Everyone has at least once encountered the appearance of a wen on the body. They can come in different sizes and form on any part of the body. There are cases when wen and lumps spread throughout the body. What is the reason for this phenomenon?
Rice. 1. Fats and bumps all over the body can be a sign of hereditary lipomatosis
Hematoma
Description
If there is a swollen lump on the gum filled with blood, most likely it is a hematoma. This tumor occurs as a result of an incorrectly removed tooth or injury. Such a lump on the gum above the tooth, as a rule, does not hurt.
Treatment
Dissolves on its own. But if the lump hurts, consult your dentist for advice. The doctor will prescribe painkillers.
Could the lump be a herniated disc?
Lumps localized along the spine may well be a large intervertebral hernia or protrusion. These are protrusions and protrusions of the jelly-like core, which fills the intervertebral disc and is held in place by a fibrous membrane in the form of a ring. The pathogenetic factor in the formation of a hernia is dehydration and degeneration of the intervertebral disc, which develop against the background of impaired blood circulation, a sedentary lifestyle, chronic diseases of the spine and musculoskeletal system (osteochondrosis, osteosclerosis, osteoporosis, etc.).
Formation of intervertebral hernia
Clinically, the hernia may not manifest itself in any way for a long time, but if the size of the protrusion exceeds 5-7 mm, the patient begins to notice pronounced pain and neurological disorders. With large hernias, the clinical picture usually consists of the following symptoms:
- stiffness in the muscles and joints of the spine, which does not go away within 10-15 minutes and usually occurs after prolonged rest (usually after sleep);
- back pain that can radiate to the arm, shoulder, lower limbs and buttocks (radiculopathy, radicular syndrome, lumbago, lumboischialgia);
- paresis, paralysis, tics, tremors and other neurological disorders in the lumbar region and limbs;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs (fecal and urinary incontinence).
Herniated disc
If the hernia has formed in the upper back (cervical and thoracic spine), specific symptoms associated with compression of the basilar and vertebral arteries also appear: dizziness, migraine, headaches, arterial instability. Hernias in the thoracic spine can cause pain in the chest area (thoracalgia) as well as difficulty breathing.
Note! You can visually notice a hernia in the form of a protruding subcutaneous lump on the back in cases where its size exceeds 10-20 mm. Of great importance in the ability to identify a formation as a result of a visual and physical examination is the constitution of the body and the localization of the hernia: in slender patients, as well as patients with hernias and protrusions in the cervical spine, a volumetric protrusion on the back is detected almost 4 times more often than in obese patients.
Microsurgical treatment of intervertebral hernia
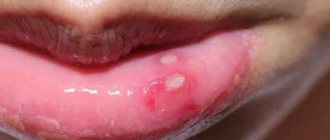
Epulis
Treatment
The lump on the root of the tooth is attached to a stalk and is either red or gum-colored. It affects the lower jaw and occurs as a result of malocclusion, permanent mechanical damage, and poor quality dentures. Often observed in women with hormonal imbalance.
Treatment
It is removed by one of three methods: scalpel, diathermocoagulation or cryodestruction. The manipulation is performed under local anesthesia.
Periodontitis
Description
A hard lump on the gum, an abscess formed at the base of the tooth root. In the absence of therapy, it transforms into a benign tumor.
Treatment
If such compaction of the gums under the tooth appears, contact your dentist. The teeth are unfilled and root canals are cleaned. After removing the exudate, oral baths with medicinal herbs or soda solution are prescribed. Treatment for periodontitis may require multiple visits to the doctor.
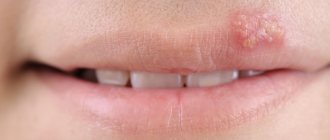
Bumps in the mouth of a non-infectious nature
If we talk about dental “growths” of non-infectious origin, then we need to mention:
- Epulis. Tumor-like formation of a productive nature. It appears due to the negative influence of local irritating factors. It is caused by injuries, incorrectly installed prosthetic structures, the habit of constantly gnawing hard objects, and malocclusion. Externally, epulis is very similar to tumors caused by gingivitis. To make a correct diagnosis, dentists take x-rays and conduct a histological examination. When treating pathology, the negative influence of the provoking factor is first eliminated. After this, the oral cavity is sanitized. In some cases, it is necessary to excise the neoplasm within healthy tissue along with the periosteum.
- Exostosis (osteophyte). A bone growth that causes the gum level to rise. Usually does not cause any discomfort. Appears after facial injuries or tooth extraction. Most often it is discovered by chance during a routine examination or during preparation for prosthetics. Therapy boils down to removing the bony protrusion and smoothing its surface.
- Hematoma. It looks like a ball filled with blood. Indicates that in a certain area the capillaries or vessels of the mucous membrane have been injured, but the damage is superficial. Hematomas appear due to chemical burns, thermal and mechanical injuries. It is important to differentiate such hemorrhages from hemangiomas and vascular tumors. The latter are very dangerous and require completely different treatment.
Flux (periostitis)
Description
An inflammatory process of bone tissue, which is accompanied by pain, elevated body temperature, enlarged lymph nodes, and swelling of the oral mucosa. The seals have purulent contents. The cause is an infection of the oral cavity resulting from untreated caries.
Treatment
A visit to the doctor is required to treat the lump. The dentist opens the tooth, places special medications in the cavity, and closes it with a temporary filling. If treatment does not bring positive results, the tooth is removed.
