Bone health is extremely important for full functioning. Together with joints and muscles, bones give a person support, movement, and strength. The skull, spine and rib cage protect the internal organs from physical influences. But their functions are not limited to this. It is also a storage facility for phosphorus and calcium. Finally, the bone marrow is the main organ of the hematopoietic system. With age, bones lose their strength. From about 32-34 years of age, irreversible processes begin in which resorption (destruction) proceeds faster than tissue restoration. The human task is to slow them down and keep the musculoskeletal system healthy and strong for as long as possible. In this material we will tell you what factors contribute to strengthening bone tissue.
What factors influence bone formation?
Primary ossification occurs in the third month of intrauterine development. This process is completely completed by the age of 25. In parallel, active bone growth occurs. Although bone tissue is formed throughout life, over time this process slows down. On average, a full cycle of remodeling (restructuring) takes 10 years. The main indicator of the quality of osteogenesis is bone tissue density, which is influenced by: • The amount of minerals: calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, silicon. • Presence of vitamins (C, D and K) in the body. • Supply of substances that help the absorption of minerals and vitamins. • Elimination of substances that promote calcium loss.
Genetic factors cannot be ruled out. If the gene responsible for encoding the calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D) receptor is mutated, bone density will be low even with sufficient vitamin D intake.
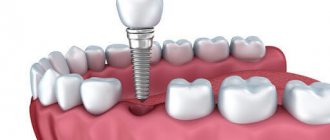
What is a sinus lift?
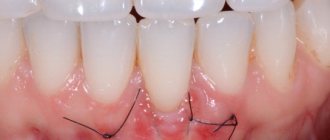
Sinus listing is an osteoplastic surgery that is widely used to build up bone tissue in the UPPER jaw.
The essence of a sinus lift is that the anatomical feature of the structure of the upper jaw, in which the paranasal sinus is located, is used to build bone.
This cavity is filled with air and lined from the inside with mucous membrane. Inflammation of this mucous membrane causes the well-known sinusitis. The distance from the bottom of the maxillary sinus to the roots of the teeth of the upper jaw is very small; sometimes the teeth even grow into it with their roots due to individual anatomical features. If the bone volume is lost, then it is impossible to install an implant without getting into the sinus. To avoid this, sinus lifting is used.
During the operation, the wall of the maxillary sinus is carefully opened, the internal mucosa is peeled off and osteoplastic material is introduced UNDER it. Over time, it integrates with the patient's jaw bone, raising the floor of the maxillary sinus and thereby increasing the volume of the upper jaw bone. After this procedure, root implants up to 10-12 mm long can be securely fixed.
There are several ways to perform sinus lift surgery: closed and open, with simultaneous or delayed implant installation. The doctor determines which one is suitable for a particular patient after a thorough diagnosis.
| Indications | Single-stage implantation | Delayed implantation | Peculiarities | |
| Closed sinus lift | The height of the bone under the sinus is more than 7 mm. | Preferably if there are no complications during the operation | Performed 4-6 months after lifting | A more gentle technique is performed when it is necessary to increase a small amount of bone. |
| Open sinus lift | The height of the bone under the sinus is less than 7 mm. | Possible with a bone height of at least 3 mm | Performed 4-6 months after lifting | Requires careful adherence to rules of behavior in the postoperative period |
Calcium value
This mineral is key to maintaining normal bone density. The range of its actions is quite wide: • participates in the formation of insulin-like growth factor-1; • activates the division of osteoblasts (young bone cells); • slows down the rate of remodeling; • regulates phosphorus metabolism.
At different periods of development, its preferred sources differ. A person receives the first portions from the placenta, then the mineral is supplied through breast milk. In childhood and adolescence (during the period of active body growth), a diet rich in calcium is important. Osteopenia and reduced bone mineral density are often diagnosed in premature infants. Without two months of calcium therapy, fractures are possible even when picked up. After age 35, food sources often become insufficient and vitamins and minerals must be taken. Otherwise, the risk of fractures increases even with minor physical impacts.
