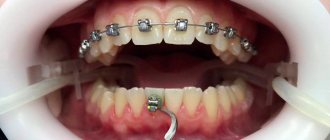
Often babies suck their fists, fingers, lower lip, and this should not cause concern if the baby is an infant.
But if a child is over a year old and continues to suck his lip, then this is already a bad habit.
Some mothers are seriously concerned about this problem and want to know how harmful it is, how to wean a child from sucking the lower lip, and is it worth doing it? Let's consider this issue in detail.
Kinds
There are several types of occlusion anomalies; in pediatric orthodontics, there are six.
The following types are distinguished:
- deep – it is characterized by excessive overlap of the upper jaw of the lower jaw;
- cross - with this violation of closure, there is underdevelopment of the jaws on one side, with a characteristic intersection of the lower and upper dental arches;
- mesial - it is typical for the lower jaw to move forward, with the lower incisors overlapping the upper ones;
- open - with this disorder there is no closure of the upper and lower incisors, the patient has a gap between them;
- distal - with this anomaly, the upper incisors move forward, this sign is combined with underdevelopment of the lower jaw and a reduction in the lower part of the face;
- underestimated - characterized by underestimated closure, due to premature abrasion of teeth.
Before starting correction, it is necessary to establish the type of occlusion violation.
Sniffles, grunts, coughs
From early childhood, children understand that during illness, parents forget about their important, adult affairs and devote all their time to the sick child. As children get older, they may deliberately blow their nose loudly, cough, or sigh while pressing their hand to their forehead. At the same time, the little pretenders feel good, they just want to attract the attention of their parents. Children want to be pitied, shown care, hugged and given warm milk. This happens, as a rule, in families where parents are busy with their own affairs and do not want to spend time with their children.
Sometimes boys and girls “get sick” so as not to go to kindergarten/school. There are a number of reasons why they behave this way.
- The child feels uncomfortable in a group or class. Perhaps he has problems with one of his students or classmates, as well as a conflict with the teacher. If there is no trusting relationship with the parents, the child cannot honestly admit why he does not want to go to an educational institution. It’s easier for him to feign illness and stay home.
- Parents make excessive demands. Even though children are full of energy and strength, they can also get tired. They also need rest. If mom and dad don’t understand this, they have to resort to tricks.
- The child lacks parental attention. Kids need their parents to spend time with them: reading, playing, sculpting, drawing. Sometimes children want to be at home with mom or dad, instead of going to kindergarten/school.
A sick child receives the necessary dose of love and warmth. If you suspect that your son or daughter is pretending to be sick, look into the situation instead of immediately scolding the child.
Ksenia, mother of 6-year-old Dasha:
“My daughter rarely gets sick; her ailments can be counted on one hand. But in the last year, I began to notice that Dasha began to cough, sneeze and sniffle in the evenings. At first I rushed with a thermometer, they even called the pediatrician several times, although there were no obvious causes of the cold. The doctor said that the girl was fine. We underwent a full examination at the medical center, but all tests and indicators were normal. I did not connect Dasha’s condition with the fact that we moved and my daughter went to a new kindergarten.
It turned out that no one played with her in the group, she didn’t find any new friends, so she didn’t want to go there. But she was afraid to admit it, because my husband and I work, and she didn’t want to upset us. I blame myself for not talking to Dasha frankly, for not finding out the reasons why my daughter was making up illnesses. We work a lot, but no work is worth forgetting about the problems of children. Now Dasha goes to a private kindergarten. She immediately made friends in the group, and now every morning her daughter runs to kindergarten with joy.”
Reasons for development
Why does a child develop malocclusion? The causes of its occurrence are divided into congenital and acquired.
Causes of congenital malocclusion:
- infections affecting the fetus;
- maternal diseases complicating the development of the fetus;
- maternal abdominal injuries;
- negative effects of poisons and drugs;
- trauma to the baby's facial bones during childbirth;
- congenital shortening of the frenulum of the tongue and lips.
Unlike congenital ones, acquired closure disorders are caused by diseases and bad habits.
These reasons include:
- pacifier abuse;
- the baby constantly sucks and chews objects (pencil, finger);
- bad habits (biting your lip, propping up your chin);
- lack of prosthetics, teeth falling out prematurely;
- Consequences of rickets before the age of one year;
- pathologies of ENT organs, with impaired nasal breathing (deformation of the nasal septum, enlarged adenoids);
- endocrinopathies;
- diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- pathological posture in sleep;
- extensive caries of molars;
- injuries to the facial part of the skull;
- malignant tumors of the facial bones;
- purulent-necrotic processes of the jaws (osteomyelitis, periostitis);
- early or delayed eruption of teeth.
