Like any part of our body, our gums can also become injured. The tactics of the planned treatment depend on the volume and nature of the damage received. Only with properly organized treatment will trauma to the gums not leave serious consequences. When any oral disease appears without the necessary treatment, manifestations of a weakened body and complications are possible.
Despite the fact that the gums are protected from the outside by the muscle tissue of the lips, they are easily exposed when talking, eating, or laughing. This is facilitated by the fact that facial muscles in humans are quite well developed. Therefore, gums can easily suffer injuries of varying severity.
Content:
- Causes
- How does pathology manifest itself?
- How is the treatment carried out?
- Surgical techniques
- Additional treatments
- Preventive measures
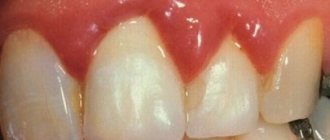
If the gums have become detached from a wisdom tooth or any other unit, you need to visit a doctor as soon as possible.
When the soft tissues subside, the neck remains unprotected and exposed. It is not covered with a thick layer of enamel, so it immediately begins to react sharply to temperature changes. The situation is aggravated by the fact that food debris gets into the formed periodontal pocket. They accumulate there and serve as an ideal breeding ground for pathogens. If such a pocket is not cleaned in a timely manner, it will increase in size. Then it will come to edentia.
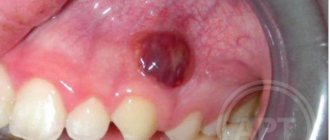
Stages of development and classification of gum abscess
A gum abscess most often has an acute course, characterized by a clear clinical picture with increasing pain and swelling. Sometimes, in the absence of treatment, the process may subside, the clinic becomes weakly expressed and erased. This means that the abscess has become chronic.
Depending on the location of the purulent focus, several types of pathology are distinguished:
- Periodontal abscess. Localized inside the hypertrophied periodontal pocket (between the alveolar process and the gum). The cause of the pathology is subgingival deposits, which are a breeding ground for the proliferation of bacteria.
- Periapical (root). The leading cause of occurrence is inadequate root canal treatment, leading to periodontal inflammation. Granulations form near the root apex. Progressive inflammation spreads to the periosteum and periodontal tissue. A connective tissue capsule with purulent contents is formed. Over time, a fistula forms with pus coming to the surface in the form of a lump.
- Desnevoy. The purulent cavity is located near the papillae between the segments. A possible cause is an injection into the gum.
Causes
Exposed necks indicate periodontal damage. Most often the problem occurs for the following reasons:
- Genetic predisposition. When exposed to this factor, a person can very diligently monitor the health of his smile, but will still periodically encounter unpleasant dental symptoms.
- Mechanical and thermal damage. The habit of gnawing on foreign objects, eating too hot food, using a hard brush are all provocateurs that contribute to irritation.
- Poor oral hygiene. If the patient neglects basic hygiene rules, a lot of plaque is deposited on the crowns. Pathogenic microorganisms spread in it. The gums become irritated, turn red, and bleed. Gradually they begin to move away from the teeth. It is important to use a brush and paste twice a day, and undergo professional hygiene at the dentist’s office annually.
- Poorly performed prosthetics or mistakes made during filling. It is necessary that the dentures fit as tightly as possible to the bases and do not fall under pressure, otherwise the gums will be constantly injured and inflamed.
- Curvature of the bite, problems with teething “eights”, uneven edges of the crowns. All this causes the gums to move away from the tooth.
- Unbalanced diet. If a person eats only soft foods and sweets, he does not actively chew food. As a result, blood circulation in the oral tissues slows down, less saliva is released, and periodontal deposits are actively formed. These are the prerequisites for a recession.
- A large amount of tartar. Despite the fact that dentists recommend removing stones annually or even more often, many patients do this very rarely. You shouldn't wait until a serious problem arises. It is easier and cheaper to prevent it than to treat it later.
