Why does the body need iron?
Men and women have different iron reserves. The discrepancy is due not only to different masses of bodies. Women regularly lose blood during menstruation, and along with it, a much-needed microelement goes away. A sufficient amount of iron is a prerequisite for erythropoiesis - the process of formation of red blood cells (erythrocytes). They contain the protein hemoglobin, which is responsible for transporting oxygen to all cells of the body.
Hemoglobin accounts for about ¾ of the total supply of ferrum in the body. The remaining ¼ is distributed between: • ferritin (the protein that accumulates it); • transferrin (iron transport protein); • tissue enzymes; • myoglobin (oxygen-binding protein of the heart muscle); • hemosiderin (a breakdown product of hemoglobin). Its deficiency disrupts metabolic processes and reduces the protective capabilities of the immune system. The endocrine system also suffers, since enzymes containing iron are needed to produce thyroid hormones.
Reasons for the formation of white plaque on the lips in adults
The causes of symptoms are divided into 2 groups:
- pathological;
- non-pathological.
Non-pathological include:
- improper oral hygiene;
- poor nutrition (eating unhealthy foods, lack of essential nutrients, etc.);
- wearing dentures;
- bad habits: addiction to smoking or alcohol;
- constant stress, depression;
- taking certain medications.
Among the pathological causes (diseases) of the appearance of a characteristic white coating on the lips in adults, the following are distinguished:
- infections;
- AIDS virus;
- tonsillitis;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- scarlet fever;
- lichen planus;
- respiratory tract diseases;
- liver diseases;
- thrush.
White plaque is a symptom of disease
This is interesting! If a film or whitish coating appears on the lips, it is not necessary that this is the cause of some pathological process in the body.
It is necessary to analyze the patient’s condition as a whole and find out if there are any other accompanying symptoms. If they are present, you should urgently visit a doctor to avoid serious health problems.
White plaque in the corners of the lips
A common disease is candidiasis (thrush). This is a fungal pathology caused by the Candida fungus. Diagnosed if additional symptoms are present:
- presence of microcracks;
- white plaque in the corners of the lips and cracks;
- the formation of small wounds or ulcers;
- cracks until they bleed;
- itching
At the same time, a person’s physical condition deteriorates: irritability, aggression appear, appetite decreases, he becomes lethargic, and quickly gets tired.
Note! The presence of a white coating often indicates that there is a bacterial infection. If therapy is not started in a timely manner, the risk of serious complications increases, such as laryngeal thrush, the growth of small wounds into large enough erosions that are no longer so easy to cure.
If you begin to notice that white plaque begins to appear in the corners of your lips from time to time, be sure to visit a medical facility. The doctor will prescribe an appropriate medical examination, and after identifying the pathogen and accurately diagnosing the disease, prescribe the necessary complex therapy.
Plaque on lips in the morning
The most common reason for the appearance of a characteristic film after sleep is saliva spontaneously flowing from the oral cavity, which dries out and forms whitish spots on the lips.
But there is also a more insidious reason - candidal stomatitis. Fungi of the Candida class are also responsible for the manifestation of this disease. They are present in the body of absolutely every person, but they begin to multiply and cause harm only when the immune system is weakened.
White plaque with this disease forms both in the lips and in the entire oral cavity. If you let the disease take its course, it will very quickly begin to progress, causing the patient a lot of inconvenience, accompanied by painful sensations.
Pathology can only be overcome with comprehensive treatment. Therapy must necessarily include taking vitamins, as well as immunomodulatory and antifungal pharmacological agents.
White plaque on the lips in men
It is generally accepted that the problem in question worries mostly the female half, but men are no less likely to exhibit this symptom. The reasons why the stronger sex may develop white plaque on their lips are the same as described above.
However, the most common of them is the presence of bad habits. A dense white film is the least of what can cause regular smoking.
Photo 2: Inhaling toxic smoke or steam from a hookah can cause serious diseases of both the mouth and lips, and the respiratory system. Source: flickr (Eugene Li).
Causes of iron deficiency
Two common reasons for ferrum shortages are insufficient supply and increased demand.
In the first case, we are talking about malnutrition, in the second, deficiency can be caused by : • active growth; • pregnancy (fetal needs); • impaired absorption; • blood loss (menstrual or internal intestinal); • taking medications for the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases (antacids, proton pump inhibitors, H2 blockers).
