Green-Vermilion method
It is based on a quantitative study of tartar and plaque. The hygienic condition is assessed according to the following scale:
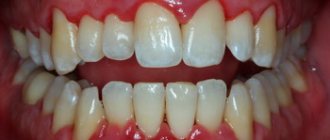
- 0 – no plaque;
- 1 – up to 1/3 of the surface of the visible part (crown) of the tooth is covered with plaque;
- 2 – plaque covers no more than 2/3 of the crown surface;
- 3 – more than 2/3 of the tooth crown is covered with plaque.
To detect plaque, the surface of the visible part of the tooth is painted with one of the special substances:
- 3-5 percent alcohol tincture of iodine;
- eosin;
- Lugol's solution.
In addition, a special tablet is used, which the patient must keep in the mouth for some time, after which the plaque turns pink. This method is often used at home for the patient to independently assess the amount of plaque. A specialist detects dental calculus without the use of dyes. The scale coincides with that for plaque.
The specialist gives a general assessment of the hygienic condition of the oral cavity based on the characteristics of the so-called “Ramfjord teeth”. The buccal surfaces of 6 specific teeth on the upper jaw and the lingual surfaces on the lower jaw are examined, since it is in these areas that the excretory ducts of the salivary glands are located.
In digital form, the level of oral hygiene is the result of dividing the sum of indicators in the area of all teeth by 6. If any of the examined teeth is removed, the specialist is limited to a smaller number or characterizes plaque on neighboring teeth of the same group (molars, premolars, incisors) .
The assessment method described above was improved by Quigley and Hein (1962). They replaced the 3-point score with a 5-point score, focusing special attention on a more detailed study of the amount of plaque in the range from 0 to 1 on the Green-Vermilion scale. Despite the fact that changes were made to more accurately assess the effect of various hygiene products, periodontists widely use the technique, since the amount of plaque in the area where the gums adjoin the tooth is of particular importance for the development of inflammation.
Up to contents
conclusions
The listed periodontal indices contain information about the hygienic situation in the oral cavity, the intensity of the spread of inflammation and the destructive process in the periodontium.
The examinations are simple to perform, do not cause pain to the person, and do not require the doctor to undergo special training.
They help to assess the general condition of periodontal tissues and formulate conclusions about the effectiveness of therapeutic and preventive measures.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags gums periodontal indices
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Silness-Lohe method
In periodontics, preference is often given to the Silness-Lohe technique, which is based on determining the amount of soft plaque in the gingival zone. The essence of the method is simple: the dentist runs the end of the probe along the neck of the tooth, capturing the gingival groove. If the instrument does not capture plaque at all, a score of 0 is given. If the amount of plaque is small - 1. If a thin layer of plaque is noticeable near the neck of the tooth, and a significant amount is retained on the probe - 2. If a large amount of plaque and food is visually determined in the area where the gum adjoins the tooth. residues - Z. The indicators of all teeth are added up, the result is divided by the number of teeth.
Up to contents
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional advice from a doctor. To make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, consult a qualified specialist.
The formula will help determine the condition of the mouth
To determine the condition of the oral cavity in medicine, there are about 80 different hygiene indices, based on the principle of staining the enamel with a special solution and identifying dental plaque.
According to the parameters they define, indices can be classified into 4 groups, assessing:
- area affected by plaque;
- thickness of plaque on teeth;
- mass of plaque;
- other parameters of dental plaque (chemical, physical and microbiological).
General overview
In dentistry, indices are a quantitative reflection of the progress of the pathological process that has developed in the periodontium.
When compared with clinical diagnostic methods, index assessment is considered relative, since it does not reflect the absolute accuracy of the ongoing process.
But periodontal indexing has some advantages that distinguish it from clinical diagnosis. With its help you can:
- measure the dynamics of tissue infection;
- monitor the spread and development of periodontal diseases;
- monitor the progress of treatment;
- evaluate its success and the results of preventive measures;
- perform epidemiological screening of the population;
- make comparisons of the results of different studies.
There are several dozen assessment indices for studying the condition of periodontium. All of them are divided into 3 groups:
- Reversible . With their help, the dynamics of diseases and the effectiveness of treatment are assessed. Reflect the severity of the inflammatory process, bleeding gums, loose teeth, the size of periodontal and gum pockets.
- Irreversible. They convey the manifestation of such signs as resorption (absorption) of bone tissue in the alveolar process, amyotrophy of the gums.
- Complex. They help to give a comprehensive description of the condition of periodontal tissues, taking into account the existing symptoms and the degree of development of pathological processes.
Iodine index of enamel remineralization.
The active permeability of iodine in tooth tissue is known. Remineralization index (RI), which characterizes the effectiveness of the remineralization therapy used. It is assessed using a four-point system:
1 point – no staining of the tooth area;
2 points - light yellow coloration of the tooth area;
3 points - light brown or yellow staining of the tooth area;
4 points - dark brown staining of the tooth area.
The calculation is carried out according to the formula:
IR = IRNP x number of teeth with hypersensitivity / n,
where IR is the remineralization index;
RRI—remineralization index of one non-carious lesion;
n is the number of teeth being examined.
Dark brown and light brown staining indicates demineralization of the tooth area with non-carious lesions; light yellow - indicates a certain level of remineralization processes in this area of the tooth, and the absence of staining or its slightly yellow color demonstrates a good level of the remineralization process of a particular non-carious tooth lesion.
