“You urgently need to remove the 48th tooth!” - such a statement from the dentist can seriously puzzle the patient, because even from a school biology course everyone knows that there are only thirty-two teeth in the mouth. Where did this mysterious 48th come from, and what is with the strange numbering of teeth among dentists? Cunning doctors have invented a diagram of a person’s teeth with numbers that only they understand, and patients get confused in these numbers, trying to understand what they are talking about and where they suddenly got “extra” dental units from.
In fact, the teeth numbering scheme in dentistry is quite simple, clear and accessible - it was created in order to facilitate the “accounting” of dental units in patients and bring it to some uniform standards. After all, if every dentist starts counting dental units as he pleases, nothing good will definitely come of it. Especially if the patient subsequently gets an appointment with another doctor and he simply does not understand what tooth numbers are indicated in the medical record and what kind of treatment was ultimately carried out earlier.
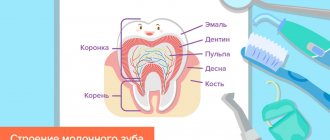
Number of roots in human teeth
There can only be one dental crown, but the number of roots a tooth has depends on its location and purpose. The number of roots is also influenced by hereditary factors. It is possible to determine how many roots a tooth has only with the help of an x-ray. The inner part of the tooth (root) makes up about 70% of the entire tooth.
Factors influencing the number of roots:
- Location of the tooth.
- The purpose of the tooth, its functionality (chewing or frontal).
- Genetic predisposition.
- Patient's age and race. In the European race, the number of dental roots is very different from the Negroid and Mongoloid races.
Causes and consequences of removing the seventh teeth
The functions, structure, and location of the sevens create favorable conditions for the development of pathology:
- Molars are responsible for chewing food and are exposed to stress every day.
- Sixes and sevens are difficult to access for hygiene procedures. The accumulation of food debris leads to the formation of plaque and carious lesions.
In addition, tooth trauma and destruction due to a deficiency of vitamins and minerals that maintain normal bone density lead to removal.
The long-term absence of seven leads to undesirable consequences for health and appearance:
- the quality of grinding and digestion of food deteriorates;
- the bite is disturbed;
- jaw atrophy develops;
- the facial muscles rest on the crown of the tooth;
- if there is no tooth, deep nasolabial folds appear and the cheeks sag.
Teeth numbering system
Dentists have developed a system in which all teeth have their own serial number. The numbering system for the teeth of the lower and upper rows will not allow you to “get confused” in the teeth.
The first number is the incisors - the frontal teeth of the upper and lower rows. There are two teeth on each side (left and right): No. 1 - central, No. 2 - lateral, behind which there are fangs, numbered No. 3. The small molars have numbers 4 and 5.
All of the listed teeth have one cone-shaped root.
Teeth No. 6, 7, 8 - large molars have three roots, and tooth No. 6 of the lower row has one root, with the exception of tooth No. 8, which can have 3 or even 4 roots.
Features of treatment of individual groups of teeth
The treatment tactics for incisors, canines, premolars, molars of the upper and lower jaws are different. Each tooth carries a different load. One part of the row is visible when you smile, while the other remains invisible to others. Let's look at the features of treatment for each area of the oral cavity.
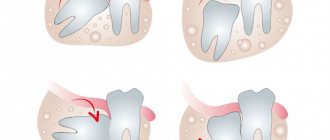
Treatment of wisdom teeth
Eights are the outermost molars in the row. They erupt later than others, practically do not participate in chewing food, and regularly cause trouble. 1, 16, 17, 32 teeth can erupt incorrectly, displacing the entire row, injuring the gums, and causing the formation of a soft tissue hood. This increases the risk of plaque accumulation and tooth decay.
| Features of wisdom teeth treatment | |
| Question | Dentist recommendation |
| Do I need to remove wisdom teeth? | In most cases, this is necessary and recommended. |
| Is it possible to treat caries on the 8th tooth? | If they do not disturb the structure of the dentition or cause discomfort, then after consultation with a doctor you can do this. |
In most cases, eights must be removed. If they grow at an angle, disrupt the bite, displace other molars, cause discomfort, or have underdeveloped enamel, it is recommended to get rid of them as quickly as possible. Extraction of teeth 1, 16, 17, 32 does not affect the chewing function or appearance of the patient.
Is caries of eights curable? If they have a normal structure, do not cause discomfort, and are involved in chewing, superficial caries can be treated using the traditional method - drilling, installing a filling. The procedure is performed at the request of the patient. If a person refuses conservative therapy, the extreme molars are removed.
