How inflammation begins
All about dental health
How to maintain beautiful healthy teeth? We tell you in detail: - how to brush your teeth correctly, - how to choose a toothbrush, - how to choose other devices for cleaning your teeth, - how to choose toothpaste, - how to preserve tooth enamel, - how to care for your first teeth, - how to use calcium for dental health. , - how sugar and other foods affect dental health, - how to use chewing gum correctly, - what are the misconceptions about dental health.
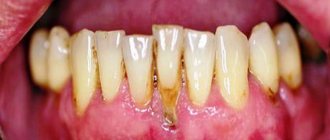
Gum inflammation, or
gingivitis
, is caused by bacteria that grow in plaque.
They penetrate under the gums and release enzymes and toxins. At the same time, the gums change color. It turns red if the inflammation is acute, or becomes bluish if the process has entered a chronic stage - and swells. However, the first sign of inflammation that you will notice on your own is bleeding gums
when brushing your teeth or eating solid foods.
Why do gums recede with crowns and veneers?
Veneers or crowns also sometimes cause gum recession.
The issue may be the quality of the restorations themselves. For example, if the edge of the prosthesis adjacent to the mucous membrane is more massive than necessary and literally does not fit under the gum. Normally, veneers and crowns are created with a beveled edge, that is, they are thinner in the area adjacent to the gum. It also plays a role how carefully the orthopedist worked and polished the edge of the restoration near the mucosa, and whether he removed the remnants of the fixing cement. The slightest roughness near the neck of the tooth can irritate the soft tissues.
And, of course, the problem arises due to improper care of veneers and crowns: aggressive cleaning with a hard brush or the use of dental floss, which is prohibited after restoration. In addition to the fact that the thread causes cuts to the mucous membrane, it can get caught on the veneer and partially peel it off from the tooth. Then its open edge can injure the gums.
See a doctor immediately
If your gums are bleeding, you need to see a dentist as soon as possible in order to begin treatment while the inflammation in the gums is still reversible. Without appropriate treatment, inflammation will progress and may progress to the next, more severe stage – periodontitis. This is the destruction of the bone tissue of the tooth socket and the formation of a periodontal pocket - the space between the tooth root and the gum. In this case, the tooth becomes mobile and, with significant bone destruction, falls out. By the way, periodontitis
is one of the most common causes of tooth loss.
Consequences of a recession: what will happen if the problem is not solved
Almost all dental diseases, if ignored for a long time, first result in a loss of aesthetics, food getting into the spaces between the teeth, the development of an inflammatory process, mobility, and then the loss of teeth. And gum recession is no exception. As the thinning and loss of mucous membranes progress, the problems intensify:
- increased sensitivity and acute pain in the teeth in the area of the gingival margin develops,
- exposed areas of the root are more susceptible to caries, which quickly reaches the inside of the tooth and affects the pulp,
- the risk of developing wedge-shaped defects increases,
- gums become swollen and inflamed or, on the contrary, become unnaturally light, whitish,
- Plaque is deposited faster at the roots, which over time expands the periodontal pockets and, among other troubles, gives a putrid odor from the mouth.
If the problem is not solved, you can lose all your teeth - they simply will have nothing to hold on to.
Also, the recession has psycho-emotional consequences. When the gum contour loses its attractiveness, a person's smile begins to appear unhealthy and completely unattractive. In addition, the teeth lengthen because... their roots are now also “included” in the smile zone. Large gaps (tremas) appear because the roots of the teeth are narrower. All this creates serious psychological barriers to communication.
How to avoid gum disease
- Visit your dentist
- at least twice a year.
A specialist will examine your oral cavity, teach you how to brush your teeth, select the hygiene products you need, and carry out professional removal of dental deposits - plaque and tartar. — Take regular and thorough oral care
: brush your teeth with a toothbrush and toothpaste, use dental floss and mouth rinses as recommended by your dentist.
— To prevent and treat
the early stages of gum inflammation, use toothpastes and rinses containing extracts of medicinal plants and essential vegetable oils.
Consult your dentist - he will select the most suitable products for you and tell you how to alternate them so that addiction does not occur. - Toothpastes and rinses with antiseptics
- chlorhexidine, triclosan, cetylpyridine chloride - are usually prescribed in the presence of inflammation.
The duration of the course of using these drugs is determined by the dentist. It is necessary to follow his recommendations to avoid negative effects on the normal microflora of the oral cavity and the appearance of dysbacteriosis. — Gum massage
helps improve blood circulation.
It can be done every time you brush your teeth - at the end of brushing, making light circular movements with the toothbrush with your teeth closed. — Hydromassage
of the gums can be done using irrigators - special devices that precisely deliver a stream of water or an antiseptic solution under pressure from 0.7 to 4.8 bar.
— Clean the interdental spaces very carefully
so as not to injure the gingival papillae located between the teeth. Chronic trauma from dental floss or toothpicks can cause changes in their contour and the formation of gaps between the teeth.
