What is acyclovir?
Acyclovir is a selective, antiviral drug, a nucleoside analogue, related to cytarabine, idoxuridine, trifluridine and vidarabine, active against 4 types of herpes virus (herpes simplex types 1 and 2, chickenpox (type 3), cytomegalovirus (type 4)). It slows down the growth and spread of the herpes virus in the body by affecting their viral cells at the DNA level. This drug does not completely cure herpes, but it reduces the symptoms of the infection and its acute course.
Acyclovir is used both for therapeutic treatment and for the prevention of relapses. It effectively eliminates skin rashes and foci of inflammation around it, prevents the spread of the viral pathogen (contamination), and reduces the complications of herpes.
The effect of acyclovir therapy is greatest when treatment is started early, especially for non-primary infections, which usually have a shorter course than the primary episode. Long-term prophylactic oral acyclovir in patients with frequent episodes of genital herpes simplex completely suppresses relapses in most patients; As with other acyclovir-responsive infections, the viral latency period is not eradicated and the pre-treatment relapse rate returns after treatment is stopped.
Caution should be exercised when using acyclovir prophylactically in the general population due to the theoretical risk of the emergence of viral strains that are resistant to acyclovir and other agents whose mechanism of action is dependent on viral thymidine kinase (viral protein).
Intravenous acyclovir is the drug of choice for biopsy-proven herpetic encephalitis (damage to the nervous system by herpes) in adults, and has also been successfully used in the treatment of disseminated herpes simplex in pregnant women and herpes in newborns. Intravenous and oral acyclovir protects against the spread and progression of varicella zoster virus infection, but does not protect against postherpetic neuralgia (a complication of herpes zoster, manifested by the appearance of serous rashes in the area of innervation of individual branches of the trigeminal nerve).
In immunocompromised patients, intravenous, oral, and topical acyclovir reduces the clinical course of herpes simplex infections, while prophylaxis with oral or intravenous dosage forms suppresses reactivation (recurrence) of the infection while taking the drug.
Ophthalmic use of 3% acyclovir ointment quickly cures herpetic corneal ulcers and superficial herpetic keratitis. Thus, despite its failure to eradicate latent virus, acyclovir, administered therapeutically or prophylactically, is now standard antiviral therapy for some manifestations of herpes simplex virus infection and does represent a major advance in this regard.
Acyclovir
Acyclovir tablets can be taken with meals, since food intake does not significantly interfere with its absorption. The tablets should be taken with a full glass of water.
Adults
Treatment of infections caused by herpes simplex virus
For the treatment of infections caused by the herpes simplex virus, the recommended dose of Acyclovir is 200 mg 5 times a day (every 4 hours, except during night sleep). Usually the course of treatment is 5 days, but can be extended for severe primary infections.
In case of severe immunodeficiency (for example, after bone marrow transplantation) or in case of impaired absorption from the intestine, the oral dose of Acyclovir can be increased to 400 mg. As an alternative, the possibility of using acyclovir in a lyophilisate dosage form for the preparation of a solution for infusion may be considered.
Treatment should begin as soon as possible after infection occurs; in case of relapses, it is recommended to prescribe the drug already in the prodromal period or when the first elements of the rash appear.
Prevention of recurrent infections caused by the herpes simplex virus in patients with normal immune status
To prevent relapses of infections caused by the herpes simplex virus in patients with normal immune status, the recommended dose of Acyclovir is 200 mg 4 times a day (every 6 hours).
For many patients, a more convenient treatment regimen is suitable: 400 mg 2 times a day (every 12 hours).
Sometimes lower doses of Acyclovir are effective: 200 mg 3 times a day (every 8 hours) or 200 mg 2 times a day (every 12 hours).
Some patients may experience exacerbation of infection when taking a total daily dose of 800 mg.
Treatment with Acyclovir should be periodically interrupted for 6-12 months to identify possible changes in the course of the disease.
