Bite pathologies are one of the most common reasons for visiting a dentist. People have been engaged in returning teeth “to their place” since ancient times - there is evidence that this issue was of interest in ancient Egypt. However, only in recent decades have doctors come to the conclusion that it is necessary to correct an abnormal bite. Timely orthodontic treatment helps to avoid serious consequences for the entire body in the future. In this article, the leading orthodontist at the ZUUB dental clinic on Lipetskaya in Moscow, Dmitry Anatolyevich Polovkov, talks about the dangers of malocclusion and ways to correct it.
Correct bite - what is it?
Normal, or physiological occlusion, is characterized by the absence of disturbances in the arrangement of the dentition relative to each other with the jaws fully closed. He can be:
- regular, or orthognathic - in this case, the upper teeth overlap the lower teeth by a third of their height and there are no pronounced gaps between the dentition;
- straight - both jaws clearly close;
- biprognathic - both the upper and lower dentition are slightly tilted forward;
- progenic - only the lower jaw is pushed forward a little, but this does not prevent the cutting edges of the teeth from completely closing.
Correct bite is the absence of pronounced gaps between the teeth when the upper teeth are in contact with the lower ones opposite them. Orthodontists determine a bite without pathologies based on the following characteristics.
- The upper front teeth overlap the lower ones by 1/3 of their height.
- The incisors and canines are arranged in an even, arched line without distortions or crevices.
- The upper teeth protrude slightly outward, the lower teeth “look” slightly inward.
- All teeth are clearly below each other.
- The center of the jaws vertically coincides with the midline of the face, there are no protruding parts of the cheekbones or chin.
It is important to remember that in order to form a correct bite, you need to be careful about teething and caring for them.
Provoking factors in adults
The cause of the anomaly in adults is acute and chronic diseases of the dentofacial apparatus and its injuries:
- Congenital pathologies of the dentofacial apparatus that were not corrected in childhood.
- Arthrosis of the TMJ (dystrophic destructive changes in the joints). They manifest themselves as a displacement of the LF towards the diseased joint, stiffness in the morning, and pain.
- TMJ ankylosis (joint immobility due to cartilage degeneration). The anomaly is noticeable at rest and increases when the mouth is opened, which in case of severe pathology does not exceed 1 cm.
The line drawn between the lower central incisors shifts towards the damaged joint. Movement of the jaw in the horizontal direction becomes impossible. - Contracture (restriction of movement) of the LF muscles. The midline is shifted towards the affected muscle.
- Odontogenic benign tumors (odontoma, ameloblastoma, steoma, osteoblastoclastoma). The jaw bones are destroyed by neoplasms, deformation occurs, which usually becomes the first manifestation of the disease.
- Malignant tumors of the upper and lower jaw (sarcomas, carcinomas). The resulting deformation is caused by tumor growth.
- Jaw defects (reduction in the volume of dental tissue) due to osteomyelitis, syphilis, tuberculosis, surgical interventions for oncological diseases. Bone deficiency causes receding of the cheeks and disruption of the oval in the lower jaw area. As the mouth opens, the asymmetry increases.
- Micrognathia – due to underdevelopment of the jaw or damage. Micrognathia HF manifests itself as a reverse overlap, LF - with a slanted chin.
- Diseases of the salivary glands.
- Periostitis. Asymmetry is caused by swelling and/or abscess under the periosteum.
- Periapical (at the root of the tooth) and periaxillary abscess. Facial deformation is caused by swelling that has spread to adjacent tissues. The pathology manifests itself as throbbing pain.
- Crossbite (transversal displacement of the jaws relative to each other). The chin appears to the side, the lip sinks on one side.
- Facial injuries, fracture of the lower or upper jaw. Temporary asymmetry occurs due to soft tissue swelling and/or displacement of the jaw bones.
In addition to the above pathologies, the anomaly can be caused by many other diseases that are not related to the dentofacial apparatus:
- Damage to the brain and meninges (meningitis, encephalitis, stroke).
- Nerve diseases (Bogorad syndrome, facial nerve damage).
- Pathologies of the salivary glands (mucocele, purulent parotitis, adenoma).
- ENT diseases leading to unilateral deformation (sinus cyst, atelectasis (collapse of the paranasal sinus)).
Facial asymmetry can occur due to hydrogen peroxide poisoning, botulism, actinomycosis (infection with actinomycetes fungi).
Treatment methods for small lower jaws in children and adults.
In this publication, read how to expand the dentition with braces on one side.
Here https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/chelyustey/ukorochenie.html we will consider the reasons for shortening the dentition and methods for its correction.
Causes of malocclusion
Malocclusion (malocclusion) is due to various reasons: congenital or acquired. An important role is played by genetic factors, as well as insufficient intake of calcium into the mother’s body when carrying a child. Hereditary problems with bite require certain nuances in treatment. Therefore, before carrying out any orthodontic manipulations, the doctor talks with the parents and learns about all the possible factors in the occurrence of pathology.
Acquired malocclusion develops gradually. It appears at different ages due to its own reasons.