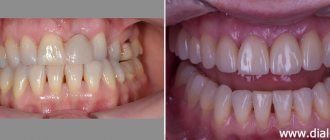
Healthy teeth, photos of patients. Photo of healthy teeth
We often see the dazzling smiles of celebrities in photographs in glossy magazines. And many people believe that this is what healthy teeth look like. Photos in such press, however, do not always reflect the truth.
After all, photographs in magazines can be processed in special programs, and in order to recognize the signs of an impending problem in time or simply make sure that you have healthy teeth, it is advisable to look at the photos provided by a specialist.
On dental websites, almost any material about the prevention of oral diseases is accompanied by at least one photo of healthy teeth. At the same time, photos are often presented from different angles, including their inner surface. Photos of healthy teeth can also be viewed in the clinic, in special catalogs. Therefore, today it is not difficult to see how strong and white teeth look in the photo.
Eat right
— Eat less foods rich in fast carbohydrates. These include flour products, sweets, and many fast food products. They contribute to increased plaque
and serve as a breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria that destroy teeth and gums.
- Include solid foods
- raw vegetables, hard fruits - that require intensive chewing, which leads to an increase in saliva flow and natural cleansing of the oral cavity.
It is advisable to eat hard vegetables and fruits after eating sweet, sticky and soft foods. — Include a sufficient amount of protein
for normal renewal of the mucous membrane of the mouth and gums.
— Avoid developing hypovitaminosis. After all, pathological changes in the gums most often develop with a deficiency of vitamins
A, C and D.
How to treat gum recession?
To cover the exposed root, a small operation is performed in the gum area.
There are many methods of gum plastic surgery, but they are fundamentally divided into 2 types:
- gum plastic surgery with local tissues (when the existing gum is “stretched” or moved to the root in a certain way so that the exposed area is closed, and fixed with small sutures, which are removed after healing).
- gum plastic surgery using a “patch” (the patch can be a special collagen-based material or the patient’s own tissue from the hard palate or the area of the far upper tooth - gum transplantation).
The choice of method is at the discretion of the doctor, according to each specific situation.
Gel for teething. How to choose?
If a child becomes restless and capricious during the teething period, first of all you need to create a calm environment for him, pay him more attention, pick him up more often, hug him, and talk to him.
Pain can be relieved mechanically or with medications. You can massage the gums with a clean finger or a rubber brush, let your baby suck on a dryer or chew on a teether, especially a cooled one. There are special dental gels to relieve gum pain in babies during teething. The advantages of children's gum gels are that they quickly relieve pain.
There are many more disadvantages to using them. The main two:
- If the gel contains the anesthetics benzocaine and lidocaine, they can be dangerous to the child’s health. Such drugs provide pain relief for a short time - the medicine is washed off with saliva and swallowed. It is difficult to accurately calculate the dosage when squeezing the gel out of the tube. If you also exceed the number of applications of the medicine recommended by the instructions, you may exceed the permissible limit. An overdose of lidocaine threatens with such dire consequences as convulsions, breathing problems, heart rhythm disorders - even death.
- Herbal gels provide mild pain relief, but help relieve inflammation. Their action does not give quick results. An allergic reaction to herbal components is possible, so after the first use you need to monitor the child’s reaction.
If you still decide to use a teething gel for your baby, choose either a herbal gel or a combination drug with an anesthetic and herbs. It will help relieve acute pain and reduce inflammation. But use combination gels very carefully, only as a last resort when other methods do not work and the child is in severe pain.
It is important!
Teething is a difficult period for the baby and his parents, but it is a natural stage of growing up, which allows the transition to solid food after breast milk.
Average cost in Moscow
Here are the approximate prices in metropolitan clinics for implantation and other dental services related to it.
| Name of service | Cost, rub. |
| Turnkey implantation | |
| Classical implantation with installation of a metal-ceramic crown | 39100 |
| Classical implantation with installation of an all-ceramic crown | 50200 |
| Removable prosthesis on implants with ball-shaped fastening | 54700 |
| Express implantation with installation of a metal-ceramic crown | 58000 |
| Classical implantation with installation of a ceramic crown on a special alloy | 60000 |
| Removable denture on implants with beam fastening | 160000 |
| Installation and removal of implants | |
| Installation of the healing abutment | 3700 |
| Implant removal | 6900 |
| Implantation of osteoconductive material in the area of 1 tooth | 9600 |
| Installation of a mini implant | 11700 |
| Implantation of a protective membrane of 1 tooth | 12700 |
| Installation of a temporary implant | 14700 |
| Express implantation (in one stage) of 1 tooth | 33900 |
| Classic implantation of 1 tooth | 44800 |
Cost of medications to relieve inflammation and pain at home
| Medication | Cost, rub. |
| Chlorhexidine 0.05% | 60 |
| Betadine 10% | 270 |
| Solcoseryl | 300 |
| Amoxiclav | 330 |
| Dexalgin | 400 |
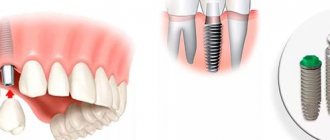
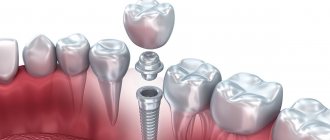
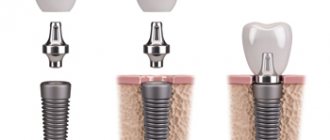
Formation of gums during dental implantation
Formation of the gingival contour is one of the most important stages in implant prosthetics.
