Often, patients seek help from a dentist with the problem of gum discoloration. The seriousness of this disease lies in the fact that blue discoloration of the periodontium in some cases can occur against the background of any somatic disease. In some cases, blue gums may be associated with problems in the oral cavity. Timely detection of pathology and timely measures taken are the key to quickly eliminating the disease without developing complications.
Bruise on the gum - where it can come from and what to do with it
The appearance of bluish areas on the gums is a symptom that usually occurs against the background of the development of systemic diseases or as a consequence of disruptions in blood circulation in soft tissues. This phenomenon, as a rule, is localized in nature - upon visual inspection it is possible to detect isolated blue spots. To prevent the development of complications, you should see a specialist. From today's article you will learn about what to do if a child or an adult has blue gums, and what this symptom may indicate.
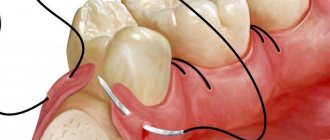
Causes of blue gums around the implant after surgery
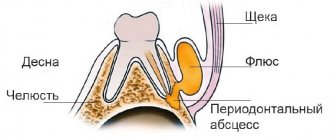
If we talk about the cyanosis of the gingival structures around the implanted tooth, then it appears under the following circumstances:
- inflammation of the operated area due to the traumatic process of implanting a titanium rod, accompanied by pain, swelling of the cheek, discharge of ichor from under the suture, and bluish discoloration of surrounding structures;
- transmission of an implant system made of metal alloys through the gums (relevant for anterior incisors).
In addition to the postoperative implantation period, pathology occurs in the following cases:
- violation by a specialist of prosthetic technology (as a result, a reduction in the process of gum nutrition, lack of oxygen in the tissues, the appearance of cyanosis and swelling);
- destructive changes in the mucous membrane;
- gingivitis (a severe inflammatory process that has a negative effect on the condition of the gum area).
What can cause your gums to turn blue?
So, why can individual areas of the gums change their color, and where do such blue spots appear on the mucous membrane? This could be due to many different factors. So, for example, if we are talking about a child, the reason may be the eruption or change of baby teeth. In adults, a similar symptom is sometimes provoked by certain diseases of periodontal tissue or the oral mucosa as a whole. Also, the area near the tooth may turn blue due to unsuccessful prosthetics or malfunctions in the internal systems of the body. Let's look at possible provoking factors in more detail.
Why do my gums turn blue?
Causes of blue gums in a child
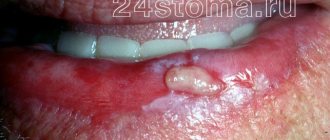
The time when a baby's first teeth emerge varies in each situation individually. When an already formed rudiment erupts, inevitable injury to soft tissues occurs, and, as is known, a large number of vessels are concentrated in them. Due to a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane, blood enters the soft tissues, and a hematoma forms. If the child is one year old and a bruise appears on his gum, namely in the place where the tooth should appear, there is nothing to worry about.
“And sometimes the teeth start to break through with a bruise. We had the same thing with the side ones. I remember looking in the morning and a blue spot appeared on my daughter’s gum. I thought that she had hit herself somewhere, so I decided to observe. And after a while a white stripe appeared.”
Marina7, Irkutsk, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
Among the pathological causes of the formation of blue areas in the mouth in children, experts in the field of pediatric dentistry and pediatrics identify the following conditions:
- inflammation of gum and periodontal tissues: the most common cause of blue discoloration is gingivitis - inflammatory processes that spread in the gums without disrupting the periodontal attachment. Redness turning blue is observed in localized areas, mainly in the cervical area. At the same time, the child becomes whiny and capricious, and his appetite is impaired. If left untreated, the next stage may be periodontitis,
Gingivitis in a child can cause blue gums - diseases of the mucous membrane: often stomatitis leads to blue gums - an inflammatory disease, the development of which is accompanied by the appearance of painful rashes on the gums, the inside of the cheeks, lips, palate and tongue. In this case, a change in the color of the soft tissues is noted around the tumors. Associated symptoms include severe pain in the oral cavity, as well as a sharp increase in body temperature.
Stomatitis is common in infants
It is worth noting that most often the diseases described above are diagnosed in children with weakened immune defenses. However, the main enemy of oral health is poor oral hygiene. Plaque and dental deposits are the key cause of most dental ailments.
Why does the mucous membrane turn blue in adults?
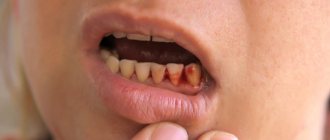
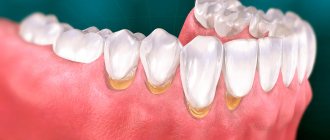
In adults, the gums most often turn blue after poor-quality dental intervention, as well as against the background of periodontal diseases and systemic pathologies of the body as a whole. Thus, the most common cause of hematoma is unsuccessful prosthetics. A small blue spot may appear above the crown if it is pushed too far under the gum. As a result, microcirculation will be disrupted, a blood clot will form, swelling and hypoxia of the mucosa will appear. Much less often, a similar situation occurs during restoration with filling materials, when the composite is carelessly applied to the gum1.
