Treatment of gums in children is a common reason for visiting a dentist. The susceptibility of delicate gums to inflammatory processes is explained by their sensitivity to all kinds of damage and poor hygiene. The remaining soft plaque on the teeth eventually turns into hard deposits in the form of tartar. Inflammation can also be caused by an infection that enters the oral cavity through dirty toys, for example. Unfortunately, parents are not always able to monitor the regularity and quality of brushing their children’s teeth or protect them from licking dirty surfaces.
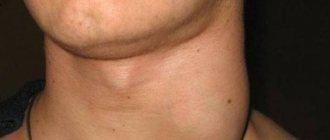
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the gums or gingivitis must be detected as early as possible and treatment begun. This is why regular scheduled examinations are so important. A delay in making a visit can result in a complication - there is a risk of transition to a chronic form, after which - to the ulcerative-necrotic stage, and, as a result, damage to surrounding tissues. Periodontitis is one of the most serious stages of gum disease.
Teething in infants is not only a painful process, but also provokes inflammation of the gums, as well as injuries, as a result of diligently sucking a rattle or a cracker offered by the mother...
Causes of gum inflammation in children
- Skipping or poor quality teeth brushing;
- Sucking dirty objects;
- Errors when installing seals;
- Pathologies of the dentition;
- Carious cavities with sharp edges;
- Bite correction;
- Breathing through the mouth;
- Abnormal structure of the oral cavity organs (attachment of the frenulum of the tongue and lips);
- Problems with the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Infectious diseases (ARVI, influenza);
- Hormonal abnormalities;
- Hereditary anomalies.
Gingivitis in children: what are the causes and symptoms
Gingivitis, or inflammation of the mucous membrane around the teeth in children, is a fairly common phenomenon. Most often, gingivitis can be detected in a child aged 1–3 years, as well as in adolescence - in both cases, the “trigger” of the disease can be active growth of the body, hormonal changes and features of the formation of the immune system
Gingivitis in children develops quite quickly. If inflammation develops in a child’s mouth, the number of bacteria increases significantly compared to the norm. Within 72 hours, the process of stone formation from soft plaque begins, and the first signs of gum erosion appear. If the situation is neglected, this can lead to the loss of teeth in children - both milk and permanent.
Symptoms of gingivitis in children
How does gingivitis manifest itself in children? The symptoms are:
- bad breath
- discomfort, pain in the mouth
- bleeding gums
At the same time, the temperature with gingivitis in children does not always rise. Therefore, it is quite easy to miss the onset of the disease. A child may tolerate discomfort without attaching any importance to it, or endure it, fearing a visit to the dentist (especially if he has already had a bad experience with dental treatment). That is why it is necessary to unobtrusively check the oral health of your son or daughter from time to time. For kids this can be done during play, but for a teenager you will have to find a psychological approach. Perhaps it would be easier (and more correct!) to “introduce” your offspring to a professional dentist whom he can trust, and periodically take him for preventive examinations.
Types of gingivitis in children
Only a competent doctor can determine what form of gingivitis a child is suffering from and, accordingly, prescribe effective treatment that quickly relieves discomfort. The disease can manifest itself in different ways:
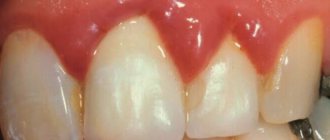
- Catarrhal gingivitis. Children aged 3–7 years are most often affected. It is accompanied by swelling of the tissues around the tooth, unpleasant taste in the mouth, pain when pressure is applied to the gums, the appearance of pink saliva, general malaise and tearfulness. This type of disease easily becomes chronic, when gingivitis occurs approximately twice a year, causes temporary inconvenience to the child and seems to go away on its own. In fact, each time the inflammatory process becomes more and more severe, hard dental deposits are formed, which can ultimately “develop” into periodontitis - a disease in which the bonds of the tooth with the surrounding tissues are destroyed, which leads to its loss.
- Hypertrophic gingivitis. Painful sensations in a child do not appear immediately. The area of the front teeth is most often affected - the gums swell, changing their color (up to purple-blue). Over time, the tissues grow, covering a significant part of the tooth area, gum pockets appear, pus begins to be released, and severe pain appears.
- Atrophic ginivitis. This form of gingivitis is characterized by “recession” of the gums: the neck (and sometimes even the root) of the tooth is exposed, the child feels discomfort from eating cold and hot food. In this case, the gums become pale and bleed slightly. This is not only unpleasant and unsightly, but also quite dangerous and difficult to treat: you will most likely have to restore the shape of the gums using mini-plastic surgery.
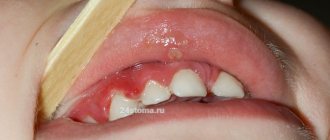
- Ulcerative gingivitis. This is one of the options for the development of catarrhal gingivitis: the inflammatory process does not become chronic, but intensifies. Bleeding ulcers appear in the child's mouth, covered with a gray film - this is dead gum tissue. The child cannot eat and sleep normally, experiences severe pain, his body temperature rises to 39 °C... This development of the disease can be avoided by consulting a doctor at the first signs of gingivitis in the child.