- Hormonal imbalance. Most often, this reason concerns women, for example, during pregnancy, menopause, and breastfeeding. With hormonal fluctuations, the mucous membranes become especially vulnerable. Even minor mechanical impacts cause recession.
Don't forget about the negative effects of tobacco smoke. According to statistics, smokers are much more likely to suffer from gum disease and exposed necks. They accumulate plaque faster. Therefore, if you want to have a healthy smile and visit the dentist less often, stop smoking.
Trauma to the mouth and teeth. What to do and where to run?
Authors : Solovyov D.V.
Injuries, especially in the facial area, scare people perhaps the most. And yet, with an adequate reaction, most often nothing terrible happens. So let's talk about what and how to do in such a situation. Do it for both adults and children. The main thing right away: due to the abundance of facial muscles and good blood supply, wounds on the face and mouth often seem much larger and more serious than they actually are. Therefore, in any situation, remain calm! Screams and hysterics will not change anything; only quick and cool-blooded actions can help!
A blow with the teeth or on the teeth. When to see a doctor urgently (at least one of the following):
- something red is visible in the tooth;
- there is severe pain;
- the tooth appears to be loose;
- the tooth apparently changed its position;
- the tooth does not hurt or become loose, but over time it began to change its color, at least slightly.
Chip of a piece of tooth.
- The chip is small, does not interfere or bother you in any way: you don’t have to do anything.
- If the edge is sharp or looks unsightly: in baby teeth it can be polished (by a doctor), in permanent teeth it can be restored with a filling or veneer.
- Large chip: restoration with a filling or veneer. At the same time, be prepared for the fact that you may have to fill the canals (this is done when the nerve of the tooth is damaged).
The tooth is loose.
- At home before the doctor: do not bite on the tooth.
- Baby tooth: it all depends on how much time is left before eruption. A little - we delete and forget, a lot - perhaps it will still serve.
- Permanent tooth: Initially, an image is taken to assess whether there is a root fracture. If, unfortunately, there is only removal, if the root is fractured, there are no methods that can heal it and prevent further inflammatory process, so sometimes the advice to wait for something is meaningless! The faster you remove it, the fewer problems there will be. If there is no fracture, the tooth is temporarily splinted (“glued”) to the adjacent teeth.
The tooth is rotated or impacted.
- At home to the doctor: do not turn back on your own!
- Baby tooth: with minor displacements, they often do nothing, because in many cases the tooth gradually takes the desired position on its own. If the displacement is serious and especially if it is impacted (the tooth has become “lower” than its neighbors), then it is undesirable to leave it this way - damage to the permanent tooth may occur.
- The tooth is permanent: there are techniques that allow you to return even a strongly displaced tooth to its place.
Which one will be used specifically in this case depends on the qualifications of the doctor, the technical equipment of the clinic and the financial capabilities of the patient. However, in any variant, it is first assessed whether there is damage to the neurovascular bundle (the “nerve” inside). If there is, then it will be necessary to treat and seal the canals. Subsequently, the tooth is returned to its place and splinted. It is impossible to determine the period of splinting in advance, but in any case, we are not talking about days, but about at least weeks and months.
The tooth fell out. Theoretically, there are methods for bringing back permanent teeth, but in practice this is difficult to achieve, so it is not done in real life.
The tooth has changed color over time. This suggests that there is something wrong with the “nerve” of the tooth. See a doctor as quickly as possible, because the situation may end in a purulent process! The ability to return a tooth to its original color depends on the stage of neglect and what kind of tooth it is (in the front teeth it is usually easier to do this, but the smallest shades of color are much more noticeable).