In childhood
- Bad habits (finger sucking, pacifiers, chewing on objects).
- Being on artificial feeding.
- Pathological bone formation.
- Teeth grinding (bruxism).
- Lack of sufficient solid food in the child's diet.
- Mouth breathing (formed as a habit or due to respiratory diseases).
- The replacement of baby teeth occurs too sooner or later.
- Pathologies associated with metabolism.
- Calcium and fluoride deficiency.
- Pronounced carious lesion.
- Injuries of the maxillofacial apparatus
In adults
- Installation of unsuitable dentures.
- Diastemas that form as a result of tooth extraction.
- Various types of injuries.
- Lack of space for eights (wisdom teeth).
- Unusual localization of the language.
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Preventive measures
Prevention of any dental diseases consists of following a number of rules that are relevant for almost every person. And although, unfortunately, they do not provide a complete guarantee of preventing dental diseases, they reduce the risk of their development. And if they have already appeared, they speed up and facilitate treatment.
This is the fight against bad habits of children, teaching them proper oral care. Quitting smoking and foods that are harmful to teeth. Using mouthguards when playing sports. And, perhaps most importantly, regular visits to the dentist for preventive purposes.
In the video, experts talk about the causes of asymmetry of the face and jaws.
Types of malocclusion in adults and children
Dentists usually divide anomalous occlusions into planes.
- Sagittal - characterized by elongated/shortened rows of teeth.
- Transversal - narrowed/expanded dentition is visible.
- Vertical - the presence of shortened/elongated certain areas in the dentition.
In addition, in dental practice it is customary to use the following classification of occlusion.
- Distal.
Sagittal occlusion with the upper jaw pushed forward. - Mesial.
Also a sagittal variety, but with the lower jaw moving forward. - Cross.
Transversal pathology with displacement of the jaws, which can only be partially formed, in one direction or another. - Open.
Vertical occlusion occurs with both partial and complete non-occlusion of teeth. - Deep.
The so-called traumatic, contributing to damage to the enamel. Characteristic is almost maximum overlap of the lower rows with the upper ones. - Vertical occlusal anomaly.
In addition to the above listed occlusion disorders, some experts identify 2 more types of anomalies:
- dystopic bite - displacement of one or more teeth;
- reducing - formed due to damaged and (or) lost teeth.
How to correct a child's malocclusion
- Children under 7 years of age
are shown a set of gymnastic exercises and massage that will help solve the problem. - Children under 10 years of age
are already prescribed trainers, with the help of which they can set the desired direction for their teeth. They must be worn for a certain number of hours during the day. But, if the pathologies are more advanced, removable plates and mouthguards are used. Correction of the anomaly takes approximately 2 years. - For children aged 10-12
years, braces are used to correct their bite - special orthodontic structures consisting of a power arch and clasps that set an individual direction for each tooth. They cannot be placed at an earlier age; it is necessary that all milk teeth be replaced by permanent ones. How long to wear braces for malocclusion is determined by the treating orthodontist.
How to correct malocclusion in an adult
A very common treatment method for adults is wearing braces. Transparent aligners (aligners) are also very popular now. They are made of transparent plastic material. Aligners are effective in correcting impaired occlusion, are easy to use and look very aesthetically pleasing. All details about this technique can be found here.
In cases where the patient is not in the mood for long-term bite correction with aligners or braces, there is another solution - microprosthetics. In this case, special overlays are installed on the teeth - veneers, with the help of which you can correct uneven teeth and gaps between them. But if there are serious malocclusions, this technique is not used.
There are bite defects for which only surgical treatment is indicated. Examples include: severe malocclusion, facial asymmetry due to trauma or hereditary causes, and chin dysplasia.
Each method of orthodontic treatment has both indications and contraindications. Only an orthodontist can determine the method of treatment after a thorough examination and full diagnosis.
Stages of development of facial asymmetry
- First stage. The functionality of the facial nerve is preserved, no significant changes are observed.
- Second. A slight curvature appears when a person closes their eyes or smiles. The patient has weakness of the facial muscle tissues.
- Third. Signs of asymmetry are more pronounced, difficulties appear in raising the eyebrows, muscle mobility is partially limited, and there may be spasms.
- Fourth. The face becomes asymmetrical even at rest, the eye does not cover completely, and the position of the mouth is disturbed.
- Fifth. The main sign is the absence of contracture; movements of the injured side are imperceptible.
- Sixth. Muscle tone decreases, the patient complains of the inability to move the muscles of the affected part of the face.
If any signs indicating a violation of the symmetry of the front sides appear, it is recommended to consult a specialist.
Consequences of malocclusion
It is a mistake to think that a pathological bite concerns only appearance and only leads to an unattractive smile. This is where the problems arise that are more serious. For example, in 90% of people with abnormal occlusion, incorrect posture is also detected. There is a logical explanation for this: with a broken bite, the center of gravity of the head shifts. This in turn affects the compensation mechanisms of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus of the maxillofacial system. The result of all this is an increase in the pathology of teeth closure.