The most unobvious cause of Fe deficiency is intense exercise. Although physical activity is beneficial for the body, it also increases its need for microelements. The more calories burned, the more iron required for erythropoiesis.
Diet-related reasons
A person receives two varieties of this chemical element with food. Heme (divalent) is found in products of animal origin, primarily in meat. It is this that predominantly becomes a component of hemoglobin, since it is better absorbed in the intestine. The non-heme type (trivalent) is obtained from plant foods. It is more difficult to absorb because it must first be broken down to divalent.
Moreover, some substances weaken the absorption of Fe3+: • tannins contained in tea; • antibiotics; • bran; • vegetable phytofibres.
Only vitamin C can increase the intensity of absorption of non-heme iron. The daily requirement of men for this element is at least 10 g, for women - at least 20 g. Against the background of eating disorders or a vegetarian lifestyle, a person develops a persistent lack of iron.
Definition of disease
Iron deficiency in the body leads to a disease - iron deficiency anemia. This is one of the forms of anemia, which is associated with impaired production of red blood cells.
Among similar conditions, it has the following differences : • According to the color indicator of the blood, it is hypochromic. This means a small amount (less than 0.86 picograms per unit) of hemoglobin in the red blood cell. Other anemias are usually either normochromic (0.86-1.1 pg/unit) or hyperchromic (more than 1.1 pg/unit). • From the point of view of the development mechanism, it belongs to the group of anemias caused by a lack of microelements. In the same category are pernicious (due to a lack of vitamin B12) and folate deficiency anemia. • According to the bone marrow's ability to regenerate, it is hyporegenerative. In this condition, young red blood cells are present in the peripheral blood, but there are very few of them (less than 0.5%). A similar phenomenon is observed in pernicious anemia.
Iron deficiency anemia is often called a disease of pregnancy. Fe is an important factor in the formation of the placenta, and subsequently ensures the supply of oxygen to the fetus. Therefore, the woman actually receives less of it.
Hypersalivation in adults: causes
In adults, hypersalivation can be true or false. When false, people think that they have high salivation, but in fact the problem is a violation of the swallowing function. Usually false is called increased salivation during pregnancy, when a woman is bothered by nausea, heartburn and other manifestations of toxicosis, as well as in smokers - their high salivation serves as protection for the mucous membrane from hot smoke, tar and nicotine. The phenomenon disappears after the cause is eliminated (a woman gives birth to a child, a smoker quits smoking).
True hypersalivation in adults has more significant reasons:
- Acute inflammatory processes in the oral cavity - for example, stomatitis, periodontitis, etc.
- Inflammatory or tumor diseases of the salivary glands, including those caused by trauma.
- Pathologies of the digestive system.
- Some nervous diseases.
- Bacterial or viral infections.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Helminthiases (helminthic infestations).
- Poisoning – food and non-food (for example, mercury vapor).
- A side effect when taking certain medications (for example, certain ophthalmic, anticonvulsant, and lithium medications).
However, most often, increased salivation still indicates infectious and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity and requires elimination of the underlying disease - for example, treatment of gums or other soft tissues, treatment of inflammation of the salivary glands.
Symptoms of iron deficiency
The first symptoms appear at the stage when the microelement is no longer sufficient, but this has not yet affected the hemoglobin level. The general condition of a person worsens. He gets tired quickly, is constantly cold, experiences shortness of breath when exerting himself, his skin turns pale, peels, and his hair begins to fall out.
More specific symptoms indicate the development of iron deficiency anemia: • Koilonychia. The nail plates take on a concave shape. • Restless legs syndrome. There is a pathological need to move the limbs at rest. • Pica. Food perversions, craving for inedible things. • Glossitis. Inflammation of the tongue, accompanied by burning or pain. • Cheilitis. Inflammation of the red border of the lips with cracks in the corners of the mouth.
If iron levels drop to critical levels, swallowing problems and loss of consciousness may occur. In children, due to a lack of Fe, development slows down.
How to replenish iron deficiency in the body?
There is no cure for iron deficiency anemia as such. If a blood test shows a deficiency of this important microelement, it is necessary to replenish it. Then the symptoms of the disease will disappear.