Causes of gingivitis in children
Of course, parents want to believe that they will not have to treat gingivitis in children, knowing the causes of its occurrence. It’s really important to know them - they can be:
- Systemic diseases of the body (failure of the endocrine, cardiovascular, digestive, hormonal systems, the influence of infection)
- Dental pathologies, bite defects and errors in their correction
- Incorrect installation of fillings or their deformation
- Advanced caries, careless attitude of parents towards the health of the child’s teeth
- Weakened immunity, lack of vitamin C, poor appetite
But the main and main reason for the development of gingivitis in both children and adults still remains poor oral hygiene. Remember this the next time you allow your baby to “so be it, don’t brush his teeth just once”!
Expert opinion
There are many reasons for the development of gingivitis in a child, and not all of them are directly related to the condition of the oral cavity.
However, treatment should begin with a visit to the dentist: he will determine the form of the disease and prescribe the correct treatment, which will effectively relieve the symptoms - that is, quickly improve the child’s well-being. After all, sometimes inflammation of the gums causes real suffering to the baby, and he cannot even explain what is bothering him! A professional dentist will immediately understand what’s going on when he sees the clinical picture of the disease, and will definitely find an approach to the most capricious young patient. After this, parents (who will also immediately feel better after their child stops experiencing pain) should fully examine the child, starting with a clinical blood test.
Perhaps the inflammation is associated with teething, the formation of roots and the formation of a bite - this is the best option, it can be conditionally classified as normal. Otherwise, you will need to consult specialists from other medical specialties - you will need to look for and treat the cause of gingivitis.
Types of inflammatory processes
Gingivitis
Inflammation of the gums at the initial stage, that is, not yet spreading to the bone tissue, is called gingivitis.
Treatment of gingivitis in children follows the same principle as in adults, with the only difference being that children are prescribed more gentle medications. When starting the procedure, the hygienist performs professional cleaning, removing plaque and stone, after which he teaches the little patient proper hygiene techniques. Helps you navigate the selection of toothpaste and brush.
Periodontitis
Inflammation of the gums and periodontal tissues - periodontitis - is an advanced stage of gum disease. If left untreated, its progression may result in one or more teeth having to be removed.
Treatment includes occupational hygiene and physical therapy. If the process is advanced, surgical intervention may be required.
Periodontal disease in children
The defeat of all periodontal tissues, in this case, is called childhood periodontal disease. This degree is quite rare. Progression can be triggered by weakened immunity and vitamin deficiency.
An effective option in this case is surgical intervention, as well as strengthening the general condition of the body.
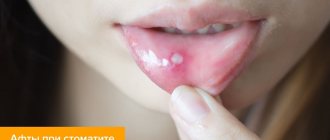
Stomatitis in children
Infectious inflammation of the mucous membrane of the gums, or stomatitis, is characterized by increased sensitivity and discomfort while eating. Therefore, you should show it to a dentist as soon as possible. A dental clinic specialist will examine the baby and prescribe appropriate procedures.
Treatment of abscesses and abscesses in a child
Depending on the nature and cause of the abscess, the doctor will choose the appropriate method of treating the lump on the gum. Most often this is:
- opening and cleaning of pus;
- treatment of caries or removal of a tooth if it is severely damaged and cannot be restored.
In this case, an abscess over a baby tooth can often be eliminated only with the removal of the tooth itself. This is an undesirable process, but it may turn out that it is impossible to fix the problem in any other way.
When treating ulcers in children, the doctor is always guided by the fact that soon the milk teeth will be replaced by molars. The formation of a cyst or abscess over a baby tooth can affect the future molar, so sometimes the decision to remove a tooth is actually advisable.
After the procedure, the child is prescribed antiseptics for home use.
Gum atrophy
A rather unique and rare disease - gum atrophy or exposing atrophic gingivitis manifests itself as itching in the area of 2, less often 4 and 6 symmetrically located milk teeth. A child experiencing discomfort constantly rubs the area of inflammation. At night, the itching usually intensifies.
The interdental papillae and other areas of the gums do not change in any way during gingival atrophy. Slight deposits of tartar are often observed on the unprotected root surface.
The manifestation of itching can be a consequence of measles or influenza, despite the fact that in most young patients such a relationship is not observed. The process of teething is also one of the factors causing itching in infants.
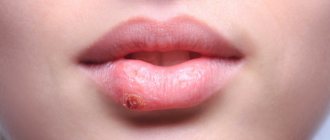
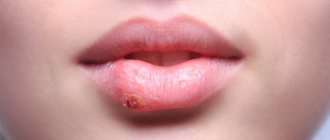
Reasons for the formation of bumps on the gums
The reason for the appearance of lump-shaped inflammation is that an infection gets into the gum tissue. It accumulates and is localized in one place under the mucosa. Pus forms there and infectious processes are activated. Often, a purulent gum abscess quickly increases in size, covering a large area.
