Bad breath is a delicate and very unpleasant problem, which often interferes with normal communication with others. Most often, the problem of bad breath is associated with dental diseases or poor oral hygiene. But there are a number of ENT reasons that also provoke the appearance of a strong odor. Why does my breath smell? What is the most effective treatment for bad breath? You will find the answer in our new article.
Have you heard of a condition called halitosis? Most likely no. Although, according to medical statistics, a quarter of the adult population is directly faced with this problem. Behind this “strange” diagnosis lies the delicate and unpleasant problem of bad breath.
In many cases, a person gets used to this smell and stops noticing it, and tactful people around them do not want to offend the person. As a result, the patient does not even try to get rid of the problem, although strong bad breath is a symptom of pathological changes in the body.
There are also opposite situations when a person literally “lives” with his unpleasant problem: he masks the bad breath with chewing gum, refreshing sweets or special sprays. But one should not expect a strong effect from these measures. They only help to temporarily hide this deficiency. As a result, the patient becomes so fixated on his problem that he tries to avoid contact with others and spends most of his time alone. But this is a step towards severe depression.
The main thing in solving a problem is not to go to both extremes. It is necessary, first of all, to understand why your breath smells, that is, to establish the causes of the strong odor, and then carry out high-quality treatment.
Treatment of halitosis, like any other disease, must begin with a visit to the doctor. It will be extremely problematic to determine the cause of a strong odor on your own, without the help of a specialist.
The causes and treatment of strong bad breath is the topic of our new article.
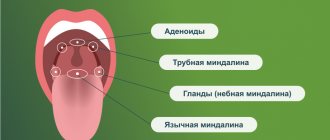
Exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis: symptoms
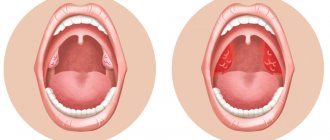
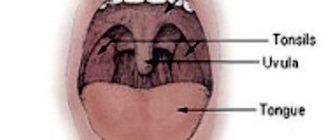
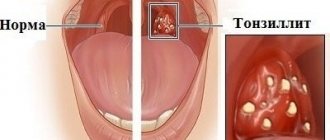
Often, for a long time, chronic tonsillitis occurs without symptoms or has scanty symptoms (in a simple form). There may be discomfort when swallowing food and liquids, a sensation of a foreign body in the throat, dry mouth, halitosis (bad odor) and tingling. Externally, the tonsils increase in size and there are signs of inflammation. The disease is characterized by exacerbations of sore throats up to three times a year, long periods of recovery, with general symptoms of asthenia and prolonged low-grade fever.
For the toxic-allergic form, more frequent exacerbations are typical, often with complications in the area of neighboring tissues (pharyngitis, peritonsillar abscesses), and the almost constant presence of asthenia and prolonged fever are typical.
The clinical picture of chronic tonsillitis during an exacerbation is as follows:
- sore throat that gets worse when swallowing;
- redness of the throat and tonsils;
- characteristic plaque;
- purulent discharge from the tonsils;
- bad breath;
- swelling of the nasopharynx;
- temperature increase;
- weakness;
- headache;
- fast fatiguability;
- arrhythmia;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- dyspnea.
Why does there be an unpleasant odor?
The oral cavity is the beginning of the digestive tract. It contains many bacteria; saliva contains enzymes that can break down carbohydrates. Therefore, after waking up, all people have bad breath. But this condition is not considered a pathology; it is enough to brush your teeth for the smell to disappear.
A persistent unpleasant aroma appears after eating dishes with garlic, onions, and some spices. When alcohol is abused, the sour stench persists for a day or more, which is associated with the metabolism of ethyl alcohol in the liver and the release of its vapors through the lungs.
A large number of unpleasant aromas accompany diseases that affect metabolism. In patients with diabetes who do not follow a diet or use insulin incorrectly, when ketone bodies accumulate in the blood, the smell of acetone appears on their breath. People suffering from kidney failure will repel those around them with the unpleasant aroma of urea, which the kidneys cannot remove from the body.
Common causes in adults are pathologies of the digestive tract. Halitosis is caused by:
- gastritis with high acidity;
- stomach ulcer, duodenal ulcer;
- cardiac sphincter insufficiency;
- esophageal diverticula;
- malignant tumors of the stomach or esophagus.
Respiratory diseases can also cause an unpleasant odor. Air from the lungs passes through the oropharynx, so it can partially leave the body through the mouth. It smells unpleasant with purulent diseases of the sinuses, chronic runny nose or tonsillitis.
Causes, main risk factors
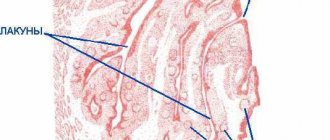
Up to 30 different colonies of pathogenic microbes can be sown on the surface of the tonsils of patients suffering from chronic tonsillitis. But in crypts and lacunae staphylo- or streptococcus is usually determined. A key role in the pathogenesis of chronic tonsillitis is played by beta-hemolytic strains of streptococcus (type A). Other flora - gram-negative coccal, fungal, viral - have an impact on local immunity, they support inflammation.
