At the age of six months, the baby begins to cut his first baby teeth. This is both a joy and a very problematic period.
The process of teething in a child takes about two years. So, for all 2 years, the baby and his family have to worry about the pain that accompanies teething? Not at all! Today there are a lot of methods and drugs that act as pain relievers during teething.
There are children who easily endure various age-related physiological processes, including the appearance of their first teeth. But, as a rule, most children react to such changes quite sharply - they lose sleep, lose appetite, become mischievous, and show their poor health in other ways. How can we help them?
Symptoms of the onset of baby teeth
First of all, parents need to be able to recognize when the teething process has begun. The appearance of the first teeth has the following symptoms:
- inflammation and redness of the gums;
- increased salivation;
- change in the child’s appetite (the baby may refuse food altogether or, conversely, try to eat inedible);
- biting and attempts to gnaw everything on the part of the child (due to the fact that the gums itch during teething);
- not a significant increase in body temperature for a period of 1-2 days (due to the fact that an increased amount of biologically active substances is released in the body);
- slight (up to 3 days, with a frequency of up to 3 times a day) diarrhea, due to the fact that salivation increases and a lot of saliva enters the child’s gastrointestinal tract;
- mild runny nose (clear nasal discharge for about 4 days);
- wet cough (also due to increased salivation);
- lack of sleep (due to discomfort).
What problems can arise during teething?
- Teeth cutting too late. A period of more than 2 months from the moment when they should have started to erupt is considered late.
- Teeth are cutting too early. Although there are cases when a child is born with teeth already erupted. But still, if teeth begin to appear for the most part too early, this is a cause for concern.
- The appearance of teeth outside the dentition.
- Incorrect formation of newly erupted teeth.
- Violation of the order of eruption of the incisors or the absence of one of the teeth.
If symptoms (fever or runny nose) last longer than a couple of days, the child should be seen by a doctor immediately!
How to choose a teething remedy
The eruption of baby teeth is a physiological process that usually begins around 4-6 months of a child’s life and ends at about two and a half years. Regularly occurring symptoms of teething: restlessness (especially at night), increased salivation, itching, swelling and soreness of the gums. Any mother, naturally, wants to make this period of development easier for the child, relieve pain in the gums, and reduce the likelihood of sleepless nights. Therefore, mothers very often ask doctors questions: what to do when teething and how to help the child?
There are several solution options with their advantages and disadvantages:
1. Homeopathic remedies.
On the one hand, ingestion of diluted chamomile and other herbal ingredients will calm the baby, however, from the point of view of scientific medicine, they are unlikely to have any direct effect on the gums.
| 2. Systemic pain relievers (eg paracetamol, ibuprofen) They are safer, but they will also act on the baby’s body in general, and not on the gums. 3. Gels based on lidocaine or benzocaine These are local anesthetics that have an analgesic effect during teething. But there are several nuances: • Firstly, with frequent use, lidocaine and benzocaine can have a toxic effect on the body of a small child. In 2014, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reported 22 cases of severe adverse events to 2% lidocaine gels in children under 3 years of age. Side effects of lidocaine included respiratory distress, decreased heart rate, decreased blood pressure, and convulsions. That is why the Department has imposed a ban on gels with high levels of it. • Secondly, age restrictions: usually from 3 or 6 months. If your baby starts teething early, these medications will not help him. In addition, such gels can have a very specific taste, and the baby may completely refuse to use it again. |
4. Gels based on natural extracts without synthetic anesthetics
These gels are based on extracts that have anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antiseptic effects.
For example, the new Italian gel for gums Dentinale® natura with herbal ingredients: aloe vera juice, boswellia and chamomile extracts, will help postpone the teething period without resorting to analgesics and anesthetics.
Dentinale® natura has a mild anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect. The gel does not contain :
• synthetic painkillers
• sugar
• parabens
It is almost impossible to overdose on such a drug, it is harmless if swallowed, side effects are not described and theoretically can only be associated with individual intolerance to the components of the gel.
Pleasant to the taste and has no age restrictions.
Easy teething and good nights!