Prevention of infections caused by herpes simplex virus in patients with immunodeficiency
For the prevention of infections caused by the herpes simplex virus in patients with immunodeficiency, the recommended dose of Acyclovir is 200 mg 4 times a day (every 6 hours). In case of severe immunodeficiency (for example, after bone marrow transplantation) or in case of impaired absorption from the intestine, the oral dose of Acyclovir can be increased to 400 mg 4 times a day. As an alternative, the possibility of using acyclovir in a lyophilisate dosage form for the preparation of a solution for infusion may be considered.
The duration of the preventive course of therapy is determined by the length of the period when there is a risk of infection.
Treatment of chickenpox and herpes zoster
For the treatment of chickenpox and herpes zoster, the recommended dose of Acyclovir is 800 mg 5 times a day (every 4 hours, except during night sleep). The course of treatment is 7 days.
In patients with severe immunodeficiency (for example, after bone marrow transplantation) or in cases of impaired absorption from the intestine, it is necessary to consider the possibility of prescribing acyclovir in a lyophilisate dosage form for the preparation of a solution for infusion.
Treatment for herpes zoster should begin as soon as possible after the rash appears, as in this case the treatment will be more effective.
Treatment of chickenpox in patients with normal immune status should begin within 24 hours of the onset of the rash.
Special patient groups
Children aged 3 years and older
Treatment of herpes simplex virus infections: prevention of herpes simplex virus infections in immunocompromised patients
- aged 3 years and older - the same doses as for adults.
Treatment of chickenpox
- at the age of 6 years and older - 800 mg 4 times a day;
- aged 3 to 6 years - 400 mg 4 times a day.
More accurately, the dose can be determined at the rate of 20 mg/kg body weight (but not more than 800 mg) 4 times a day. The course of treatment is 5 days
Prevention of recurrence of infections caused by the herpes simplex virus in patients with normal immune status; Treatment of herpes zoster There are no data on the dosage regimen.
Elderly patients
The likelihood of renal failure in elderly patients must be taken into account, and doses should be adjusted according to the degree of renal failure (see subsection "Patients with renal failure"). It is necessary to ensure that adequate water balance is maintained.
Patients with impaired renal function
Caution must be exercised when prescribing Acyclovir to patients with impaired renal function. It is necessary to ensure that adequate water balance is maintained. In patients with renal failure, taking acyclovir orally at recommended doses for the treatment and prevention of infections caused by the herpes simplex virus does not lead to the accumulation of the drug to concentrations exceeding established safe levels. However, in patients with creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/min, the dose of Acyclovir is recommended to be reduced to 200 mg 2 times a day (every 12 hours).
For the treatment of chickenpox and herpes zoster, the recommended doses of Acyclovir tablets are:
- with creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/min - 800 mg 2 times a day (every 12 hours);
- with creatinine clearance 10-25 ml/min - 800 mg 3 times a day (every 8 hours).
Symptoms of acyclovir overdose
You should stop taking acyclovir if you experience these symptoms:
- easy bruising or bleeding, purple or red dotted spots under the skin;
- changes in behavior (motor restlessness and emotional agitation, confusion, hallucinations);
- disorders of the urinary system (anuria (lack of urination), painful or difficult urination), swelling of the lower extremities;
- feeling tired, shortness of breath.
Uncomplicated side effects of acyclovir include:
- skin allergic manifestations (itching, soreness of the skin when touched, rashes);
- nausea, which may be accompanied by vomiting, stomach upset (diarrhea);
- headaches and/or dizziness;
- pain in the mouth when taking acyclovir tablets buccally (by the cheek).
Typically, cases of acyclovir overdose have been recorded extremely rarely, but common manifestations are allergic reactions, which entail a number of symptoms:
- hives, blisters, itching;
- difficulty breathing and swallowing;
- swelling of the face, throat, tongue, lips, eyes, hands, feet, ankles, or legs;
- hoarseness;
- cardiopalmus;
- general weakness;
- pale skin;
- confusion and/or loss of consciousness;
- the appearance of unusual bruises on the body;
- blood in urine and stool;
- numbness, burning or tingling in the upper and lower extremities;
- temporary inability to move parts of the body.