There are a number of factors contributing to the occurrence of the disease:
- hypothermia;
- decreased immunity;
- microtrauma of the tonsils;
- foci of inflammation in the mouth and in the head area (caries, sinusitis, adenoids, etc.);
- smoking;
- poor nutrition;
- allergy.
Viruses and bacteria that cause tonsillitis can come from the external environment.
Why is tonsillitis dangerous?
Chronic tonsillitis is very dangerous: if you do not consult a specialist in a timely manner and self-medicate, complications may develop, among which the most dangerous are diseases of the heart and blood vessels, and rheumatic joint damage.
Tonsillitis in adults often leads to damage to the kidneys ( tonsillorenal syndrome ) and heart ( tonsillocardiac syndrome ). This is due to the fact that infectious and toxic factors that damage internal organs enter the body from the palatine tonsils. Streptococcus, for example, secretes a toxin, the effects of which can cause myocardial dystrophy and heart disease or rheumatism . In addition, purulent contents entering the gastrointestinal tract from the lacunae of the tonsils can provoke dysbacteriosis.
Classification
Doctors distinguish various clinical forms of chronic tonsillitis, differing in clinical manifestations, severity of the condition and prognosis, risk of complications, as well as treatment tactics.
The simple form of chronic tonsillitis is characterized by a predominance of local symptoms. If general manifestations and lymphadenitis occur, this is referred to as a toxic-allergic form of tonsillitis. It comes in two versions:
Toxic-allergic chronic tonsillitis 1st degree . Sore throats are typical for him, which can worsen after ARVI, combined with general symptoms.
Toxic-allergic chronic tonsillitis of the 2nd degree - the symptoms are more pronounced, associated with diseases that have common factors of etiology and pathogenesis.
According to the degree of compensation of the process, the disease is divided into two options:
- chronic tonsillitis, compensated form - the source of infection is in a dormant state, there are no reactions from the body, repeated sore throats do not occur; The function of the tonsils and general reactivity are not impaired.
- chronic tonsillitis is a decompensated form - relapses of sore throat occur, complications of the heart, damage to the paranasal sinuses, middle ear, and renal complications are possible.
According to pathomorphological criteria, the process is divided into the following options:
- lacunar tonsillitis with predominant damage to the area of the lacunae;
- parenchymal-lacunar, involving in addition to the lacunae also the area of the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils themselves;
- phlegmonous - inflammation is predominantly localized in the area of lymphoid tissue;
- sclerotic with abundant growth of connective tissue fibers in the area of the tonsils and surrounding tissue.
Complications of chronic tonsillitis
Against the background of a chronic inflammatory process in the tonsil area, various complications are possible. Therefore, it is important to know why chronic tonsillitis is dangerous. Thus, the tonsils themselves, losing their function as a barrier to infection, become its breeding ground. Inside them are pathogens with the products of their metabolism. The infection can spread throughout organs and tissues, affecting the renal parenchyma, joint and heart tissue, and liver. In addition, tonsillitis adversely affects the functioning of the immune system and can be a provocateur of collagen diseases - lupus, scleroderma, dermatomyositis, periarteritis. The skin and peripheral nerve fibers may also be affected. With prolonged intoxication against the background of the disease, damage to blood vessels (vasculitis) and platelets (purpura) is possible.
Sinusitis
Sinusitis is the general name for inflammatory processes occurring in the paranasal (paranasal) sinuses. The paranasal sinuses include: maxillary, sphenoid, frontal and cells of the ethmoid labyrinth. The maxillary sinuses are also called maxillary sinuses, and their inflammation is, accordingly, sinusitis.
Inflammation of the frontal sinuses is called frontitis, the sphenoid sinuses are called sphenoiditis, and the cells of the ethmoidal labyrinth are called ethmoiditis. The most common type of sinusitis is sinusitis.
Sinuses are air cavities in the skull that perform a number of important functions, for example, warming and humidifying inhaled air, reducing the weight of the skull, participating in the formation of the timbre of the voice, etc. Each sinus communicates with the nasal cavity through small openings - anastomoses, through which the nose The secretion produced in them is released from the sinuses. If bacteria become active in the sinuses, inflammation occurs. The orifices become swollen, narrowed or completely blocked, as a result of which mucous masses cannot exit into the nasal cavity. Mucus accumulates, mixes with waste products of bacteria, and pus is formed. It is the purulent masses that emit an unpleasant odor that is noticeable to others. It disappears immediately after proper treatment.
Treatment of sinusitis includes antibiotic therapy, washing the paranasal sinuses from purulent masses in the clinic and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis occurs on the basis of complaints, examination of the patient, and questioning of the patient. Objective signs, manifestations of chronic tonsillitis, and the general condition of the tonsils are important; the doctor determines the stages of the process and the form.
The following diagnostic procedures are also carried out:
- throat swab for flora;
- general blood and urine tests;
- blood test for antibodies to streptococcus.
This helps determine treatments for chronic tonsillitis.
Why then wash the tonsils?