A cut of the skin or lip with bleeding. Don't be afraid of the amount of blood or the visible strong separation of the edges of the wound! This happens very often on the face due to the characteristics of the facial muscles and does not necessarily lead to noticeable consequences in the future. The main task is to stop the bleeding, so the first and most urgent action is to simply clamp the wound. You can do it with your hand, but it’s better with some piece of cloth. Why? Because, firstly, your hands will quickly slip, and secondly, with serious bleeding, you essentially chain yourself to the victim, without even being able to call for help. (We deliberately do not consider here methods of stopping bleeding on the limbs and other parts of the body; there are separate articles for this.) If you are on the street, the bleeding is heavy, and there is nothing clean at hand, do not be afraid to cover the wound with a dirty bandage. Dirt may get inside, or maybe not; even if you get it, the infection may or may not develop, but if you don’t stop it as quickly as possible in case of severe bleeding, the person will die right here and now, simply before the infection develops. - Apply a pressure bandage. First, we apply a rectangle of fabric folded in several layers (“pillow”), then either tie it with a bandage around the head (as best we can, specialists will do this more professionally later), or stick on an adhesive plaster. You can apply cold on top of the bandage, but for no more than 20-30 minutes; there is no need to apply ice for half a day. (If there is time and opportunity, it is better to repeat the application of the cold one for another 10-15 minutes every 2 hours.) If there is a protruding foreign body in the wound (precisely protruding, and not lying on top), it is absolutely forbidden to pull it out! Do not forget that after stopping the bleeding, any wound must be washed. If we are at home, we rinse with saline solution or just a stream of tap water, then pour a soap solution into a bottle (liquid soap or scrape out a little solid soap with a potato peeler) and pour it over the wound. We finish again with clean water. We are in nature and there is no clean water - we take any (including from a lake, river, etc.). The point is that the dirt already in the wound is much more dangerous than what is in the water of even an ordinary lake. Therefore, you must choose the lesser of two evils: if there is no clean water, wash it with what you have. It is strictly forbidden to pour iodine or brilliant green onto a wound! This is one of the most serious everyday misconceptions, because once these substances get into a wound, they seriously slow down its healing. The maximum that can be done is to treat the wound edges, but nothing more! After washing the wound, cover it again with a bandage or adhesive plaster (make sure that the sticky edges of the plaster do not stick to the wound itself). Any damage to the facial skin requires examination by a doctor as quickly as possible (within 6 hours)! Inspection is especially important if the wound is a bite wound! However, don't worry too much, modern cosmetic surgery can do a lot even in cases of really serious injuries. Do not forget also that any damage to the skin requires a tetanus vaccination (especially if more than 10 years have passed since the previous one).
Biting the cheek or tongue. Despite the often severe pain, it usually goes away completely on its own. Close attention is required only when biting off a large area of the cheek or tongue, when the wound may need to be stitched. A special case is completely biting off a piece of the tongue. We put the bite in an ice pack and go to the hospital. Yes, they sew it on. You can alleviate the condition by putting something cold in your mouth, even just ice cream or a piece of ice (just remember that if the child is small, you should not give him any small pieces). Separately, we need to dwell on the much-loved “washing with potassium permanganate.” In short, you don’t need to rinse anything with it, especially in your mouth! The bottom line is that the standard dilution of potassium permanganate is 10 g per liter of water. Dilute this amount somehow just for fun, and you will see that it is a very dark “tea”. The minimum dilution at which at least some disinfectant effect is observed is at least 1 g per liter. Those. all this has absolutely nothing to do with that pale pink solvent, made from one or two crystals, and which is used most often. It doesn't disinfect anything! Actually, in such procedures “to calm one’s own thirst for activity,” there would be nothing terrible if it were not for the ability of permanganate crystals (i.e., that same potassium permanganate) to lead to severe burns if they suddenly accidentally fall in an undissolved state on the mucous membrane (thus more, being accidentally swallowed). If you gape, an almost imperceptible crystal will bounce off even just onto the edge of a cup - you will get a terrible problem. Therefore, it’s better not to, it’s not worth it.
See a doctor immediately if:
- blood flows in a stream;
- the bleeding does not stop within half an hour;
- general health worsens;
- the temperature has risen;
- the pain does not decrease over time (or even worse increases);
- the tumor continues to grow;
- numbness appeared;
- There is any symptom that you do not understand.