If you experience any of the above symptoms, you should contact your doctor immediately.
Acyclovir - instructions for use
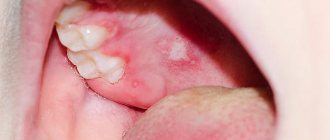
When treating stomatitis caused by the herbes virus, it is customary to use acyclovir tablets, since creams and ointments are not able to have the desired effect due to the impossibility of fixing fat-based medications in the oral cavity. Therefore, such compositions are recommended for use when infection spreads in the skin tissues.
The course of the disease in severe form often requires the administration of drug solutions intravenously.
Acyclovir tablets
The course of taking tablets is from five to ten days, during which the drug is taken 4-5 times a day. For both adult patients and children starting from two years of age, the dosage of the drug is 200 mg at a time, and for children under two years of age the dose is halved, which is 100 mg.
Diseases that occur in severe forms often require an increase in dosage and therefore the drug can be prescribed in an amount of 400 mg per dose.
It should be taken into account that tablets should be taken during the daytime, which allows the drug not to settle in the kidneys and not cause side effects in the genitourinary system of the body. In addition, it is recommended to increase the volume of fluid consumed by the patient, which helps reduce the concentration of acyclovir in the urine and prevent the development of kidney disorders.
Treatment of the so-called “chickenpox” with drugs containing acyclovir is not recommended for children, since their age allows them to tolerate this disease in a milder form than adults.
Powder forms of acyclovir
Compositions for administering the drug through a dropper are prepared on the basis of physiological solution, for which bottles containing a certain amount of the drug are filled with liquid, according to the instructions, shaken thoroughly until the suspended particles are completely dissolved, and the finished solution is poured into containers for drip infusions.
Before the first use of the composition, it is necessary to test the tolerability of the drug, which allows you to avoid allergic reactions of the body when using it. The test involves applying the drug to a shallow scratch made with a needle on the inside of the forearm and observing for several minutes. If an area of inflammation forms around the damaged surface, the use of acyclovir should be avoided.
Drip administration of the drug is justified by the fact that the content of the drug in the patient’s blood should increase gradually, since otherwise this procedure can provoke complications. Therefore, one-time procedures are carried out within an hour, and sometimes longer.
Acyclovir ointment - instructions for use
Acyclovir ointment, the use of which is recommended for the local treatment of ailments caused by the herbes virus, is offered in tubes of 2, 5 or 10 g, the content of the active substance in these compositions is exactly 5%, which makes it possible to use the drug in the initial phase of the disease. Thus, products in the form of ointments and creams are recommended to be used at the first signs of the disease:
· when itching occurs;
· minor pain.
The procedures should be continued for 5-10 days, applying the composition to the skin, without rubbing the product, into the damaged area.
Acyclovir helps reduce the intensity of skin lesions, promoting rapid healing and crust formation. However, the crusts that form when using the drug should not be removed independently, since such an initiative significantly reduces the effectiveness of treatment and provokes infection of others with the herbes virus.
In addition, the use of the drug for medicinal purposes does not prevent the spread of the disease through sexual contact.
Eye ointment containing acyclovir
Such products are commercially produced in small tubes containing up to five grams of the drug, with an acyclovir concentration of 3%.
The use of the composition involves placing the product behind the lower eyelid, a thin strip up to one centimeter long, which helps the composition spread across the cornea and absorption into the surrounding tissues.
It is recommended to use the drug up to 5 times a day, for 5-10 days, however, if signs of intolerance occur, you must see a specialist and change the medicine.
Cost of drugs
Drugs in various forms are produced by both domestic and foreign pharmaceutical companies, therefore the choice of products that include acyclovir is quite diverse. In addition, the cost of these antiviral agents is affordable.
Thus, acyclovir in tablets, the price of which from domestic manufacturers does not exceed 250 rubles, allows people of any income to purchase and use an effective remedy.
