to cut off all dental units from the construction platform and remove the supports.
Usually the platform is cut with a band saw or circular saw, which very often is already available in the dental laboratory.
There are support pillars under the crown, and they are pointed at the end. This is done specifically for their easy removal. Almost all 3D printers print this way, so that later there is less post-processing.
Manual processing of a part, where a Dremel or its equivalent is used to smooth the surface and remove residues from the support.
Ceramics will never stick to a smooth, glossy part. The part must be prepared, the part must be matte. Therefore, they must be sandblasted or shot blasted. Accordingly, the process from the router is absolutely the same - all this is sandblasted.
Direct production. Production assessment
Milling center
Number of units: 40 units; Time - 13 hours Number of units: 80 units: Time - 26 hours
3D Printer (Concept Laser Mlab)
Number of units: 40 units; Time - 6 hours Number of units: 80 units; Time - 11.5 hours
1 kg of KHS powder - 550 units 1 kg of KHS disk - 46 units Unit weight ~1.5 g.
Summary data on the router. We are no longer talking about casting here, and casting is omitted as an archaic process, long, dirty, not environmentally friendly, outdated.
At the top is a disk for a dental milling cutter, the material is cobalt-chrome. Accordingly, on the left side of the plate you see the number of units that fit on this disk - it’s only 24 units. And the number of units that fit on a similar platform is already 80 units.
What does this give? For 1 kg of cobalt-chromium powder we will get about 550 units. From a kilogram disc of cobalt-chrome we will get only 46 units of crowns. In my opinion, this is where face printing excels.
The difference between 1 kg of powder and a kilogram disc is only about 4 times in favor of the disc. That is, the math is still in favor of a 3D printer. Plus speed. Look at the speed shown in the table - milling takes longer. And it is so, and it is true. Plus you will have wear and tear on the cutting tool.
Suitable machines for direct production:
» Realizer 50. 185,000 € » Realizer 125. 250,000 € » Concept Laser Mlab. €220,000 » EOS M100. €240,000
» SLM 125. 200,000 €
» Sisma MySint 100. 250,000 € » 3D Systems Prox 100 Dental. 200,000 €
Want more interesting news from the world of 3D technology? Subscribe to us on social media. networks:
Regenerative Dentistry
One of the most interesting and promising areas in dentistry is dental regeneration and caries prevention. Bioactive replacement of hard tooth tissue (dentine) allows dentists to completely rethink dental treatment methods.
Regenerative medicine today relies heavily on research into the use of stem cells and, in particular, research is currently underway to find the source of mesenchymal stem cells that have the ability to form teeth.
Several years ago, scientists from Harvard and Nottingham Universities already developed a dental filler that allows teeth to heal on their own. This substance works by using stem cells to stimulate dentin growth, allowing the patient to regrow diseased teeth. Imagine that you were able to get rid of your artificial teeth, which will replace your own in old age.
New discoveries made by Swedish researchers at Karolinska Institutet in 2022 could accelerate developments in the field of regenerative medicine. They were able to create a map of all the cells that make up human teeth. They also discovered new cell types and cellular layers in teeth that may influence their sensitivity.
What is digital dentistry?
Digital dentistry
– an innovative direction in medicine that widely uses computer software. This makes it possible to obtain the greatest effect and maximum aesthetics in the treatment of diseases of the dental system. Important components of this approach are comfort during diagnosis and treatment, as well as obtaining results that are more long-term than the use of less advanced technologies.
Innovations are most noticeable in orthopedic dentistry, because the success of implantation or installation of metal-free dentures is already unthinkable without modern technologies. However, digital dentistry methods are no less in demand in other industries, when aligning the bite and eliminating dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint.
CRISPR
CRISPR is the latest method of genome editing, which nature itself provides us with and which scientists have only now learned to use. Already today, research is being conducted into the possibility of using this method to combat cancer and other serious diseases; it can also be used in dentistry.
Researchers believe that dental specialists will soon be able to identify genes associated with many oral pathologies. And when this becomes known, it will be possible to find a CRISPR solution that will allow you to properly edit the structure of the defective gene and get rid of dental problems in early childhood.
In the near future, CRISPR will be able to achieve a lot in dentistry. Chinese researchers are conducting research using technology to isolate and disable genes associated with oral cancer. Other researchers are using CRISPR to change the functioning of bacteria responsible for plaque formation. Their efforts may even lead to a reduction or complete prevention of caries and periodontitis.
The review used materials from The Verge, Medical Futurists, MedCity News, WebMD, Dental Products Report, Nature