On a note! There is an opinion that the soft tissues surrounding the structure may turn blue due to metal-ceramics. This is a common misconception based on the assumption that the metal is oxidizing. In fact, changes in the gums around the crown only indicate its incorrect installation. The metal in the crown does not oxidize and certainly does not rust. To create such orthopedic structures, a special alloy is used, which fully meets all the necessary requirements.
In some cases, darkening of gum areas may indicate the development of certain pathological conditions of internal organs and systems. These include the following factors:
- thin blood vessel walls or blood clotting problems,
- violation of microcirculation,
- gingivitis and periodontitis,
- deficiency of vitamins and microelements in the body,
- anemia.
Blue gums in adults may occur after the installation of crowns.
In the case of anemia, a lack of iron, vitamin B12 and other vital substances in the body leads to a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in red blood cells. As a result, the patient experiences pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, including the appearance of cyanosis.
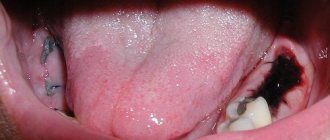
Blackening of the gums
A change in gum color does not always indicate the onset of inflammatory processes. If the gums at the site of the incision become whitish, this is considered one of the normal variants. This is how fibrin manifests itself, which tightens the wound and protects it from bacteria getting inside.
However, if the bed and adjacent fabrics have turned dark blue or black, this is a cause for concern. Blueness indicates the transition of inflammation to the third stage, which can lead to complete atrophy of the gum tissue.
The gums begin to turn black already when the irreversible process of decay has begun. This is usually accompanied by purulent discharge, a strong and very unpleasant odor from the mouth, and severe pain that cannot be controlled with conventional painkillers.
Associated symptoms
In addition to changes in soft tissue color, patients usually experience associated symptoms. Most often these are swollen gums and soreness, but if the cause is banal staining with food pigments, there will be no other pathological manifestations. As for inflammatory diseases that lead to the appearance of blue spots on the mucous membrane, patients also complain of the following symptoms:
- pain, which is especially acute when chewing food,
- increase in body temperature,
- itching,
- swelling of soft tissues,
- bleeding
Bleeding can be a concomitant symptom.
When the cause of the problem is incorrect installation of the orthopedic structure, numbness of the mucous membrane is often noted, as well as discomfort even at rest.
What can you do as an emergency?
It was already mentioned above that the most common cause of symptoms in childhood is the process of teething or changing teeth. To help your baby endure this difficult and painful period more easily, special ointments and gels with an anesthetic effect will help: “Kalgel” or, for example, “Cholisal”. As a rule, such a problem does not require medical intervention - the process of “punching” the tooth out usually takes several days. To speed up this process, you can resort to the help of special baby teethers. The blue spots will gradually resolve on their own.
If the cause of the blue discoloration is a growing tooth, then the symptoms may resolve on their own
As for other causes of hematoma, including in adults, you cannot do without the help of a doctor. During a visual examination and examination of the clinical picture as a whole, the specialist will determine whether the symptom is a consequence of a disease of the oral tissues, a pathology of the body, or an incorrectly fixed crown. Only after this the doctor will be able to begin treatment. If the problem is gingivitis or stomatitis, then the patient will be prescribed a course of appropriate anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs - both for oral administration and for external treatment of the affected areas.
If the problem is the result of an incorrectly installed crown or prosthesis, you will have to completely remove the orthopedic device and undergo anti-inflammatory therapy. The prosthetic device is sent for correction or completely replaced with a new design, which is certainly the best option. When a bruise becomes the result of mistakes made by the doctor during filling, a temporary filling is applied and a course of anti-inflammatory drugs is also prescribed.
Treatment of blue gums
When the gums turn blue, the dentist carries out the following diagnostic measures:
- facial configuration analysis;
- examination of the oral cavity;
- taking a targeted x-ray of a nearby tooth;
- orthopantomogram;
- biopsy;
- analysis for an immunohistochemical marker with the HMB antibody - 45.
Based on the cause of the blue gum, as well as the results of the diagnostic examination, the attending physician prescribes treatment.
For the eruption of primary and permanent teeth, as well as for bruises and chronic injuries, the following are prescribed:
- treatment of the inflamed area with anti-inflammatory and analgesic gels (Kalgel, Kholisal, Kamistad);
- intraoral baths with herbal preparations (infusion of chamomile, Rotokan, Stomatofit);
- rinsing the mouth with an aqueous solution of chlorhexidine 2-3 times a day.
The key to a quick recovery is to eliminate the cause of blue periodontal tissue. Removing overhanging fillings, correcting dentures and orthodontic structures will help cure inflammation in a short time.