Drugs produced in the form of ointments and creams are also not very expensive, which makes it possible to successfully cope with the disease in its initial stages without resorting to hospital treatment.
Powder forms of acyclovir, used for drip administration by professional medical workers, are produced mainly abroad, which affects the cost, but their use helps to cure severe viral infections.
What you need to know before you start taking acyclovir
You should not take this medication if you are allergic to acyclovir or valacyclovir (Valtrex). The use of Sitavig buccal tablets is not recommended if you have an allergic reaction to milk proteins.
To make sure this medication is safe for you, check with your doctor before taking it if you have a history of the following conditions:
- kidney disease;
- weakened immunity (as a result of taking some medications or caused by any disease).
It is especially important to consult a specialist if you are pregnant or planning a pregnancy, or if you are breastfeeding a child. Because herpes can be passed on to your baby during birth if you develop genital lesions at birth. If you have genital herpes, it is very important to prevent herpes during pregnancy.
During lactation, this medication may be unsafe. You should consult with your doctor to identify and determine any possible risks to your newborn baby.
Acyclovir can be used in children from 2 years of age.
How to take acyclovir?
You must take acyclovir exactly as indicated in the instructions or as individually prescribed by your doctor. Do not use the drug in doses that do not comply with the instructions and do not exceed the permissible duration of use.
To use this medication in children, be sure to consult a doctor and carefully study the official instructions for the drug.
To use buccal acyclovir, do not crush, chew, suck, or swallow the tablet; simply place the flat side of the tablet on the herpes-affected area.
Note!
Giving buccal tablets to children is strictly prohibited, as this can lead to suffocation.
If you take acyclovir in the form of a suspension, be sure to use a special dosing measuring cup to measure the dosage. It is not recommended to use ordinary cutlery (a kitchen spoon) for this purpose.
The calculation of the dose of acyclovir used depends on the weight category (especially important for children). When losing or gaining body weight, the dose may vary.
During treatment with acyclovir, it is important to drink as much fluid (drinking water) as possible to maintain normal kidney function.
When prescribed a course of treatment with this drug, it is necessary to strictly follow it, even if your symptoms improve after the first days of using acyclovir, since interrupting treatment or skipping doses may increase the risk that the virus will become resistant to acyclovir, and there is also a high likelihood of frequent relapses.
The drug should be stored out of the reach of children, away from moisture and heat.
Consequences of an overdose of acyclovir
Cases of overdose with acyclovir have not been recorded, but if a dose of acyclovir is taken too high, the following symptoms may occur:
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea;
- headache, dizziness, clouding of consciousness;
- dyspnea;
- anaphylaxis (immediate allergic reaction);
- febrile symptom (increased body temperature);
- swelling;
- visual impairment;
- general malaise;
- myalgia (muscle pain).
If you have taken a high dose of acyclovir and experience any of the above symptoms, you should seek emergency medical help as soon as possible.
What should you not do while taking acyclovir?
When using buccal acyclovir until it is completely dissolved in the mouth, you should avoid brushing your teeth, chewing gum, and wearing dentures. You can rinse your mouth with caution. It is recommended to drink plenty of water to prevent dry mouth.
It is worth remembering that herpes infections are contagious, even if you are treated with acyclovir you can still infect other people, so avoid contact of infected areas with other people. When touching the infected area, do not touch the mucous membranes of the eyes with your hands. Wash your hands with soap as often as possible to prevent the spread of infection.
With genital herpes, even during treatment with acyclovir, the risk of infecting a sexual partner does not decrease. It may still be contagious even if you don't have any symptoms.
Recommendations for use
Indications for the use of formulations containing acyclovir are:
- eye diseases caused by herbes simplex virus;
- herbes of the red border of the lips and skin tissues;
- viral stomatitis of the oral cavity;
- genital herpes;
- hepatic encephalitis.
For successful treatment of the disease, experts recommend:
- 5 percent creams, effective for external use;
- 5 percent ointments;
- ophthalmic 3 percent formulations;
- tablet forms, dosed at 200 and 400 mg;
- powders, for solutions, doses from 200 mg to 1 g.