Usually the reason for washing is the so-called “plugs” or tonsillitis. Among patients and, unfortunately, often among doctors, there is a belief that these “traffic jams” are manifestations of a chronic infection. Sometimes you can hear the term “purulent plugs”. This description is incorrect. Indeed, in the lacunae (pores) of the palatine tonsils, food debris, calcium salts, dead and obsolete cells of the palatine tonsils and bacteria that normally live in the oral cavity sometimes accumulate. Together they form a white conglomerate, usually dense. Tonsilloliths themselves are not a sign of any disease. In the event that they physically interfere with the patient, as a rule, proper independent care of the oral cavity and teeth is sufficient.
Treatment methods in adults
In most cases, they resort to conservative treatment of chronic tonsillitis. Source: Modern methods of treating chronic tonsillitis. Ryazantsev S.V., Eremina N.V., Shcherban K.Yu. Medical Council, 2022. p. 68-72:
- therapy for inflammation in the head and oral cavity;
- procedures that increase immunity (hardening, taking vitamins, physical education, etc.);
- hyposensitizing drugs (to suppress allergic reactions);
- immunomodulators (normalize the immune system);
- means of reflex action (acupuncture, manual therapy);
- washing the tonsils with antiseptics;
- administration of drugs to the tonsils.
The treatment plan is complemented by physical therapy for chronic tonsillitis.
A radical method of treating chronic tonsillitis is surgical removal of the tonsils (tonsillectomy). The operation is performed in cases where inflammation occurs more than five times a year and does not respond to complex conservative treatment of chronic tonsillitis. Source: Choosing an antibiotic for exacerbation of tonsillitis. Karpishchenko S.A., Kolesnikova O.M. Medical Council, 2015. p. 40-43.
Cost of treatment
| Name | Cost, rub. | |
| 1 | Initial appointment with a doctor, doctor of medical sciences | 7500* |
| 2 | Procedures included as prescribed by a doctor: | |
| UZIS | 2700 | |
| Ozone ultraviolet sanitation | 450 | |
| Laser photoreactive therapy | 1800-2600 | |
| Application of a microcompress into the nasal cavity | 700 | |
| Application of gum-propolis suspension to mucous membranes | 600 | |
| 3 | Final examination by a doctor based on the results of treatment | 1000 |
* — When paying for the full course of treatment procedures, the cost of a doctor’s appointment is included in the amount of treatment. The course of treatment is prescribed by a doctor. The course duration is 7-12 sessions depending on the diagnosis.
Prevention of chronic tonsillitis in adults
Preventive measures to prevent chronic tonsillitis include:
- proper hygiene;
- hardening;
- balanced diet;
- maintaining cleanliness in the home and workplace, eliminating dust;
- timely treatment of inflammationSource: Treatment and prevention of chronic tonsillitis. Atagulova G. Zh. Medicine and ecology, 2012.
Chronic tonsillitis is a very common disease that causes a lot of inconvenience to the patient. But is it possible to cure chronic tonsillitis? If your tonsils often become inflamed, then do not self-medicate, but consult a doctor who will select the optimal treatment regimen for you and determine how to get rid of chronic tonsillitis. You can make an appointment with a medical specialist in St. Petersburg by calling the phone number listed on the website.
Article sources:
- Treatment and prevention of chronic tonsillitis. Atagulova G. Zh. Medicine and ecology, 2012
- Chronic tonsillitis in the practice of an otolaryngologist and cardiologist. Yalymova D.L., Kostyuk V.N., Vishnyakov V.V., Yalymov A.A., Shekhyan G.G., Zadionchenko V.S. Cardio Somatics, 2014. p. 60-65
- Choice of antibiotic for exacerbation of tonsillitis. Karpishchenko S.A., Kolesnikova O.M. Medical Council, 2015. p. 40-43
- Modern methods of treating chronic tonsillitis. Ryazantsev S.V., Eremina N.V., Shcherban K.Yu. Medical Council, 2022. p. 68-72
Ways to combat unpleasant odor
It is not always possible to independently guess that your breath smells bad. A person does not perceive an unpleasant aroma, so he can judge its appearance by indirect signs. If you have any suspicions, you can use the edge of a spoon to collect plaque from your tongue and smell it. The condition of the saliva is judged by licking the wrist and waiting for it to dry.
You can get rid of an unpleasant odor using traditional methods. At home, a decoction of dill is used to rinse the mouth. At home you can prepare an infusion of medicinal herbs with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects:
- chamomile;
- Oak bark;
- sage;
- mint;
- calendula;
- St. John's wort.
At home, a decoction is prepared from a mixture of several herbs to increase effectiveness. The infusion must be highly concentrated to suppress the growth of bacteria and cleanse the oral cavity.
If halitosis is associated with eating foul-smelling ingredients, parsley or celery root will help get rid of it. They block foul odors, and chewing the fibrous structure cleanses the teeth. Observance of a drinking regime relieves halitosis. Clean water cleanses the oral cavity and keeps saliva in a liquid state.
The reason why these methods do not help are pathologies of digestion and metabolism. You can get rid of them at home only under the guidance of a doctor.