Aesthetically, occlusion abnormalities lead to facial asymmetry. A weak-willed chin becomes pronounced, and lips protrude unattractively.
What is the danger of malocclusion?
In addition to visual problems, more serious dysfunctions often occur, including internal organs.
- Due to increased and uneven load on the teeth, periodontal disease develops and teeth begin to decay.
- Inadequate chewing of food leads to disruption of the digestive system.
- The functioning of the temporomandibular joint is impaired.
- The respiratory system also begins to malfunction.
- Slow metabolism.
- Increased risk of developing caries, especially with cross-closing teeth.
- Problems with pronunciation of sounds.
In addition, with malocclusions, daily dental care becomes much more difficult, which contributes to the constant accumulation of plaque on them.
Make an appointment
right now!
Polovkov Dmitry Anatolievich
Orthodontist
Lack of distances between teeth at the age of 5-5.5 years.
At the age of 5-5.5 years, the jaws should already be very actively preparing for the replacement of milk teeth with permanent ones. The jaws must grow - after all, permanent teeth are wider than baby teeth, they will need more space. Gaps should appear between primary teeth - both on the upper and lower jaws. If you notice that your child's baby teeth are tightly spaced and there is no space between them, this indicates that there will not be enough space for the permanent teeth to erupt and they will begin to grow unevenly.
These signs will help you identify problems in your child’s bite development in the early stages. in this case, the orthodontic correction will be shorter and simpler. And in some cases, a problem noticed in time can prevent orthodontic treatment in the future.
What to do to avoid malocclusion.
The consequences of malocclusion can be avoided by taking measures in time, namely in childhood. Here the responsibility falls largely on parents, who can promptly pay attention to problems and carry out prevention. It is important to take into account the risk of congenital disorders, hereditary predisposition, and also eliminate unfavorable factors:
- prevent the development of rickets and other diseases that impair bone growth;
- bottle feed your baby correctly;
- monitor the position of the child’s body during sleep (posture without tension, head not tilted back, etc.);
- maintain correct posture;
- timely wean your child off the pacifier, thumb sucking habit, toys and other objects;
- treat baby teeth immediately, because their early loss (as well as too late) can negatively affect the bite;
- to prevent nasal breathing disorders, namely to treat diseases of the ENT organs and ARVI.
When anomalies in the development of teeth are identified in childhood, timely assistance from an orthodontist will help solve problems faster than in advanced cases in adults. In children, as a rule, there is no need for surgical intervention yet, and even a complex of therapeutic exercises for the facial muscles can significantly help in correcting the bite.
Publisher: Expert magazine about dentistry Startsmile.ru
Treatment methods
The variety of causes and nature of the disease determines a wide range of possible treatment methods - from cosmetic to surgical.
Depending on the root cause, cosmetic, conservative, orthodontic and surgical treatment can be used. As well as massage and therapeutic exercises.
Massage
Massage has multiple therapeutic effects:
- Relaxes and tones muscles, relieves hypertension.
- Activates blood and lymph circulation in the affected area, relieves swelling and inflammation.
- Stimulates nerve fibers.
- Reduces pain.
Manual therapy in children is more effective than in adults due to the plasticity of children's muscles. The earlier the anomaly is diagnosed, the more effective manual therapy is.
Cosmetology procedures
Cosmetic treatment consists of getting rid of hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles, which causes facial asymmetry. Technologically, the procedure involves injections of Botox into the masticatory muscles.
The drug relaxes overstrained muscle fibers, straightens the face, returns it to harmonious proportions, and gives a calm and confident expression.
Conservative therapy
Conservative therapy is determined by the nature of the pathology and provides for the treatment of pulpitis, caries, periodontitis, periodontitis and other diseases of the teeth and periodontium, which make it possible to do without surgical intervention.
Analgesics (for pain), antibiotics (for infections), antiseptics (for local inflammation and wounds on the mucous membranes), NSAIDs (for severe inflammation) may be prescribed.
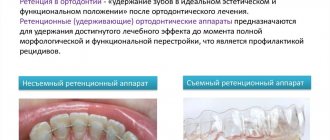
Orthodontic correction
Orthodontic treatment is used for crossbites, narrowing of the jaws, and other dental anomalies. Treatment is carried out with the help of splints, mouthguards, extra- and intraoral devices, braces and other fixed and removable orthodontic appliances.
Surgical intervention
The type of surgical intervention is determined by the nature of the disease and is divided into:
- for dental (removal of tumors and cysts, removal of teeth, opening of abscesses);
- maxillofacial (lavage, arthroscopy, phlegmonectomy, TMJ endoprosthetics, rhinocheilognatoplasty);
- eliminating the consequences of injuries (splinting and regeneration of jaw bones, tying with a ligature);
- otolaryngological (ectomy of paranasal sinus cysts, etc.).
If asymmetry is caused by damage to the brain and meninges, according to indications, ectomy of tumors and abscesses, transcranial or endoscopic removal of hematomas, areas of the brain crushed by TBI, and other surgical protocols are performed.