CPITN (periodontal disease treatment need index)
This method covers 10 teeth, allowing the dentist to see the condition of the gums of the upper and lower jaws. Grades are given as follows:
- 0 – no disease symptoms;
- 1 – gums are bleeding;
- 2 – tartar was found above and below the gum;
- 3 – gum pocket 4-5 mm deep;
- 4 – gum pocket more than 6 mm.
It may come as a surprise to many that the condition of teeth can be determined using a formula, but this is the truth. Therefore, do not neglect maintaining oral hygiene, so as not to be a poor student in this calculation.
The iOrtho clinic network provides high-quality services for correcting malocclusion with Invisalign aligners, sign up for a consultation now!
Children's hygiene
What is the Fedorov-Volodkina index? It can be used to determine whether the patient takes good care of his teeth. This indicator should be used to assess the oral health of children under 5-6 years of age. To establish it, the labial edge of six teeth is studied.
Using special solutions, teeth are stained and the presence of plaque on them is assessed. Determination of sub- and supragingival calculus is carried out using a dental probe. The calculation of the coefficient consists of the numbers obtained for each of its elements, divided by the number of planes studied, followed by the addition of both values.
Php Index
Scientists Podszadlej and Haley developed an oral hygiene performance index. First, a dye solution is applied to the teeth, then the patient rinses his mouth with water, and 6 teeth are examined. In this case, their surface is divided into 5 sections: medial, distal, mid-occlusal, central, mid-cervical. The absence of staining is determined by zero, and the presence - by one.
When calculating, use the formula: IG = ZN/n, where ZN is the sum of codes for all teeth; n – number of teeth examined. With a value of 0, the condition of the oral cavity is considered excellent, and with a value of 1.7 or more, it is considered unsatisfactory.
RNR
Six teeth are coated with a dye that allows plaque to be found. To indicate the total number, you need to determine the number for each surface by summing the code values of individual areas. Then these values are added up and divided by how many teeth a person has in total.
- Oral candidiasis
RHP index
The bite is assessed by the dental aesthetic index. It characterizes the health of the bite, dental location in the sagittal, vertical and transversal directions.
Important! Assessment begins at age twelve.
An external examination using a button probe is used.
Button probe
An aesthetic assessment characterizes each component of the index and allows them to be arranged according to various pathologies of the rows of teeth and occlusion.
The score is expressed as a percentage. The number of people who were diagnosed with caries is divided by the total number of participants in the control group, and then the resulting number is multiplied by 100.
Cliche
The calculation formula is attached as follows:
IGR-u = sum of plaque values/number of planes + sum of stone values/number of surfaces.
The interpretation of the index (the IGR value at the level of medicine) is proposed as follows:
- 0.0-1.2 - flawless;
- 1.3-3.0 – acceptable;
- 3.1-6.0 – low.
The Green-Vermilion index has the following values for dental plaque standards:
- 0.0-0.6 – impeccable;
- 0.7-1.8 – tolerable;
- 1.9-3.0 – bad.
CPU in dentistry
Dentists should use these calculations during the initial examination of the patient. So, for example, the average values of the indices KPU, kp. KPU+KP of teeth and cavities in dentistry allows you to determine the intensity of carious lesions. These abbreviations contain the following meanings:
- K – carious permanent teeth;
- P – permanent teeth in which a filling is installed;
- U – extracted molars;
- j – temporary teeth affected by caries;
- p – filled temporary teeth.
- According to the World Health Organization, the average CP index for children 12 years old should be from 2.7 to 4.4, and for citizens aged 35-44 years 6.3-12.7.
Norm
The Fedorov-Volodkina index (1968) is still used in our country today.
First, the labial surface of the six front lower teeth is stained with a potassium-iodine-iodide solution. The hygienic index is determined by the intensity of the resulting color, then it is assessed using the five-point method and calculated using the formula Kcp=(∑Ku)/n, where:
- Ksr – general hygienic cleaning coefficient;
- Ku – healthy indicator of cleaning one tooth;
- n – number of teeth.
Coloring the entire plane of the crown means 5 points; 3/4 – 4; 1/2 – 3; 1/4 – 2 points; lack of color – 1. Normally, a healthy indicator should not exceed 1.
PMA – papillary-alveolar-marginal index
When calculating the PMA index, a solution of iodine or Lugol is used, which is applied to the gums and the degree of tissue inflammation is determined by the reaction to the irritant.
The evaluation criteria are:
- 1 – if the papilla (P) is inflamed;
- 2 – in case of inflammation of the marginal edge (M);
- 3 – inflammation of the alveolar part of the gum (A).
Formula RMA = Sum of points/n*3 (in percentage), where n is the number of teeth (up to 6 years – 20 teeth; 6–12 years – 24 teeth; 12-14 years – 28 teeth; over 15 years – 30 teeth) .
If the value is less than 30%, then the degree of damage is mild, 31-60% is moderate, 61% or more is severe.
Mouth rinse
Many patients ask: “What should I rinse my mouth with?” If your gums are inflamed, you can use antimicrobial (antiseptic) and anti-inflammatory agents. Antiseptic drugs act on pathogenic bacteria that cause suppuration. Anti-inflammatory drugs have virtually no effect on viruses, but they can slow down the development of the disease.
So what should you rinse your mouth with if your gums are inflamed? Doctors recommend:
- For periodontitis or gingivitis, use both types of products, although antimicrobial ones will be more effective.
- When the socket of an extracted tooth becomes inflamed, antiseptic agents, for example, Chlorhexidine, should be used.
If you always wash your hands before eating and brush your teeth and tongue afterward, you will have a sparkling smile for many years to come.