What are the side effects of acyclovir?
Common side effects after taking acyclovir may include:
- headaches and dizziness;
- pain in the gastrointestinal tract, feeling of nausea;
- hives (itchy skin with large red rashes);
- fast fatiguability.
If you observe the following symptoms, you should contact an ambulance as soon as possible:
- skin hemorrhages on the body;
- vomit;
- problems with urination;
- behavioral changes;
- pain in the mouth when using the buccal form of acyclovir.
Possible applications
These products are recommended by experts for the treatment of herbes, as they have the ability
- prevent the formation of new sites of infection;
- reduce the possibility of spreading infection through internal organs;
- speed up the healing of ulcers;
- reduce pain in the acute phases of the disease;
- stimulate the body's immune system.
The variety of forms of the drug containing acyclovir, which are offered by the pharmaceutical industry, makes it possible to use the drug both for local treatment and in a system with other formulations.
Directions for use and dosage of acyclovir
For the treatment of herpes virus types 1 and 2:
Adults: 1 tablet at a dose of 200 mg 5 times a day with an interval of 4 hours between doses. The course of treatment lasts up to 10 days on average.
The maximum dose taken per day is 1000 mg (5 tablets).
Children: used for children from 3 years of age: from 3-6 years - 400 mg (2 tablets) per day.
For children from 6 years of age, it is used in the same dosage as for adults. The course of treatment is determined by the doctor. On average, it is used up to 5 days.
For the treatment of herpes virus types 3 and 4:
Adults: prescribed at a dose of 800 mg up to 5 times a day (dosing interval 4 hours). The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor, but on average the course is about 10 days.
Children: from 3 to 6 years, 400 mg (2 tablets) 4 times a day.
Children over 6 years of age are prescribed in the same dosage as for adults.
In old age, the process of removing the drug from the body (clearance) slows down, so it is necessary to take care of drinking plenty of fluids during treatment with acyclovir, and if renal function is impaired, the dose of the drug should be reduced.
It is worth remembering that for each person, based on the state of health and the specific type of herpes virus, the dose may vary, so acyclovir should be prescribed by a doctor.
Dosage forms
Products containing the active substance are produced by the following companies:
- in tablets;
- in powders intended for the preparation of solutions used for intravenous drip administration of the drug;
- in a thick cream or ointment consistency.
The use of the product, regardless of the release form, does not impose any age restrictions and is generally recommended based on the indications in each individual case. However, the use of compositions used to prepare solutions for drip administration implies hospital treatment, as it requires compliance with certain precautions.
Drugs produced in the form of creams, ointments and tablets are recommended for outpatient treatment.
Interaction of acyclovir with other drugs and substances
If you are using medications to treat tumors, osteoporosis (low bone density), gastrointestinal disorders, or rheumatoid diseases, then taking them together with acyclovir may increase the negative effect on the kidneys (nephrotoxicity). Therefore, you should be careful and when using any medications, you should consult your doctor.
Be careful!
When taking acyclovir simultaneously with Probenecid (a drug for gout), the half-life of acyclovir increases and its biotransformation (redistribution in the body) decreases. This is especially important for those who have impaired kidney function.
This is not an exhaustive list of drugs that may interact with acyclovir. You should tell your doctor about any medications you start or stop using.
What you need to know about acyclovir
Do not forget that acyclovir, like all other medications, must be stored out of the reach of children. Never share your medications with other people, so as not to harm their health. Remember that acyclovir should be used only for its intended purpose.
Always consult your doctor to make sure the information on this page applies to your individual situation.
Sources
Acyclovir / Drugs.com (English)
Acyclovir / State register of medicinal products (ukr.)
apteka24.ua provides comprehensive and reliable information on issues of medicine, health and well-being, however, diagnosis and choice of treatment methods can only be made by your attending physician! Self-medication may be unsafe for your health. apteka24.ua is not responsible for possible negative consequences arising from the use by users of apteka24.ua of the information posted on the site.