Fibroma
Description
Benign tumor of epithelial cells. Initially, the bumps on the gums above the tooth are small in size and do not hurt. However, mechanical stress and other negative factors can lead to the transformation of fibroma into a malignant tumor.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out surgically. The doctor excises the tumor, applies stitches, and prescribes rinses. Further follow-up visits may be required to monitor the recovery process.
Millums (millet)
This type of bump occurs with equal frequency on the upper and lower eyelids. Millet grains can range in size from a poppy seed to a grain of rice and usually form in groups. Millums are the most harmless of all formations and cause only aesthetic discomfort. At its core, these are whiteheads localized in the eyelid area.
Millet removal should only be done by a cosmetologist. Since they do not carry the risk of complications, they are not considered an ophthalmological disease, but fall within the competence of a dermatologist-cosmetologist.
Prevention of millums includes caring for the eyelids, timely removal of dead epidermal cells, ensuring the cleanliness of the ducts of the sebaceous glands and pores of the skin around the eyes, as well as a balanced diet that excludes excessive consumption of fatty foods.
Cyst
Description
A hard, bone-like compaction of gums under a tooth, up to 1 cm in diameter. Occurs in people with weakened immunity, genetic predisposition, as well as due to acute infectious diseases, mechanical damage to the soft tissue of the oral cavity.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out in the same way as for fibroma - by excision. After surgery, mouth rinses and baths are necessary, as well as repeated visits to the doctor to monitor recovery.
Rheumatic bumps
Painless bumps in the form of subcutaneous nodules can be a manifestation of erythema nodosum, characteristic not only of rheumatism, but also of some severe infectious diseases, for example, erysipelas or tick-borne borreliosis. Rheumatism is a connective tissue disease in which mainly the membranes of the heart become inflamed, as well as large joints, such as the joints of the legs, knees or hip joints. Rheumatism of the back is diagnosed quite rarely and accounts for no more than 8.4% of the total number of patients with this diagnosis.
Clinical signs of erythema nodosum
Cones with rheumatic inflammation of the spine are painless, have a dark red, purple or burgundy color and clear contours. The structure of the formations is dense, motionless (less often, inactive). The size of the nodules can range from a few millimeters to a chicken egg, and their occurrence is preceded by high fever and other symptoms, which may include:
- intense aching pain in the back (mainly in the area where the nodules are located);
- progressive curvature of the spine;
- numbness, trembling in the limbs;
- pale pink rash;
- minor hemorrhages against the background of increased pallor of the skin;
- increased sweating.
Nodules on the skin
The disease is caused by an infectious pathogen - group A β-hemolytic streptococcus - and often develops after illnesses of the oropharynx (sore throat, tonsillitis, scarlet fever, pharyngitis).
Gum cancer
Description
A rare dangerous disease. It is characterized by the formation of a dense lump on the gum at the root of the tooth; it can develop asymptomatically for several months.
Treatment
Requires serious medical intervention, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, long-term recovery and follow-up.
Gum cancer, if detected early, is curable, otherwise it ends in death. Red and white bumps on the gums appear in both adults and children. Only a doctor can correctly identify the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment. The sooner you see a dentist, the greater the chances of a quick recovery.
Don't self-medicate! If a ball is inflated on your gum and you don’t know what to do, contact a dentist in Odintsovo. The doctor will conduct a full examination of the oral cavity, accurately diagnose the disease, and prescribe effective treatment.
You can make an appointment for a consultation, as well as find out the cost of admission and treatment by calling the clinic in Odintsovo.
Lumps on the back due to injuries
Spinal injuries and bruises of paravertebral soft tissues (muscles, ligaments, tendons) are one of the most common causes of lumps and lumps on the back. Spinal injuries are divided into two groups: fractures and bruises. Dislocations and subluxations, as well as damage to joint capsules and ligaments without signs of vertebral displacement, can also be classified as a separate category. Provoking factors for spinal injury can be not only falls and blows, but also sudden lifting of heavy objects, various accidents, unsuccessful diving into water and other traumatic situations.
Signs of a spinal injury
The following signs indicate that a lump on the back appeared as a result of physical or mechanical impact:
- a history of any traumatic impact of external factors on a given area of the body (for some types of injuries, clinical manifestations may be noticeable only after several days or even months);
- pain in the area of the damaged segment (may intensify during any physical activity);
- swelling and redness of the tissues around the lump;
- the presence of hematomas, bruises and hemorrhages;
- muscle spasm.
Causes of spinal injuries
Neurological disorders (numbness, paralysis, tic, tremor, paresis) are typical for closed fractures with damage to the spinal cord, which is located in the central spinal canal, along the spinal tube. Pain during fractures has a very high intensity and often provokes the development of traumatic shock - a life-threatening condition that occurs against the background of heavy blood loss.
Immobilization for spinal contusion
What to do in case of injuries and bruises?
Even if a person is able to move independently and does not experience pain when moving, it is important to show the lump on the back to a traumatologist, since pain with some types of fractures has a reflected course and may appear only a few days after the injury. If a patient is diagnosed with a bruise, treatment will consist of applying cold compresses for 2-3 days (5-6 times a day for 10-15 minutes), as well as using local anti-inflammatory drugs that have angioprotective, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. Such drugs include ointments and gels from the NSAID group (Diclofenac, Nise, Ibuprofen), venotonic and venoprotective agents (Troxerutin, Troxevasin), complex preparations (for example, Dolonit gel with dimexide and sodium heparin in the composition).
Ointments for back bruises
Treatment for fractures includes surgical methods, immobilization of the spine (plaster splints, special beds), the use of corsets and fixing splints, drug therapy aimed at relieving pain and correcting the consequences of heavy blood loss.
"Troxevasin"