Causes of infection in the gum tissue:
- deep caries,
- poor oral hygiene,
- teething,
- injuries to teeth, jaw or gums,
- poor quality treatment
- weakened immunity,
- braces that limit oral hygiene.
New growths above a baby tooth and bumps during eruption often go away on their own after the tooth appears on the surface. However, if such a problem occurs, it is still recommended to show the tumor to a dentist to eliminate risks.
If a lump appears on the gum, you should not try to diagnose its nature yourself. When it comes to children's health, it is better to make an appointment for an examination once again, even if the last one took place just a month ago.
Diagnosis of gum disease in children
A routine oral examination should be performed by a pediatric dentist every six months. And as necessary, if a small patient exhibits any deviations in the development of teeth or symptoms of disease of the oral mucosa. Since it is advisable to diagnose the inflammatory process at the earliest stage.
If redness, swelling and bleeding are detected, the cause of which is an excessive amount of soft plaque or food debris on the teeth, the dentist will make a diagnosis and prescribe procedures.
If a bacterial infection is suspected, a clinic specialist can take biomaterial from the inflamed areas of the gums for clinical tests. Based on the results of the analysis, the specialist prescribes a treatment plan and the date of the next appointment to ensure the final recovery of the little patient.
Treatment
Therapy for this pathology must be comprehensive. It includes medication and special procedures.
For this purpose, the following methods are used:
- Treatment of all forms of gingivitis begins with getting rid of plaque. They are removed by the dentist using ultrasound, then polished using brushes and a special composition. If professional cleaning is not performed, home treatment is ineffective. As soon as it ends, the disease worsens again.
- Rinsing with antiseptic agents is used. For this purpose, solutions of Miramistin, Furacillin, Chlorhexidine and infusions of medicinal herbs (eucalyptus, chamomile, calendula, sage) are used. Rinse your mouth with them three or four times a day, after meals. Before rinsing with herbs, remove all food debris. The course of treatment lasts up to ten days.
- Lubricate the gums with gels that have anti-inflammatory properties. The following drugs are used in gel form: Cholisal, Soloseryl, Asepta (no age restrictions) and Metrogyl Denta (used in children over six years old). The drug is applied to the gums twice a day. After this, you should not eat or rinse your mouth. Drinking is not prohibited. The course of treatment lasts up to ten days.
- In severe forms, antibiotic therapy is used. The medicine is selected by the doctor individually, based on the sensitivity of the bacterial flora.
It is necessary to cure all the child’s teeth affected by caries, followed by fluoridation and silvering. Alcohol preparations are not used for treatment. They increase irritation.
Treatment of gums in children
Medicines prescribed by a doctor have analgesic, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects. They help restore the proper condition of the mucous membrane. Methods of using drugs are different, but the principle is the same: rinsing, irrigation.
For gum disease in infants, the dentist will prescribe special gels to relieve symptoms, namely itching and pain. Parents should pay special attention to cleaning their mouths from food debris.
Antibiotics are prescribed by a dentist in rare cases. Indications for the use of antibiotics is a form that reaches a complex (ulcerative-necrotizing gingivitis) or chronic stage. Antibacterial or antifungal drugs are prescribed when the problem is caused by an infectious process, and the goal is to eliminate its causative agent.
Preventive actions
The best prevention of inflammation of the mucous membrane is daily and high-quality hygiene from an early age and proper nutrition.
Hygiene
The concept of “quality hygiene” includes brushing your teeth at least twice: in the morning and in the evening, in conjunction with cleaning the palate and tongue.
Parents should take a very responsible approach to hygiene from the day the first tooth appears. And after he grows up a little, learn the rules of brushing his teeth: regularly and efficiently. The toothbrush and toothpaste should be selected according to the age of the small patient.
Nutrition
In addition to hygiene, parents need to approach the diet wisely: it should be balanced and include vitamins and minerals. Sweets and carbonated drinks should be consumed by the child in limited quantities. In addition, after finishing eating sweets, the baby should rinse his mouth with water and, if possible, brush his teeth. Note that a diet that promotes the proper development of a growing body includes nutritious and timely meals. Snacking and disordered eating should be kept to a minimum.
Treatment of children at RAIDEN
In the RAIDEN network of dental clinics, the treatment and prevention of oral diseases of young patients is treated with the utmost attention and reverence - the health of the younger generation is very important to us!
All medications used in our clinic meet the highest quality requirements. Before using them, we conduct a blood test of the baby to determine drug tolerance. The safety of your children, our little patients, is paramount to us.
Complications and consequences
If the above symptoms occur, you should immediately visit your dentist. Treating the disease at home can significantly aggravate the situation and also lead to irreversible consequences. Only a doctor can correctly diagnose the disease, prescribe effective treatment and prevent complications.
In case of delayed or self-selected treatment, which turned out to be ineffective, gingivitis can cause periodontitis, mobility and tooth loss. Children may complain of pain from contact with any food, be capricious and refuse to eat and drink.