To overcome Fe deficiency, the following are usually prescribed: • A therapeutic diet. The diet must include meat, offal (tongue, liver), and seafood. • Oral iron supplements. Usually presented in the form of salts (sulfates, fumarates, gluconates). • Injections. Recommended in extreme cases (if oral medications are ineffective or there is large blood loss) due to the risk of complications.
The standard course of treatment is at least six months. In the first two months, the disease itself is eliminated, and in the remaining time the level of the microelement is normalized. Usually, a course of vitamin C is prescribed in parallel. It improves the absorption of ferrum and, accordingly, increases the effectiveness of therapy.
Homeopathic treatment for white plaque on lips
Attention! Homeopathy remedies should be taken only when the characteristics of the medicine match the symptoms of the pathology to the maximum extent possible.
For the treatment of diseases accompanied by symptoms such as whitish plaque on the surface of the lips, the following homeopathic remedies are recommended:
- Borax – heals erosions due to stomatitis. Symptoms: excessive salivation, incorrect perception of taste, presence of bitterness in the mouth. It helps very well if stomatitis progresses inside the oral cavity;
- Kalium bichromicum - used in the presence of plaque on the lips, as well as in the oral cavity. The drug is especially effective against deep erosions on the inside of the lips and cheeks. The patient may feel dry mouth;
- Kalium muriaticum - quickly heals wounds with stomatitis, eliminates thrush in the mouth and on the lips. There may be foul breath, enlarged lymph nodes;
- Arsenicum - effective for small red canker sores that cause severe pain, which subsides after the patient drinks a warm drink;
- Antimonium crudum – prescribed for dry lips and milky plaque;
- Mercurius solubilis - prescribed for complicated forms of stomatitis, as well as for bleeding gums. The aphthae are large and saliva flows heavily.
To strengthen the immune system, complex homeopathic medicines such as Engystol, Galium-Heel, Edas-308, Echinacea compositum, Mucosa compositum are .
Prevention of iron deficiency anemia
This is important for adults and children, men and women. If you keep your health under control, iron deficiency can be prevented. It is necessary: • Eat well. Giving up meat cannot be beneficial for the body, unless we are talking about allergies. But even in this case, you can choose relatively safe varieties (rabbit or lamb). • Have medical examinations annually. They will help to identify hidden pathologies that cause blood loss (vascular ectasia, gastric ulcer, hemorrhoids). • Women should receive timely treatment for gynecological diseases. Heavy menstruation is not normal. Their volume is no less important than frequency and painlessness. • Take vitamin and mineral complexes. They are especially recommended for children, pregnant women and athletes.
A biochemical blood test performed once a year allows you to monitor the level of Fe in the body and take timely measures. At the latent stage, it is easier to solve the problem. The more advanced the disease, the higher the risk of complications.
Candidiasis as a superinfection in cancer patients: clinical picture and treatment
IN
Currently, in cancer patients there is a significant prevalence of fungal infections caused by opportunistic fungi, which include candidiasis.
Mycosis is caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida
, widespread in nature.
They can be found in the air, soil, water, on household items, food, as well as on the mucous membrane of the digestive tract, genitals and skin in humans. More than 10 species of yeast-like fungi are considered pathogenic, of which the main one is Candida albicans
, although in recent years there has been a steady increase in other species of
Candida
, called
Candida non-albicans (Candida krusei, Candida tropicalis, Candida parapsilosis)
, other yeast-like fungi (
Mucor, Fusarium spp
., etc.).
Candidiasis is an opportunistic mycosis that is widespread among fungal infections. The incidence of candidiasis over the past 15–20 years has reached 17% in the overall structure of purulent-inflammatory diseases
.
The causative agents of candidiasis are isolated on average from every third person from the intestines, genitals, and bronchial secretions. Primary colonization of the body occurs in the birth canal, and after birth - through contact and nutrition. Infection of a child can occur due to candidiasis of the mother's nipples, from service personnel, through household items, etc. There have been outbreaks of candidiasis in newborns in maternity hospitals. A sexual route of infection is possible, and in the transmission of infection from woman to man, the frequency and severity of infection, the depth of penetration of fungi into the tissue of the urethra, trophic changes in its mucous membrane due to past inflammatory diseases, as well as the general condition of the body are important. In the epidemiology of genital candidiasis in men, the main route of transmission is considered to be sexual transmission.