Injury. Actions:
- a pressure bandage for at least 10-15 minutes (if it is not possible to tie it on, just hold it with your hand; in extreme cases, pressing with your fist will do);
- cold on the site of the injury (necessarily through a cloth) - for about half an hour. Ideally repeat every couple of hours for 10 minutes.
It is forbidden:
- Warm up earlier than after about a couple of days.
- Accordingly, a variety of “warming” ointments.
- Rub the bruised area.
The point is that immediately after a bruise we must stop the bleeding (which is inside) and the spread of swelling, for this we need cold and pressure. Warming and rubbing at this time only promotes further bleeding and inflammation. After a couple of days, everything changes - the bleeding has stopped long ago, resorption therapy is needed, which is what heat does.
Remember that identifying a fracture is sometimes not so easy, so if in doubt, consult a full-time doctor at the first opportunity. Immediately consult a doctor if you have the same symptoms as described in the previous paragraph about cheek bite.
Jaw fracture. You can suspect if there is:
- Unnatural jaw position.
- Sharp pain when trying to move it.
- Inability to fully close the teeth or a feeling of a changed bite.
- During the injury, a crunching sound was heard.
- Rapid swelling or rapidly spreading bluishness at the site of injury.
There is only one action: see a doctor immediately! At home before the doctor: if possible, do not move your jaw, do not try to squeeze it in the “correct” position. What the doctor will do depends on the severity of the injury and where exactly the fracture is located. But in any case, an X-ray examination and at least splinting of the jaws are carried out. Splinting in this case is essentially tying the jaws together in a special way (in the mouth, through the teeth). Whether any additional surgery or removal of some teeth is needed is decided depending on the situation.
For any head injury, see a doctor immediately if:
- The swelling continues to worsen.
- Redness appears that was not there, or the one that was there increases.
- The skin over the injury site became hot.
- The general condition worsens (temperature rises, poor health increases).
- Bruises have appeared under the eyes or behind the ears.
- There was even a short-term loss of consciousness.
- Vomit.
- Loss of coordination or speech.
- Discharge of any fluid from the nose and ears (for example, immediately after an injury a runny nose appeared that was not there before).
- Unusual sleepiness or unusual behavior.
- Cramps.
- Pupils of different sizes.
- Within two days there was absolutely no improvement.
- Any symptom that you do not understand.
I hope that what is written here will never be useful to you. However, a person still cannot survive without injuries, and therefore it is better to be prepared for this in advance.
But the choice, as always, is yours. 
Consultations by Dmitry Solovyov at ClubCom
published 05/02/2014 16:50 updated 27/09/2016 — Diseases of the teeth and oral cavity, Dentistry
How does pathology manifest itself?
Symptoms depend on how far the gum has receded from the tooth. Most often patients complain of:
- increased bleeding and soreness of the gums;
- bad breath that cannot be eliminated with standard hygiene products;
- taste of pus;
- separation of purulent masses from the inflammatory focus;
- the appearance of deep periodontal pockets;
- loosening of individual units.
In the first days of the disease, patients may not experience any significant discomfort. They are just beginning to notice that in certain areas of the jaw the tissue seems to have sagged and become less voluminous. Because of this, the crown part of the tooth, on the contrary, looks elongated.
If the gums have peeled off, there is no need to try to do anything on your own. Without qualified help, it will still not be possible to cope with the recession. Postponing competent therapy until later is fraught with even more serious violations.
Stages of development of gum abscess
| Disease stage | Description |
| Initial | The beginning of inflammation. If the immune system is functioning well, the process may stop on its own. Symptoms are absent or mild. If the immune defense is insufficient, bone or soft tissue begins to melt. Hyperemia of the mucous membrane and discomfort appear. |
| Subacute | The inflammatory process intensifies. Pus accumulates in the pathological area (near the root, inside the periodontal pocket, near the gingival papilla). The pain intensifies. The tooth reacts to irritation. |
| Acute | Progression leads to abscess formation: a cavity with pus forms in the central zone of infiltration. The clinical picture is clearly expressed: the pain is constant, sharp, swelling appears. A lump appears on the surface of the gum, inside of which there is purulent exudate. Inflammation spreads to the submandibular lymph nodes. |
| Chronic | The abscess on the gum spontaneously opens and the contents of the cavity come out. Signs of acute inflammation subside. |
How is the treatment carried out?