Often the formation of closure defects is caused by several reasons. They need to be identified in order to determine the optimal tactics for correcting the defect.
Price
The tables show approximate prices in Moscow for the correction of underbite in children.
| Name of service | Price in rubles |
| Correction of occlusion anomalies with aligners | from 180000 |
| Orthodontic plate with bite pad | from 11000 |
| Correction using the Frenkel apparatus | from 70000 |
| Correction of the defect using surgical methods | from 200000 |
| Treatment using a trainer | from 11000 |
| Braces | from 63000 |
Timely correction of malocclusion in children is a significant undertaking. In adults, this feature is practically not corrected. It is important to treat this condition because it is not only an aesthetic anomaly. The patient develops dangerous conditions that threaten life.
How to suspect the development of a defect
How to identify malocclusion in a baby. Even a non-specialist can suspect the formation of this problem.
We list the most characteristic signs:
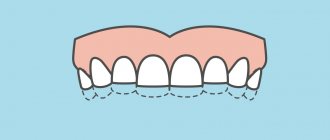
- uneven dental arches;
- crowding of teeth and their rotation around their axis;
- growth of units in the wrong place;
- gaps between teeth;
- presence of extra units;
- excessive overlap of the upper or lower jaw arches;
- no closure of incisors;
- facial asymmetry;
- moving one of the jaws forward;
- constantly open mouth;
- difficulty in nasal breathing;
- pathological abrasion of teeth;
- traces of injuries on the inner surface of the lips, tongue, cheeks;
- increased tone of facial muscles;
- difficulty chewing food;
- difficulty producing sounds.
Having discovered one or more of the listed signs in their baby, parents should take him to an orthodontist as soon as possible.
What is the pathology characterized by?
Deep bite is a type of disocclusion, which is characterized by excessive overlap of the upper teeth with the lower ones.
This type of violation has other names:
- deep incisal occlusion;
- declining;
- traumatic;
- deep incisal (frontal) overlap.
Occasionally, excessive overlap is detected on the side of the lateral teeth. It is believed that in infancy, up to 80% of babies have a similar disorder. In some of them, as they grow and develop, this anomaly disappears by the time the permanent bite is formed. The rest require orthodontic correction. The baby should be regularly shown to the dentist in order to identify the need for it in time.
At what age is it better to carry out correction?
At what age can you start correcting your bite in children?
It is impossible to determine malocclusion in a 1-year-old child. It is possible to suspect it if your parents have it. Malocclusion in a child from 2 years to 3 years of age can be corrected only with the help of preventive measures.
These include:
- breastfeeding up to one year;
- timely introduction of hard foods into the diet;
- use of orthodontic pacifiers;
- monitor the baby’s posture during sleep;
- promptly treat caries of primary teeth;
- if they are lost early, prosthetics are necessary.
The baby needs to be treated for somatic diseases that can disrupt the development of the dental system.
At what age is the bite corrected in children? Active correction begins in the age range from 3 to 5 years.
The following activities are carried out:
- stopping bad habits;
- use of vestibular shields;
- facial myogymnastics;
- In case of early tooth loss, prosthetics are performed.
At the age of five, plastic surgery of the short frenulum of the tongue and lips is performed.
At the age of 7 years and older until adolescence, correction is carried out with various devices for removable correction.
These include:
- orthodontic plate devices;
- trainers;
- mouth guards;
- extraoral devices.
Starting from adolescence of 12–13 years, the defect is corrected using various models of brace systems.
In adolescents over the age of 16, veneers and crowns are used to correct minor cosmetic defects in the smile area.
How to correct a child’s bite and what correction methods to use is decided only by the orthodontist.
Why does a child suck his lip?
Before you figure out why the child began to suck his lower lip, it is worth considering the main reasons for this phenomenon.
- Often the baby has a need to suck something if he is hungry. Many parents have noted that some time before feeding, the baby begins to pull his fingers into his mouth or suck his lip. This is a normal process for infants, he just wanted to eat before the time allotted for feeding came. It is often for this reason that pediatricians recommend feeding newborns on demand.
- If the baby is breastfed, the mother has thin milk, and he does not get enough, so you need to put the newborn to the breast at the first call. You should also give your baby only one breast during feeding. If you give your baby only foremilk, satiety will occur faster, but the feeling of hunger will come in a short time.
- The reason may also be simple satisfaction of the sucking reflex, which is natural in infancy. The habit of sucking the lower lip occurs more often in artificially born children. When feeding a baby from a bottle, the feeling of fullness comes very quickly, which cannot be said about breastfeeding. The sucking reflex thus remains unsatisfied.