It depends on the gums how your crown on an implant will look, how indistinguishable it will be from your own tooth, how physiological and comfortable it will be.
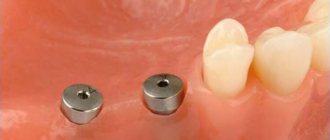
So, when the installed implants are integrated and the patient comes for prosthetics, the implantation area is a flat area of \u200b\u200bthe gums with protruding formers.
If you unscrew the gum formers, you will see just “holes” in the gums with implants in the depths.
Prosthetics with permanent crowns in conditions of immature gums will not give the desired result. Very often the crowns in such cases look like mushroom caps on a stem. That is, a wide upper part of the crown at the level of the chewing surface and a significantly narrowed part of the crown in the gingival area. Or they make crowns with edges and undercuts hanging over the gums, because it is not possible to install a crown on an implant in any other way due to the density and volume of the gums. All this gives only a short-term positive effect and the joy of new teeth gives way to disappointment, since the overhanging edges of the crown are difficult to clean, smell and inflammation of the gums appear. Due to prolonged irritation, the gums sag, further aggravating the situation. Naturally, appearance also suffers.
All this threatens a more serious complication – peri-implantitis!
To avoid many problems with prosthetics on implants, you need to correctly form the gum.
Gum formation is carried out with temporary crowns for at least 3 months. You can read about temporary crowns here…….
With all this, despite the name, temporary crowns are already full-fledged teeth both anatomically and functionally, but thanks to the material from which they are made (plastic or composite), adjustments in shape are possible to achieve the desired gum profile.
There may be several such adjustments, depending on the result achieved, and they are carried out approximately once a month.
What size should the gums be in the area of crowns on implants?
Between the crown and the natural tooth, as well as between the crowns on implants, interdental papillae must be formed, just like in natural teeth.
Only in this case we will not get “black triangles” between the crowns and the crowns on the implants will look as natural as possible.
Another requirement when forming gums is that there must be sufficient gum volume not only on the side of the tooth or adjacent crown, but also on the side of the cheek or palate!!! That is, along the entire perimeter of the implant!!!
An example of gum formation in the area of the installed implant 46.
Fixation of the temporary crown in all cases is only screw, no cement! The crown should move smoothly from the gum level towards the implant. During the fixation of the temporary crown, the gums are compressed and displaced. This procedure is performed under local anesthesia to avoid discomfort. The temporary crown is gradually, sometimes within 5-10 minutes, screwed onto the implant; faster and more aggressive fixation of the crown can lead to significant ischemia and necrosis of the gums. Therefore - no rush!
A fixed permanent crown should best match the tooth being restored, both functionally and aesthetically!
If the permanent crown is fixed with cement, an individual abutment is made along the formed gum contour and the crown is subsequently fixed onto it.
The abutment in this situation looks like a tooth that has been ground down for a crown.
The formation of gums in the case of manufacturing a bridge supported by implants also has its own characteristics. Since there is an intermediate overhanging part, it is necessary to create such a gum profile and such a shape of the intermediate part (facet) so that hygiene is maintained in this area as physiologically as possible. What does it mean? Since we cannot avoid the intermediate part and, as a consequence, the possibility of food residues getting under this part, we need to make this area accessible for hygiene and self-cleaning.
The intermediate (overhanging) part should not have overhangs or undercuts, it should not sit on the gum like a saddle, but be convex and absolutely smooth. If food remains stuck in this area, the smooth and convex surfaces will allow you to clean this surface without any problems.
This approach is used for prosthetics of both lateral and frontal areas.
The intermediate part can also be modified at the stage of temporary crowns until the optimal shape of this area is achieved.
All these manipulations with the gums are performed by an orthopedist. However, it is the surgeon’s task to create sufficient gum volume above the implant. It is the implant surgeon who, taking into account the gum biotype and the planned design of the future prosthesis, must carry out the correct installation of the implant. If there is not enough soft tissue above the integrated implant, then no prosthodontist will be able to create an optimal gingival contour. Plastic surgery to increase gums is often ineffective or the results do not last long.
The examples shown above are just special cases. Each person is unique and requires an individual approach! However, the stage of temporary prosthetics and the formation of the gingival contour is mandatory for everyone.