Some people think that they can be cured with regular rinses. Unfortunately, it is not. The first step is to make an appointment with a dental hygienist. The doctor removes soft and hard deposits from the surface of the crowns and subgingival area in one session.
The following methods are used to remove stone:
- Instrumental. Involves the use of special scrapers that remove deposits. It is considered outdated and is extremely rarely used by doctors, as it is traumatic.
- Ultrasonic. Using an ultrasonic scaler, the doctor crushes the stones into tiny particles. This equipment produces waves of the required frequency, which easily destroy dental plaque.
- Sandblasting. It is the most modern and safe. The doctor delivers the cleaning solution under high pressure. Abrasive particles wash away deposits from crowns and effectively flush out existing pockets. The advantage of the technique is to achieve the effect of teeth whitening by one or two shades.
If the hygiene procedure does not help and the problem is serious, the patient is prescribed surgical treatment.
Why does pain occur?
Soft tissue may hurt due to:
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- A wisdom tooth that is starting to erupt
- Getting food between teeth
- Injuries received as a result of a fight, blow or bad fall
- Suppuration.
One of the causes of pain is injury. In dental practice, they are usually divided into two categories:
- Mechanical damage to the gums. A fairly common type that occurs in both adults and children. The reasons can be very diverse, but they are all related to physical effects. Falls or impacts may cause damage in one way or another. People often injure the soft tissues of the oral cavity and teeth during sports activities. Mechanical injuries are easier to diagnose because their presence can be determined visually during an examination by a doctor. They are accompanied by swelling, bruising and bleeding. An experienced dentist will help solve the problem, write out prescriptions, and select appropriate medications.
- Chemical. This category includes injuries caused by exposure to harsh chemicals. There are situations when a person, in a hurry and confused, drinks vinegar instead of water, resulting in a burn to the oral cavity. Exposure to various acids will inevitably lead to serious consequences. Teeth also suffer.
Surgical techniques
In advanced situations, plaque removal alone is not enough. Then there may be a need for open or closed curettage. It is indicated if the gums are very severely detached from the dental neck and the bone structure is changed.
The dentist-surgeon treats the lesion with an antiseptic, makes a small incision and removes purulent deposits and affected tissue . Then the gum is sutured. All manipulations are performed under local anesthesia. This means that the patient is conscious and can communicate with the doctor, but does not feel pain.
For a speedy recovery after curettage, antibiotics and mouth rinsing with an anti-inflammatory solution are prescribed. If the pain after surgery is very severe, the patient can use painkillers.
Traditional therapy
Herbal decoctions, used mainly for rinsing, have some anti-inflammatory and at the same time anesthetic effects for stomatitis.
First. Onion peel infusion:
- chop dry onion peel;
- 3 tsp. pour the resulting mixture with 500 ml of hot water;
- boil;
- leave for 7-8 hours;
- strain
Second. Horse sorrel decoction :
- Signs of stomatitis in adults and its treatment
- chop horse sorrel roots;
- 1 tbsp. l. pour the resulting mixture with 1 tbsp. water;
- boil for 15 minutes;
- strain.
Third. Calendula decoction:
- Pour boiling water over calendula flowers in the proportion of 1 tbsp. l. flowers for 1 tbsp. water;
- leave for 15 minutes;
- strain.
Traditional medicine methods are also effective in combating oral pathologies
Fourth. Nettle infusion:
- finely chop nettle leaves;
- 1 tbsp. l pour 2 tbsp. boiling water;
- let stand for half an hour;
- strain;
- use if the gums are bleeding and the oral cavity is “decorated” with ulcers.