- Also, the reason for sucking the lower lip may be a lack of feeling of security. If during the suction process the child becomes calmer and falls asleep, then he simply lacks his mother’s protection. This is usually observed if the child is picked up only when needed: to change, feed, bathe, and the rest of the time he lies alone in the crib.
- If drooling occurs when sucking on a lip or fist, then the child may be teething , causing biting and severe anxiety. The baby is capricious and behaves nervously.
If you feed your baby from a nipple and at the same time notice that he is sucking his fist or lower lip, then this is the first and most striking sign that the reflex is not satisfied.
Defect correction
Correction is carried out using conservative and surgical methods.
Conservative therapy
For hardware correction, removable and non-removable correction devices are used.
These include the following devices:
For correction use:
- vestibular shields - used to wean the baby from sucking fingers and other objects;
- Trainers are used to correct minor anomalies and align the positions of individual units in the dental arch;
- correction plates are plates made of plastic and metal, used to correct anomalies during tooth replacement, they are self-regulating devices;
- aligners are silicone molds made of silicone that give a physiological bend to the dental arch.
- braces are a non-removable orthodontic structure for correcting the most complex dental defects and anomalies;
- extraoral devices – used to correct severe anomalies when braces cannot be installed.
Devices for correcting malocclusion and the position of individual teeth are selected based on the severity of the defect and age. Is it possible to correct the bite using only conservative methods? In most cases, the use of these devices is sufficient.
Surgical treatment
I use surgical techniques only in the most difficult situations, when the use of conservative methods has not eliminated the defect. They are used only in adolescence and in adults only in cases of serious deformities of the facial skeleton.
Indications for this are:
- gross facial asymmetry;
- gross anomalies of occlusion;
- underdevelopment of the chin.
After the operation, long-term rehabilitation is carried out for at least five months.
Diagnostics
The dentist carefully examines the patient's face and oral cavity. He examines the size, shape of the upper and lower jaw, the relationship of the dentition. The doctor studies the patient's complaints in detail.
The following additional diagnostic methods are used:
- teleradiography with subsequent analysis;
- orthopantomography;
- study of front and profile photographs;
- produce diagnostic models of the jaw and study;
- occludogram study;
- tomography of the maxillary joint;
- rheography;
- electromyography of the face.
Treatment of a deep bite in a child requires a careful examination of the facial skeleton.
Complications
If anomalies are not corrected, then not only the baby’s appearance suffers. The consequences of impaired occlusion are numerous somatic pathologies.
What does the anomaly affect:
- diseases of the digestive tract develop;
- widespread caries;
- formation of dental plaque;
- inflammatory processes in the oral cavity;
- poor posture;
- respiratory disorders;
- disruption of the process of chewing food;
- previous tooth loss.
The baby develops articulation disorders, and the pronunciation of sounds suffers.
Classification
There are several degrees of pathology; the classification is based on the degree of overlap of the lower incisors with the upper ones.
The following degrees of defect are distinguished:
- deep (incisal) overlap - a defect in which the edge of the lower tooth reaches the palatal tubercle of the upper one;
- reducing bite - it is characterized by the fact that the incisors of the lower jaw do not rest on the dental cusps of the upper teeth, they slide to the edge of the opposite gum;
- traumatic disocclusion - in which the edges of the lower incisors rest against the upper palate or gum.
This process means a gradual deterioration of the condition. If nothing is done, the pathology steadily progresses and moves to the next stage.
Prevention
Prevention of disorders begins as early as a one-year-old child. It is necessary to ensure that the baby does not suck a finger or other foreign objects so that proper closure is formed. Only orthodontic pacifiers should be used.
For an older child, preventive measures include:
- treatment of carious lesions;
- prosthetics of teeth lost prematurely;
- prevention of the development of rickets.
It is necessary to take your child for examination to an orthodontist in a timely manner in order to promptly identify closure disorders and resolve the issue of correcting it.
Violation of occlusion is a defect that threatens not only cosmetic defects, but also the development of a large number of serious diseases. Parents should, if they have the slightest suspicion of the development of this anomaly, take their child for examination to an orthodontist.
Is lip sucking a bad habit?
If an older child begins to suck his lower lip, then this is not just a bad habit, but the result of the discomfort that he feels.
A situation that traumatizes the psyche forces the fragile body to look for means of calm and protection to relieve negative experiences.
The child should not be scolded, shamed or reproached.
It was his body that chose such protection for itself. Blame in this case can only make things worse.
But you cannot let the situation take its course, since over time you may encounter more serious problems: poor academic performance, lack of communication, the child will completely withdraw into himself.
You should observe the child, talk to him more often, and contact a child psychologist who will help understand the child’s condition.