Phosphorus value
Phosphorus (its salts) is an important component of bone tissue. It is part of hydroxyapatite, a mineral component of bone that forms about half of bone mass. On average, phosphates contained in the human skeleton account for from 500 to 700 grams of its weight. When hydroxyapatites line up between the fibrils (thread-like protein structures) of collagen, biomineralization is triggered - the starting point of osteogenesis. This indicates the direct participation of phosphorus in the formation of bone tissue.
Effect of training on bone mass
Leading a sedentary lifestyle has the most negative impact on the condition of the skeleton. The statement is a fact proven by numerous studies and medical observations. Doing physical work, all kinds of exercises, morning exercises, on the contrary, help strengthen bone structures.
How to build bone mass through exercise? Doctors recommend doing physical activity at least 30 minutes a day. Among the most effective workouts that strengthen the skeleton are:
- Walking.
- Jogging.
- Going up and down stairs.
- Dancing class.
- Biking, roller skating, skiing, skating.
- Performing jumping rope.
Professional trainers advise resorting to strength training. It's about lifting weights, using machines that provide resistance. Various parts of the body should be worked out qualitatively: legs, arms and shoulders, back, chest. However, it is not at all necessary to use all muscle groups in training every day. It is enough to alternate workouts.
Absorption of minerals for strong bones
Calcium and phosphorus are the main minerals that give bone strength. A child needs them for normal growth, and an adult needs them to prevent fractures. But the direct intake of these substances into the body is not enough. Equally important is their absorption, which is facilitated by: • Vitamin D. Regulates the process of calcium absorption. • Protein. Promotes the absorption and accumulation of minerals. • Magnesium. Improves calcium metabolism. • Silicon. Important for phosphorus absorption.
It is believed that lactose is necessary for the absorption of minerals. But its significance should be assessed from a different perspective. Dairy products contain large amounts of calcium and phosphorus (mainly in the form of lactates, which are easily digestible and easily provide the daily requirement). If a person is lactose intolerant, they cannot consume them, so they are forced to make up for the deficiency in other ways (by taking medications).
What materials are used to build bone tissue?
| Type of graft material for bone grafting | pros | Minuses |
| The patient's own bone tissue - autograft | Fully biocompatible, take root well | Obtaining the material is traumatic, because additional surgery is needed to remove it. |
| Donor human bone tissue - allograft | They also have a high survival rate and do not require additional surgical intervention. | They have a psychological barrier to use, because are often cadaveric material. |
| Synthetic bone tissue substitutes - alloplasts | They are becoming more and more popular as their quality improves all the time. Very common as additional material. | May cause allergies. |
| Bone tissue of animal origin - xenografts | It survives worse than human ones, but is accessible and does not require additional surgical intervention. | Unacceptable for some patients due to religious beliefs. |
What foods can replenish calcium reserves?
99% of this mineral is found in bones and teeth. Regardless of the measures a person takes to strengthen them, without calcium the density will decrease, which can lead to fractures.
It is important to get enough of this substance for bone health. In addition to dairy products, its sources are: • fish (especially sardines and salmon); • seafood (crabs, shrimp); • sesame; • all types of cabbage; • nuts; • legumes; • hard cheeses; • eggs; • greens (basil, parsley, watercress); • sunflower halva.
Many of them (fish, eggs, milk) are also sources of vitamin D. Therefore, they not only give a person calcium, but also help to absorb it.
Rules of patient behavior after osteoplastic surgery.
The speed of rehabilitation, the absence of complications and the quality of the result obtained depend 80% on how the patient behaves AFTER THE OPERATION. All prescriptions of a dental surgeon in this regard are not advisory, but MANDATORY.
After bone grafting, the patient is prohibited from:
- Eat and drink hot.
- Take a bath, go to the bathhouse, sauna, swim in the pool.
- Engage in sports and physical labor.
- Lift weights.
- Fly on an airplane for 3 months.
- Drink alcohol.
- Smoking.
After bone grafting, the patient should:
- Eat light, liquid and only warm food.