The main factor in the development of candidiasis is the background condition
or diseases of the body in which opportunistic pathogens acquire pathogenic properties. These include: paraneoplastic processes, primary and secondary immunodeficiency states, autoimmune processes, diseases associated with environmental disturbances, etc. The widespread use of drugs with immunosuppressive activity - glucocorticosteroids and cytostatics - plays a certain role in the development of candidiasis. The increase in morbidity is facilitated by the frequent and not always justified prescription of broad-spectrum antibiotics, including for prophylactic purposes. In recent years, many researchers have come to the conclusion that the main predisposing factor for the occurrence of superficial forms of candidiasis, including in cancer patients, is mainly impaired cellular immunity.
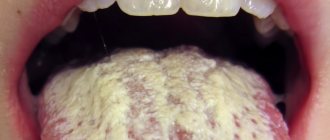
One of the most common localizations of fungal superinfection is the oral cavity (oropharyngeal candidiasis, oral thrush).
Oropharyngeal candidiasis
occurs in approximately 30% of cancer patients after chemotherapy and in more than 90% of patients with AIDS, and is characterized by damage to the mucous membrane of the cheeks, palate, pharynx, tongue, gums, and corners of the mouth.
The disease begins with hyperemia of the mucous membrane, later single or multiple pinpoint plaques of white color appear, often of a cheesy nature, they can merge to form larger lesions. Plaques, when scraped, are easily separated, when they exist for a long time (more than 3 months) they become dense, and when rejected, erosions and erosive surfaces are observed. In the chronic course, on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, along with the usual plaques, areas of keratinization of a grayish-white color, flat, reminiscent of leukoplakia, form. Cracks appear in the corners of the mouth with maceration of the stratum corneum of the epidermis. Subjectively, patients are bothered by burning and pain when eating. Less common is vulvovaginal candidiasis
.
The disease can occur in acute and chronic form. The acute form of candidiasis is characterized by hyperemia of the genital mucosa, swelling, and the presence of small blisters, when opened, small erosions are formed with layers of cheesy or delicate white deposits. In the chronic form, the mucous membrane of the vestibule and vagina is congestively hyperemic, swollen, infiltrated, and there are deposits of a cheesy nature in the form of individual foci or a continuous surface. In the area of the vestibule and perineum, erosions and bleeding cracks are sometimes observed, and less commonly, phenomena of atrophy of the mucous membrane are observed. In acute and chronic forms of vulvovaginitis, discharge of a cheesy or creamy consistency is noted. Subjectively, patients are bothered by itching, which intensifies during menstruation, as well as in the afternoon after a long walk. A burning sensation in the scratching area when urinating can lead to urinary retention. Balanoposthitis
is characterized by hyperemia and swelling of the glans penis and inner sheet of the foreskin, vesicles, when opened, point erosions are formed, and a grayish-white coating in the form of small islands or larger ones.
When plaque is removed, an eroded surface is revealed. The lesions have clear boundaries, around them small, pinhead-sized erosions (screenings) are visible. Patients are concerned about itching and a burning sensation in the area of the head of the penis. Superficial cutaneous candidiasis
occurs in 5–6% of cancer patients . Its main localization is large (inguinal-femoral, intergluteal, under the mammary glands, axillary cavities) and small (interdigital) folds, but rashes can occur on the smooth skin of the trunk and extremities, including the palms and soles. In cancer patients, the lesions may be outside the folds. Small bubbles the size of millet grains appear, and sometimes pustules, which open to form erosions. Due to peripheral growth, erosions quickly increase in size and merge, forming large areas of damage. The lesions are dark red in color with a burgundy tint, shiny, with a moist surface, irregular in shape, with a strip of exfoliating epidermis along the periphery. Fresh small erosions (screenings) form around large foci. Candidiasis of smooth skin outside the folds (chest, abdomen, shoulders, forearms, legs, etc.) has a clinical picture similar to lesions in the area of large folds. But sometimes in adults the disease can appear in the form of erythematous spots with peeling in the center and small blisters along the periphery. Candidiasis of smooth skin of small folds (interdigital erosion) most often occurs between the 3rd and 4th, 4th and 5th fingers of the hands, less often of the feet, and is characterized by the formation of eroded foci of a rich red color with a smooth, shiny, as if varnished surface, clear boundaries, with peeling of the stratum corneum of the epidermis along the periphery. The disease can begin with the appearance of small blisters on the lateral touching hyperemic surfaces of the skin, then spreads to the area of the interdigital fold, swelling, maceration, and peeling appear. Interdigital candidal erosion is observed mainly in individuals who have prolonged contact with water, which contributes to the development of skin maceration; in addition, favorable conditions are created for the development of candidal infection. In addition to the third and fourth interdigital folds, others can be affected, not only on one, but also on both hands. Patients are concerned about itching, burning, and if there are cracks, pain. The course of the disease is chronic, with frequent relapses.