Teething in children can be made easier by surgically cutting the gingival hood. This frees up the passage for the new tooth and reduces pain.
Gingivitis, periodontitis and other inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity are treated with anti-inflammatory therapy and strengthening the general immune system.
In addition to dental applications and rinses, professional oral hygiene is carried out using ultrasound. During the dental procedure, tartar and bacterial plaque, which are the causes of unpleasant periodontal symptoms, are removed.
It should be remembered that self-medication will only worsen the course of dental disease, therefore, if your gums turn blue, you need to consult a dentist for medical help as soon as possible.
When is it time to go to the doctor?
If a blue spot appears on the mucous membrane, it is better to see a doctor immediately. However, it is not always possible to urgently contact a specialist. Therefore, you need to know exactly when you can’t postpone a visit to the dentist. So, you need to seek help urgently if you have the following symptoms:
- the stain remains on the mucous membrane for more than 3 days,
- hyperthermia with signs of fever is noted,
- the patient complains of severe pain in the gums,
- general condition worsens, appetite is impaired.
A timely visit to the dentist will help to avoid the problem.
A problem that is not resolved in a timely manner significantly increases the risk of developing serious complications. Among these are possible suppuration, the appearance of a benign tumor and the formation of a cyst.
Symptom of diseases of internal organs
Blue gums may indicate pathological processes caused by systemic diseases. Due to pathologies of the blood, heart, and endocrine system, blood vessels become thinner, become brittle and create local internal bleeding.
According to doctors, blue gums are observed in the following cases:
- iron deficiency, anemia;
- kidney disease; • thyroid problems;
- diabetes.
Other factors
Gums can turn blue due to thermal, chemical, or food burns due to the abuse of spicy, sour, hot, or cold foods. The symptom is also often observed in smokers.
- The mucous membranes can be damaged after consuming aggressive compounds containing alcohol, manganese, iodine, and hydrogen peroxide.
- Injuries in the maxillofacial area due to falls or contact sports are a common cause of blue gums.
- The most harmless factors are natural food dyes, pigmenting teeth, gums, tongue (beets, blueberries, etc.).
Signs you need immediate medical attention
The need to immediately visit a dentist occurs when the following symptoms occur:
– cyanosis of the gums persists for 3–5 days;
– significant pain occurs in the area of blueness;
– the temperature rises;
– lack of appetite;
– the area of blue discoloration expands, spreading along the gum.
Traditional medicine tips
Many medicinal herbs have proven themselves to be excellent in the fight against inflammation in gum tissue. Infusions and decoctions are made from them, which are then used to rinse the mouth several times a day. Antiseptic plants that additionally have pronounced anti-inflammatory properties include chamomile, sage, and oak bark. Some sources provide recommendations for treating the mucous membrane with aloe juice or honey to relieve pain. In order to restore soft tissues after an incorrectly installed orthopedic structure, stimulation of blood circulation is required. A decoction of nettle leaves, as well as propolis ointment, helps with this.
Chamomile infusion is great for rinsing
It is important to understand that any folk recipes can be used only after consultation with the treating specialist. Otherwise, you can provoke the development of a serious complication and only make everything worse. And certainly traditional medicine cannot become a full-fledged alternative to drug therapy. The use of medicinal plants is justified only as an additional measure.
What can you do
The first thing to remember: when the very first symptoms of an incipient inflammatory process in the oral cavity appear, it is important to contact a medical facility as quickly as possible. It is almost impossible to independently identify the cause and stage of development of the pathology, and treatment with folk remedies can lead to more serious consequences.
Inflammation at the initial stage is easily eliminated by rinsing. For this purpose, certain medicinal herbs may be prescribed, for example, thyme, sage or oak bark. They are ideal for regular rinsing, reduce pain and swelling, and have a powerful antibacterial effect.
The doctor may also prescribe analgesics, for example, Dolaren or Ketanov. Unfortunately, when the inflammatory process enters an advanced stage, such therapy will not bring the desired result. In this case, the dentist may prescribe washing the infected hole and treating it with medicinal applications. General recommendations include preventive rinsing of the mouth with antiseptics at home, for example, Chlorhexidine solution. It is also best to temporarily stop taking blood thinning medications, smoking, and drinking any alcoholic beverages.
previous post
How to make teeth whiter?
next entry
How to prevent the problem
High-quality care and systematic teeth cleaning are two basic rules, the observance of which will, to a certain extent, protect oneself from inflammatory and carious processes. In addition, do not forget that every time after eating you need to thoroughly rinse your mouth and use dental floss. It is also important to choose the right toothpaste and brush, especially if you have sensitive gums. And of course, don’t forget to visit the dentist regularly.
If a bluish spot appears on your gum, do not put off your visit to the dentist. The longer you ignore the problem, the higher the likelihood of developing truly serious complications.
- Balakhnichev, D.N. The influence of fixed orthopedic structures on the periodontium of abutment teeth, 2011.