- Maintain oral hygiene, but do it very carefully.
- Take all medications prescribed by your doctor strictly as scheduled.
- Use antibacterial mouth rinses.
What foods can harm bone health?
The diet needs to be carefully planned. The effect of healthy products can be neutralized by the effect of harmful ones - then it will not be possible to give strength to the bones. To avoid this, you should minimize your consumption of: • Sugar. A large amount of it negatively affects the intestinal microflora, which interferes with the absorption of minerals. • Caffeine. It accelerates the excretion of minerals from the body in urine. • Alcohol. On the one hand, it causes loss of fluid and salts, on the other, it has a toxic effect on bone tissue.
Phytic acid also interferes with the absorption of minerals. This substance, found in grains, blocks digestive enzymes. However, this does not mean that oatmeal, buckwheat or corn are prohibited. Before consumption, the grains are fermented or roasted to neutralize phytic acid.
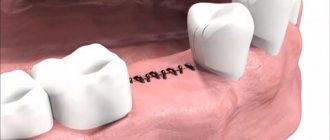
How can you build up your jaw bone?
The purpose of bone augmentation surgery is to transplant bone material into those areas of the jaw where there is not enough bone and thereby stimulate the body’s own regeneration of bone tissue. After some time (from 2 to 6 months), the bone material takes root, blood vessels and nerve endings grow into it, and it actually becomes the patient’s own bone.
Osteoplastic operations are performed using various techniques. They are selected depending on whether bone augmentation will be performed on the upper or lower jaw, the condition of the patient’s bone tissue, and what bone material will be selected for transplantation.
Tips for Promoting Bone Health
Osteoporosis, which causes decreased bone density, does not occur overnight.
Therefore, even when the first signs appear, you can take measures to slow down the process: • adjust your diet by including more healthy foods and eliminating harmful ones; • stop smoking; • increase physical activity, which will have a beneficial effect not only on bones and joints, but also on the body as a whole; • visit an endocrinologist to prescribe hormone replacement therapy (for women during menopause); • start taking vitamin D and drugs that affect phosphorus-calcium metabolism.
In more serious situations, when general useful recommendations cannot solve the problem, the doctor prescribes treatment with antiresorptive drugs. These are bisphosphonates (alendronate, ibandronate, risedronate), which slow down the metabolism of bone tissue and suppress its destruction.
The importance of hormone replacement therapy for bone tissue
Decreased estrogen levels are one of the risk factors for osteoporosis. These are female sex hormones, which are also present in small quantities in the male body. They are natural antiresorptive agents (that is, substances that prevent the destruction of bone tissue). In men, hormonal status remains relatively stable. In women, with the onset of menopause, the amount of estrogen decreases sharply, so they are more prone to osteoporosis. During menopause, bone metabolism accelerates by 30%. Due to age, the rate of tissue restoration does not keep pace with the rate of its destruction. As a result, the skeleton of women over 60-65 years old becomes very fragile.
Timely initiation of hormone replacement therapy can prevent this. By ensuring normal levels of estrogen, it also prevents a decrease in bone density.
When is bone augmentation contraindicated?
Any surgical operation requires a thorough preliminary examination of the patient’s condition and cannot be performed on everyone without exception.
Bone augmentation is contraindicated if:
- blood diseases and bleeding disorders
- diabetes mellitus
- acute inflammation in the oral cavity
- mental disorders
- autoimmune diseases, immunodeficiency, HIV/AIDS
- osteoporosis, loose bones
- oncology
- heavy smoker
- pregnancy and lactation
In addition, a sinus lift cannot be performed for sinusitis, nasal polyps and after surgery on the maxillary sinuses.
How to strengthen bones through exercise?
Regular physical activity helps not only build muscle mass or improve joint mobility, but also slow down the degenerative processes of bone tissue. There are special sets of exercises for the prevention of osteoporosis, but you can start with a minimum of: • walking; • climbing stairs; • stretch marks; • hanging on the horizontal bar.