If there is significant damage to the visible part of the figure eights, their removal is indicated. Artificial crowns are not installed on them due to their location and anatomical features. For acute pain, the only way to solve the problem is extraction. The figure eights are located in the far corners of the oral cavity, which makes depulpation and endodontic treatment impossible. Lack of visibility and access to instruments prevents nerve removal and canal filling.
Extreme molars are unreliable and often destroyed, so they are not recommended for use as a support for bridges. If eights are lost, prosthetics are not performed; there is no such need or possibility.
Treatment of molars
2, 3, 14, 15, 18, 19, 30, 31 teeth are molars that bear the main load when chewing. They are large, with a wide crown, have several roots, so they are firmly held in the jaw. They are not visible when you smile, but the defeat or absence of one of them causes severe discomfort to the patient. When treating this group, they pay attention to strength and strive for complete restoration of function.
| Features of treatment of molars | |
| Question | Dentist recommendation |
| What treatment methods are there if a molar is severely damaged? | In case of severe destruction of molars, ceramic inlays are most often used. |
| Which crowns are best for molar prosthetics? | More often, patients are recommended to install metal-ceramic crowns in the molar area. |
| What to do if you lose molars? | The best option in this case is implantation; patients also consider removable dentures. |
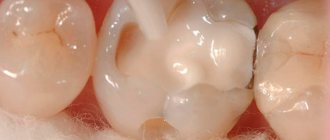
The main method of treating caries of sixes and sevens is drilling and filling. If the process does not affect the canal with the neurovascular bundle, the doctor drills out the affected areas and closes the defect with a filling made of composite materials. If the affected area is large, it is advisable to use ceramic inlays. They are made from impressions for each patient and close the cavity formed after treatment. The use of inlays allows you to increase the service life of the molar and ensures its resistance to chewing loads.
If the visible part of the six or seven is significantly destroyed, but the root is preserved, restoration is carried out using a crown. The best material for prosthetics of 2, 3, 14, 15, 18, 19, 30, 31 teeth is metal ceramics. Such designs are very durable and allow you to chew even hard food. A thin strip of metal that is visible between the metal-ceramic crown and the gum is not a disadvantage when restoring molars. It is completely invisible because these teeth are not located in the smile area. You can choose crowns made of zirconium dioxide, but they will cost more than metal-ceramics. Ceramic structures are not installed on chewing teeth.
The loss of molars affects the condition of the gastrointestinal tract and leads to displacement of the entire dentition, so prosthetics are necessary. To replace 6-k bridges, bridges are often used. If nearby units can serve as support, this is the fastest, least expensive, painless option for restoring mastication. For multiple defects, removable clasp and plate prostheses are used.
The optimal way to replace molars is implantation. The condition of adjacent teeth does not matter. With the help of titanium structures, it is possible to restore both one and several units. In most cases, root-shaped prostheses are used for prosthetics. They are able to withstand heavy loads. Such implants can serve as a support for artificial crowns and bridges.
Treatment of premolars
Teeth 4, 5, 12, 13, 20, 21, 28, 29 are premolars. They also perform the function of chewing, but are not as large and massive as molars. Some premolars are located in the smile zone, so when treating them, not only strength and functionality are important, but also beauty and naturalness.
| Features of treatment of premolars | |
| Question | Dentist recommendation |
| What to do if premolars are destroyed? | In case of significant destruction, ceramic inlays or crowns are used. The best material for premolar restoration is zirconium dioxide. |
| What to do if there are no premolars? | In this case, there are several treatment options - bridge structures, butterfly prosthesis or implantation of a missing tooth. |
The most common lesion of fours and fives is caries. Destruction occurs especially often in patients with deep fissures and narrow interdental spaces.
Due to the location of small molars, caries on them can be noticed in the initial stages. Sometimes even patients themselves pay attention to the problem and seek dental help. If a carious lesion is detected at the spot stage, modern clinics carry out treatment without drilling using the ICON system. Careful removal of damaged enamel using an etching gel allows you to save the tooth, and sealing the cavity with a special compound stops further destruction. For deeper lesions, destroyed tissue is removed using a drill or laser. Small defects are restored with durable photopolymer materials. You can choose the shade of the filling that perfectly matches the color of the enamel. In case of significant destruction, leading dentists recommend using ceramic inlays, which are made in a dental laboratory using individual impressions.