The patient has AIDS. The palate and uvula are covered with a rich cheesy coating, which is easily removed with a gauze swab. White plaques are colonies of Candida albicans, red spots on the mucosa are foci of atrophic candidiasis
Redness and cracks in the corners of the mouth in an HIV-infected person.
In addition to the lips, candidiasis affects the oral cavity and pharynx. Candidiasis of the palms and soles is rare
.
On the palms, the disease can occur as dry lamellar dyshidrosis (superficial lamellar, ring-shaped or garland-shaped peeling); vesicular-pustular form (vesicles and pustules against the background of hyperemic and edematous skin); according to the type of hyperkeratotic eczema (against the background of diffuse hyperkeratosis or individual areas of keratinized skin, sharply limited wide skin furrows with a dirty brown color are observed). Candidiasis of the skin of the soles is observed mainly in children and is characterized by the presence of small blisters and pustules, hyperemic spots with peeling and exfoliating macerated epidermis along the periphery. Candidiasis of the nail folds and nails
(candidal paronychia and onychia). The disease begins from the posterior ridge, most often in the area of its transition to the lateral ridge, with the appearance of hyperemia, swelling and swelling of the skin. Then the inflammatory phenomena spread to the entire roller, which becomes thicker and seems to hang over the nail, and peeling is observed along the edge of the roller. The skin of the roller becomes thin, shiny, and the nail skin (eponychion) disappears. When the roller is pressed, ichor, a lump of white crumbly mass, or a drop of pus may be released (due to the addition of a secondary infection). Later, the nail plate changes: it becomes dull, in the area of the lunula it is separated from the bed, destroyed as onycholysis, or transverse grooves and elevations appear. These changes are associated with impaired blood supply in the matrix area, i.e. trophic in nature, and with inflammation of the cushion. When the fungus penetrates the nail plate, and this happens from the lateral edges, the nails become thinner, separate from the bed, acquire a yellow-brown color and look as if they are trimmed on the sides. In young children, inflammatory phenomena in the area of the cushion are more pronounced, and the nail plate changes from the distal edge. Candida infection of the nails without inflammation of the ridge is rare.
Since the mid-80s, fluconazole (Mikosist)
– azole compound (capsules of 50, 100, 150 mg and solution for infusion: 1 bottle – 200 mg), which is a derivative of bistriazole.
The mechanism of action of the drug is due to inhibition of the synthesis of ergosterol, which is part of the cell membrane of fungi. Mikosist has a highly specific effect on fungal enzymes dependent on cytochrome P450. in vitro
activity of this drug against
C. albicans
is high.
Thus, among the strains isolated from oncohematological patients, only 3.2% of C. albicans
were resistant to fluconazole and 2.4% of strains had intermediate sensitivity.
Among C. non-albicans,
C. krusei
is resistant to fluconazole .
Resistance to the drug is demonstrated by individual strains of C. glabrata
.
The drug is poorly metabolized by the liver and is excreted by the kidneys mainly unchanged. The advantage of Mikosist, in addition to high efficiency, is the absence of hepatotoxicity and good tolerability. Fluconazole is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. After oral administration, more than 90% of the drug enters the systemic circulation. 60–75% of the drug unchanged is excreted in the urine, 8–10% in feces. 11% of fluconazole is bound to plasma proteins. The drug penetrates well into saliva, sputum, urine and other tissue fluids. The concentration of the drug in the cerebrospinal fluid is 70% of the level in the blood serum.