Dancing, swimming, and yoga help give extra density to your bones. If there are signs of demineralization, it is important that exercises do not involve sudden movements and the risk of falls to avoid fractures. If osteoporosis has already manifested itself, patients suffer from pain in the back and limbs. In this case, you should refrain from lifting heavy objects, which may aggravate the syndrome.
When should bone augmentation be performed?
Bone augmentation is recommended for patients with insufficient bone volume. But its decline is not always the result of delayed prosthetics after tooth extraction, which we discussed above.
Causes of bone atrophy can also be:
- elderly age,
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity – periodontitis, cysts, periostitis, purulent infections, etc.,
- heredity,
- wearing unsuitable dentures,
- periodontal diseases,
- injuries.
The patient needs to increase bone tissue if:
- he wants to restore the dentition using single or multiple prosthetics on implants, but the bone volume is insufficient for this.
- he is going to switch from wearing removable dentures to more comfortable and reliable fixed or conditionally removable dentures on implants.
- he needs to restore bone volume during treatment of periodontal disease to strengthen loose teeth.
- The task is to carry out facial rejuvenation.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are effective in treating diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Electrotherapy includes the following techniques:
- electrophoresis;
- phonophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- inhalation therapy;
- EHF;
- ultrasound.
The following treatment methods are also used:
- To improve blood circulation and get rid of swelling in the limbs, lymphatic drainage massage is prescribed. If there is pain, paresis, or weak muscle tone, the doctor prescribes electrical stimulation.
- Light treatment. It is an effective method as part of the complex treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
- Electromagnetic treatment. Helps in the treatment and prevention of diseases, reduces the severity of the inflammatory process, improves metabolic processes, and relieves post-traumatic consequences. The procedure is performed by exposure to alternating electrical impulses of a certain frequency.
- Treatment with water. It is represented by different types of therapeutic showers and baths. They have a positive effect on bone structures, joints and muscles. Hydromassage is effective because it improves blood flow.
- Massage. Thanks to therapeutic massage, you can get rid of clamps on nerve bundles, fight neuralgia, and remove stagnation of salts and toxins from the body. This procedure helps improve lymph flow and blood circulation. You must take at least one course every 6 months.
- Ozokerite. Helps reduce the severity of the inflammatory process, relieves pain and swelling, and removes toxins. After completing the course, the results last for several months.
- Acupuncture. Helps in rehabilitation after injury and surgery. Accelerates tissue regeneration and restoration of their integrity.
A mandatory step in the treatment of osteoporosis is a properly formulated diet. The body must receive the required amount of calcium and vitamin D. If it is not possible to meet the daily requirement of these elements, the doctor prescribes appropriate medications that contain these components. These multivitamins and calcium supplements will need to be taken over an extended period of time.
Therapeutic exercises should be prescribed by a doctor. In each specific case, an individual treatment regimen is selected. Therefore, it is not recommended to perform any exercises on your own. This can only be done after preliminary consultation with a doctor and work with a rehabilitation specialist.
Is it possible to independently restore damaged cartilage?
Chondrocytes are cells within cartilage that produce the necessary substances for its restoration. They have a high metabolic rate and regenerate quickly, but there is one problem. The composition of cartilage contains only 2-3% chondrocytes, so cartilage tissue does not completely recover on its own.
Damaged cartilage rubs against each other if there is not enough synovial fluid, causing pain to the person. For the treatment of arthrosis or osteoarthritis, taking chondroprotectors is not enough, since the destruction process occurs faster than recovery. Experienced orthopedists recommend intra-articular injections of the synovial fluid substitute Noltrex. The drug separates rubbing surfaces and acts as a shock absorber.
Noltrex does not restore cartilage, but it does stop its breakdown and relieve pain.
How to detect the disease
The main danger of the disease is that in the initial stages of its development there are no manifestations that prompt a person to consult a doctor. Most often, the diagnosis of osteoporosis is made after a person goes to the hospital with a fracture. Such damage occurs even with minor injuries, bruises and falls. The most common fractures are the hip, spine, forearms and shoulder.