The destroyed outer part of the premolar is an indication for the installation of crowns. If only the root remains, a stump tab is installed to securely secure the prosthesis. The choice of crown material depends on the financial capabilities of the patient. The best choice is zirconium dioxide. Such designs are aesthetic and resistant to chewing loads. Their only drawback is their high price. Metal ceramics are available to everyone. It is strong and durable, but the strip of metal under the gum can be very noticeable for some. Ceramics are not suitable for fours and fives. This material is too fragile; with intensive chewing, chips will quickly appear on it.
The absence of premolars in a person is immediately noticeable to others. When they are lost, most turn to dentistry for prosthetics. If you want to quickly restore chewing and restore an attractive smile, installing an inexpensive bridge will help. The design consists of several interconnected crowns made of metal ceramics or zirconium dioxide. The outer crowns are placed on the supporting teeth, and the middle ones cover the defect in the dentition. The main disadvantages of this type of prosthetics are the need to grind healthy teeth and uneven distribution of load on the jaw.
If installing a bridge is not possible, the prosthetist will suggest a removable clasp prosthesis. Typically, the design is used when several teeth are missing. This method saves the budget and has virtually no contraindications. Lightweight butterfly prostheses are used to temporarily replace the defect. They last no more than six months, but this is enough for patients who are awaiting the manufacture of a permanent prosthesis or implantation.
The best method of replacing a lost premolar is implantation. If there are no contraindications and your budget allows, it is better to choose this modern method. A titanium rod is inserted into the jaw bone tissue and becomes a support for an artificial crown. To install such a prosthesis, you do not need to grind down the adjacent teeth. In addition, the load during chewing is distributed physiologically. Externally, an artificial premolar is difficult to distinguish from your own. Even a dentist will not always do this at first glance.
When treating 4- and 5-k, it is important to maintain a balance between practicality and aesthetics. For this reason, this group is the most difficult for dentists.
Treatment of fangs
There are four fangs in the oral cavity. These are 6, 11, 22, 27 teeth according to the universal numbering system. They have a different shape from other teeth, so during restoration it is necessary to have experience working with this group.
| Features of canine treatment | |
| Question | Dentist recommendation |
| What treatment options are there for lost fangs? | In this case, implantation of the lost canine is recommended. |
| How can you correct abnormally growing fangs? | After consultation, the patient is offered options for either orthodontic treatment or the installation of veneers or crowns. |
The fangs do not bear the chewing load. They help you bite off small pieces of food. In the process of evolution, the role of fangs in humans was lost; we do not use them to hold food or tear it into fragments. That is why the treatment of triplets is aimed at restoring their natural appearance.
In case of carious lesions, the preparation of fangs is carried out carefully, trying to preserve healthy tissue as much as possible. This will allow for high-quality restoration. With superficial caries, it is possible to preserve the volume of hard tissue necessary for high-quality filling, but deep lesions serve as an indication for installing a crown. To maintain a natural smile, it is recommended to use structures made of ceramics or zirconium dioxide.
If 6, 11, 22, 27 teeth are lost, implantation is recommended. Manufacturers offer titanium prostheses of a special configuration, taking into account the anatomical features of the jaw. Such prostheses are already classic, they have a special thread that allows you to securely fasten the structure in the narrow alveolar process.
A popular dental service is canine shape correction. Some patients have teeth that are too long, pointed, or significantly narrower than the incisors, which makes the smile less attractive. The best way to give the fangs the ideal shape is to use ceramic onlays made from individual impressions, as well as modeling with composite materials.
How many canals are there in teeth?
The number of tooth canals does not always coincide with the number of roots. The number of channels can only be determined using x-rays. The upper incisors usually have two or three canals. Some teeth have only one canal, which branches into two parts.
Number of canals in teeth:
- Upper Lower four – 1, less often 2 channels;
- Upper second – 1, less often 2 and even 3 channels;
- Bottom five – one channel;
- Upper first molar 3, 4 canals;
- Lower first molar – 3, less often 2 canals;
- Upper and lower seven – 3, 4 channels.
Removal of a wisdom tooth before implantation of the 6th tooth
The patient went to the Dial-Dent clinic to see dentist S.V. Tsukor. with the desire to carry out prosthetic replacement of one missing tooth in the jaw.
The patient was offered implantation to replace 1 missing tooth. During diagnosis and preparation for dental implantation, the patient was given a panoramic image, which showed the presence of a hidden problem - a wisdom tooth. The treatment plan was changed: first, the patient had to remove the wisdom tooth, then treat the 7th tooth, and only then proceed with dental implantation.