Fifth:
- Pour 1 part of onion juice into an enamel-coated container;
- dissolve 1 part honey in a hot bath;
- pour onion juice with 2 parts water and honey;
- cool;
- Make lotions and compresses from the result in case of inflammation of the gums and oral mucosa.
Sixth:
- 2 tbsp. l. St. John's wort and 1 tbsp. l. pour chamomile into porcelain dishes;
- pour boiling water;
- stir, close the lid;
- hold for 1.5 hours;
- strain through a sieve.
St. John's wort and chamomile help eliminate inflammation
Seventh:
- 1 tbsp. l. chop sage leaves and calendula flowers;
- put them in a pan covered with enamel;
- pour one and a half cups of boiling water;
- stir;
- put in a water bath;
- Cook over medium heat for 10 minutes, covering with a lid;
- cool to ambient temperature;
- strain through cotton cloth.
Eighth:
- 1 tsp each fresh onion juice and Kalanchoe juice, as well as 3 tbsp. l. pour water into porcelain dishes;
- stir.
Ninth:
- 1 tbsp. l. Brew one and a half cups of boiling water for green tea;
- wait 40 minutes;
- at this time dissolve 1 tbsp. l. honey in the bath;
- strain the tea;
- add honey;
- mix.
Tenth:
- 2 tbsp. l. plantain pour 1 tbsp. boiling water;
- close the lid;
- hold for 15 minutes;
- strain through a fine sieve;
- cool.
You need to rinse your mouth with decoctions regularly
Important ! You need to rinse your mouth with such decoctions every two hours every day.
Additional treatments
Considering that gums become inflamed for various reasons, it is important to try to find out the provoking factor. Then the risk of relapse of dental pathology can be reduced to a minimum.
If the doctor determines that the disorder is related to hormonal levels, it is necessary to select hormonal therapy . In case of malocclusion, consultation with an orthodontist is indicated. If the diet is unbalanced, the patient is told what the diet should be like after recovery.
Often, when fighting gum that has receded from a tooth, anti-inflammatory drugs, immunomodulators, glucocorticosteroids, and antiseptics are used. It is very important that the patient strictly follows all medical prescriptions and does not engage in amateur activities. An integrated and responsible approach to treating recession is a guarantee of a speedy recovery.
If the tissues become so inflamed that the teeth begin to loosen, splinting may be required. If there is a deficiency of bone tissue, their deficiency is compensated with special compounds.
Complications that a gum abscess can cause
Without treatment of the disease and inadequate medical care, complications may develop. Adverse consequences arise due to the spread of inflammation to neighboring organs and tissues, as well as the spread of infection throughout the body with the formation of secondary septic foci. The most common pathological conditions that occur are:
- lymphadenitis - infection of the lymph nodes;
- sinusitis - infection in the maxillary sinuses;
- periostitis of the jaw (inflammation of the periosteum);
- osteomyelitis of the jaw bones (destruction of bone tissue due to purulent-necrotic melting of osteocytes);
- phlegmon - diffuse odontogenic inflammation of soft tissues, accompanied by progressive swelling of the face;
- destruction of the alveolar processes with significant loosening of teeth or their loss;
- peri-implantitis with implant rejection;
- sepsis.
Purulent lesions of soft periodontal tissues are always accompanied by general intoxication of the body. The temperature rises and chills appear. There is a headache, tachycardia, and the pulse quickens. Pain relief with medications brings short-term relief, but symptoms return after the medication wears off.
Preventive measures
To prevent gums from moving away from the tooth, you need to follow simple recommendations:
- brush your teeth twice a day;
- use a properly selected brush and paste;
- visit the dentist in a timely manner;
- prevent tartar from forming;
- no smoking;
- eat more solid foods;
- Healthy food.
At the first sign of a recession, you should see a doctor. Then the disease can be stopped very quickly.