Other signs of osteoporosis include:
- decreased growth;
- reduction in body weight, since after eating a person becomes full faster;
- there are signs of esophagitis-reflux, which is accompanied by attacks of heartburn, painful sensations in the chest;
- the stomach begins to protrude forward;
- systematic pain occurs in the back and hip joints, difficulties in movement appear;
- the spine begins to sag so that the lower ribs and hip joints come into contact.
Most often, the disease develops when the body’s production of certain types of hormonal substances decreases. But scientists have found that today this diagnosis is given even to teenagers; it is not associated with hormonal imbalances. The reasons for the development of the pathological process are the deterioration of metabolic processes, a sedentary lifestyle, and lack of quality nutrition. In women, this disease is diagnosed quite often.
Menu for strong bones
Let's summarize: what food products on our table contain the beneficial substances that we talked about here - calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, vitamins D and K?
Where can I get all the necessary vitamins and minerals?
Calcium
- Dairy products,
- Eggs,
- Spinach,
- Hard cheese,
- Sesame,
- Fresh greens,
- Nuts and seeds,
- Dried fruits.
Vitamin D
- Fish fat,
- Cod liver.
Magnesium
- Bran, oat flakes,
- Bananas,
- Legumes,
- Dried fruits,
- Cereals.
Phosphorus
- Milk,
- Eggs,
- Cheese,
- Nuts,
- Seafood,
- Legumes,
- Buckwheat,
- Yeast,
- Potato,
- Dried fruits,
- Seeds.
What food groups need to be consumed regularly so that the baby receives all the elements he needs in the right quantities, and are there additional factors, besides food, that affect his health?
Milk and dairy products
Milk contains large amounts of calcium. To satisfy the daily requirement for this element, it is recommended for an adult to consume 3 servings of dairy products. During pregnancy, this need increases by almost a third, so you can add one or two additional servings to the three main ones. Dairy products (kefir, sour cream, cheese, yogurt) also contain calcium. So we recommend introducing a variety of milk products into your diet.
You can give milk as a drink or prepare other dishes based on it (porridge, puddings, jelly, cocktails). If your baby has an allergic reaction to milk, seek advice from your pediatrician or allergist. They will tell you what you can replace this product with.
Fish
If your baby is not allergic, be sure to include fish puree in his diet (not earlier than 8 months). Fish is a complete source of protein and fat, containing a large amount of polyunsaturated fatty acids, including class 3, as well as vitamins B2, B12, and minerals. Fish is introduced into the diet of children from 8 to 9 months with caution, taking into account individual tolerance. It is given to the child 1 – 2 times a week instead of a meat dish.
Meat products
Meat contains complete animal protein, the amount of which in beef, lean pork, rabbit, chicken, chicken, turkey, and horse meat reaches 20–21%, as well as well-absorbed heme iron, magnesium, zinc, vitamins B1, B2, B6, B12. It is recommended to introduce meat puree into the diet of children older than 6 months.
Eggs
Egg yolk is an excellent source of vitamin D, and eggshells are rich in calcium. Proteins and vitamins are what makes this product valuable from the peel to the very core. The old advice from nutritionists was that you should eat eggs 2-3 times a week. Modern experts say that it is optimal for health to eat 6–7 eggs during the same time. If you are allergic to chicken egg whites, quail eggs are recommended; they contain a higher concentration of vitamins.
Vegetables and fruits
Vegetable puree contains organic acids, potassium, iron and dietary fiber, including pectins. Certain types of vegetables (carrots, pumpkin, spinach, etc.) are rich in carotene, a precursor of vitamin A. At the beginning of complementary feeding, puree should consist of vegetables of the same type with delicate fiber, such as zucchini or cauliflower. Next, it is advisable to use a combination of 3 - 4 vegetables. Juices contain natural sugars (glucose, fructose, sucrose), organic acids (malic, citric, etc.), which have a positive effect on digestive processes. Fruit purees are similar in composition and nutritional value to fruit juices , especially with pulp. At the same time, the percentage of sugars, organic acids and dietary fiber in them is higher than in juices.