In this case, correct diagnosis (panoramic image of the teeth) helped specialists correctly plan treatment and dental implantation.
Situation at the time of application
Clinical case No. 3
Installation of a lower tooth implant
Below, the jawbone is denser and stronger. Its volume is higher than that of the upper jaw. This allows for better fixation of the implant, increases the survival rate of titanium roots, and accelerates fusion - the process lasts 2-4 months.
If molars are missing for a long time, there is a need to build up the jawbone. The procedure will eliminate the volume deficit due to resorption and create conditions for reliable fixation of the titanium support.
Osteoplastic surgery on the lower jaw is performed in several ways:
- Splitting of the alveolar ridge.
The alveolar process is sawed in two, the inside is filled with synthetic material, and an implant and barrier membrane are installed. Sutures are placed on the gum. After 4-6 months, the artificial root is loaded with a crown. - Autotransplantation of bone blocks.
The bone is grown with natural donor material. It is borrowed from the thigh, chin or jaw in the area of the patient's wisdom teeth. The blocks take root well when installed correctly. The disadvantage of this method is the need for two interventions in the area of sampling and installation of the material. - Guided bone regeneration.
Granules made of synthetic material are placed in the well and covered with a membrane. Depending on the clinical case, the procedure is compatible with implantation. This technique is the least traumatic. After six months, the bone chips and artificial root are integrated into the jaw.
To replace sevens, implants are used that are as close in size as possible to the natural root in order to withstand chewing loads.
The main method of implanting sevens is a classic two-stage protocol with delayed loading of the prosthesis. Single-stage with immediate loading is not recommended. This is due to the location of the tooth, which is actively involved in chewing, and is at risk - the implant may move.
Stages of complex tooth extraction
Complex removal surgery is carried out only after x-ray diagnostics, during which the shape, length and depth of the roots are determined. If the patient has inflammation, he is prescribed treatment with antibacterial drugs.
Technique of the procedure
Wisdom tooth removal is carried out in the following order:
- the gum is separated from the neck of the tooth by making an incision in the soft tissue;
- if necessary, the interroot septum is sawed or sections of bone tissue are cut out at the location of the tooth;
- then, using forceps, the tooth is rocked and pulled out of the socket;
- Sutures are placed on the gum.
Painkillers are not required after the procedure, since the effect of the anesthetics is still present.
Stages of implant installation
- Preparation and diagnostics.
A diagnosis is carried out, the doctor draws up a treatment plan, and selects an implantation system. Carious lesions and gum disease are eliminated. Before implantation of the upper jaw, it is necessary to cure inflammation of the maxillary sinuses. - Bone tissue augmentation.
If there is a lack of volume, the bone is increased with osteoplastic material. Engraftment lasts 2-6 months. If the clinical situation allows, this stage is combined with implantation. - Implant installation.
The artificial root is introduced under local anesthesia through an incision, a plug is placed, and the soft tissue is sutured. Osseointegration lasts 2-6 months. - Gum formation.
After the implant has fused with the bone, the gum above it is cut, the plug is removed and a gum former is installed for 10-14 days. - Prosthetics.
The former is replaced with a permanent abutment. A crown made of metal ceramics or zirconium dioxide, created from impressions in a dental laboratory, is attached to it.
Recommendations after removal
Regardless of the method by which the tooth was removed, in the first 2 days the patient must observe a special diet, activity and hygiene. This is necessary to preserve the blood clot in the wound, which helps maintain the sterility of bone tissue and promotes its regeneration.
In the first 48 hours after removal you cannot:
|
Failure to comply with these recommendations most often causes the clot to fall out of the socket and the development of alveolitis or bleeding.
After tooth extraction it is recommended:
- make oral baths from chamomile and sage decoctions (the decoction prepared according to the instructions is taken into the mouth and held there for 10 minutes, without rinsing or moving the tongue) 2-3 times a day;
- take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (especially after atypical removal, when the tissue is severely damaged and swelling occurs) - nimesulide, diclofenac sodium, ibuprofen, paracetamol, etc. (it is important that the medicine does not reduce blood clotting).
Sometimes patients need preliminary preparation for removal. People taking aspirin and other medications that impair blood clotting should stop taking them a week before the procedure. For those who suffer from increased excitability and anxiety, you can start taking valerian or motherwort 1-2 weeks before removal, having previously agreed with your dentist and your therapist.
Even if the removal was painless and quick, you should not ignore the doctor’s advice. The right approach to rehabilitation will help you avoid complications and recover faster.