The half-life of the drug with normal renal function of the patient is 27–34 hours. In case of renal failure, the doses are reduced, but the first dose is usually 2 times higher than the subsequent ones and is a loading dose.
The daily dose of fluconazole (Mikosysta) depends on the nature and severity of the mycotic infection.
Treatment must be continued until clinical and laboratory remission is achieved. For the oropharyngeal form of candidiasis, it is prescribed to adults at a dose of 50–100 mg 1 time per day daily, and on the first day a double dose is used; the course of treatment in cancer patients is 7–14 days. For vaginal candidiasis, Mikosist is prescribed as a single dose of 150 mg. For frequent relapses of chronic vaginal candidiasis, the drug is prescribed in a dose of 150 mg once a month for 4–12 months. For candidiasis of smooth skin – 150 mg once a week. The course of treatment is 2–4 weeks. Literature:
1. Klyasova G.A. Mycotic infections: clinical picture, diagnosis, treatment. – Infections and antimicrobial therapy, 2000, vol. 2., N6, p. 184–189.
2. Richardson M.D., Cocchi M. Guidelines for the treatment of systemic mycoses, 1999, 64.p.
3. Sergeev A.Yu., Sergeev Yu.V. Candidiasis. Nature of infection, mechanisms of aggression and defense, laboratory diagnostics, clinical picture and treatment. – Moscow, 2000, 472 p.
4. Ally R., Schurmann D., Kreisel W. et al. A randomized, Double–Blind, Double–Dummy, Multicenter Trial of Voriconazole and Fluconazole in the Treatment of Esophageal Candidiasis in Immunocompromised Patients. – Clin Infect Dis, 2001; 33; 1447–54.
5. Bodey GP Disseminated candidiasis in neutropenic patients. – Int J Inf Dis, 1997, 1 (Suppl 1), S.2–5.
6. British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Working Party. Management of deep Candida infection in surgical and intensive care unit. – Intensive Care Med, 1994; 20; 522–528.
7. Eggimann P., Francioli P., Bille J. et al. Fluconazole prophylaxis prevents intra-abdominal candidiasis in high-risk surgical patients. – Crit Care Med, 1999; 27; 1066–1072.
8. Marr KA Seidel K., Slavin MA et al. Prololnged fluconazole prophylaxis is associated with persistent protection against candidiasis–related death in allogeneic marrow transplant recipients: long–term follow–up of randomized, placebo–controlled trial. – Blood, 2000; 96; 2055–2061.
9. Pelz RK Lipsett PA, Swoboda S. et al. Candida Infections: Outcome and Attributable ICU Costs in Critically Ill Patients. – J Intensive Care Med 2000; 15; 255–261.
10. Vincent J.–L., Anaissie E., Bruining H. et al. Epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment of systemic Candida infection in surgical patients under intensive care. – Intensive Care Med, 1998; 24; 206–216.
11. 14. Walsh TJ Global expamsion of nosocomial candidiasis. – Int J Inf Dis, 1997, 1 (Suppl 1), S.1.
12. 15. Warnock DW Fungal infections in neutropenia: current problems and chemotherapeutic control. – JAC, 1998, V.41 (Suppl.D), 95–105.
13. 16. Winston DJ, Hathorn JW, Schuster MG et al. A Multicenter, Randomized Trial of Fluconazole versus Amphotericin B for Empiric Antifungal Therapy of Febrile Neutropenic Patients with Cancer. – Am J Med, 2000; 108; 282–289.
Complications of iron deficiency anemia
They don't appear right away. It often takes several years since iron levels dropped below normal. Immune disorders occur first: a person becomes more susceptible to viruses and bacteria. Chronic deficiency of ferrum aggravates the course of : • bronchial asthma; • coronary heart disease; • chronic cerebral ischemia; • diabetes mellitus; • Parkinson's disease. Due to constant oxygen starvation, the nervous system suffers. The person becomes emotionally unstable, absent-minded, and his memory deteriorates. Patients with Alzheimer's disease often have a history of iron deficiency anemia. The threat of emergency conditions also increases. More often it is a heart attack or stroke. In some cases, the patient falls into a hypoxic coma.