PRODUCTS BY THEME: Dentinale
You can read the reviews at the link: https://www.babyblog.ru/td/itog/41
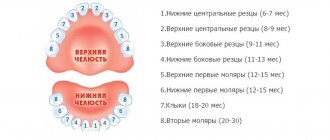
The order of appearance of baby teeth
The appearance of teeth has a strict sequence, which indicates the correct formation of the masticatory apparatus:
- At the age of 9-10 months, the first lower and upper incisors appear.
- Up to a year (up to 12 months), the second upper and lower incisors erupt.
- The first upper and lower chewing teeth will appear at the age of 12-19 months.
- Fangs erupt between 16 and 22 months of age.
- The child will acquire second upper and lower chewing teeth between 20 and 30 months.
In general, the process of teething is the natural course of things. And it’s definitely not worth accelerating it with mechanical influences. But it is possible to help a child survive it with the least discomfort. The first symptoms of teething may appear a month or two before the actual appearance of the tooth! To prevent a child from feeling discomfort all the time, there are many everyday tricks and even medications designed to relieve pain and inflammation from children’s gums.
“Painkillers” for teething in children: types, methods of use
To facilitate the process of teething, you can use various painkillers, local and general. What types of means are there and are there any restrictions on their use?
To make the process of teething as easy as possible, dentists recommend massaging the child’s gums. The gums are massaged for 1-2 minutes with gentle circular movements with clean hands, while the fingers are wrapped in a sterile napkin. In this case, Asepta napkins, made in the form of a fingertip, have proven themselves to be excellent. Extracts of chamomile and witch hazel in the impregnation have a soothing and anti-inflammatory effect on inflamed gums, reducing pain and swelling.
In addition, it is important to constantly wipe your baby's drool if it drips onto the chin to avoid irritation or rash there. Teething is accompanied by copious salivation; during this period the child must be carefully monitored.
It is necessary to constantly maintain contact with the baby, take him in your arms often and try to distract him with some activities. It is recommended to talk a lot with the child in order to “drown out” his pain.
During teething, you can offer your baby special teethers - toys of various ring-shaped shapes rubberized or filled with cooling thermogel. Before giving such a thing to your child, experts recommend cooling it a little in the refrigerator. But not too much, since the child will refuse very cold toys, and if he does not refuse, he may catch a cold due to contact with a surface with a low temperature.
If the baby refuses special devices for teething and prefers to chew something chosen independently, there is no need to prevent this. However, it should be borne in mind that the object that the child puts into his mouth must be:
- is devoid of sharp protruding parts so that the baby does not cut himself;
- without small parts that a child can “gnaw off” and swallow/chokes on;
- consist of a substance that will not harm the child upon contact.
Many children love to chew on bread crusts or bagels while teething. This is a rather dangerous activity, since the child may choke on crumbs or damage the delicate oral cavity with them.
Ways to relieve teething pain
How can you help your baby cope with teething?
Teething is a difficult time for both children and parents. Most often, children become excitable, capricious, and irritable. Additionally, there are other signs of teething such as increased drooling or drooling. There is no need to worry too much as there are several ways that can help reduce discomfort and pain.
What is teething?
When teething occurs in babies and children, the growing teeth begin to penetrate the gum tissue that hides them and come out. Some children experience more severe pain, others less. Here are some signs and symptoms that can tell you your baby is starting to teethe:
- The gums in the area where the tooth is expected to erupt become inflamed and swollen.
- Your baby's cheek on the teething side may become red and hot.
- Children may constantly rub the ear on the teething side.
- The child begins to chew everything that comes to hand.
- Salivation increases, which can result in irritation on the chin.
- The child becomes irritable and shows other signs of discomfort, such as restless sleep and refusal to eat.
- During this time, children's temperature may periodically rise slightly.
What is the average duration of teething in children?
Typically, the first tooth appears between 6 months and one year of age.
A baby is born with all 20 baby teeth already under the gum - just waiting to emerge. And there is a clear pattern or order of teething. The front teeth (incisors) usually erupt first, and all subsequent teeth, upper and lower, appear one after another. The first molars at the end of the gums begin to appear around 12–15 months of age, while the canines usually erupt by the age of one and a half years. All baby teeth usually appear by age three.
How to soothe teething pain:
There are several options for helping your baby teething to make this difficult period of his life more comfortable:
Chew toys
You can purchase special chewing rings in a wide variety of shapes and materials designed for a child during this period. These rings help to significantly reduce the child’s discomfort and help the tooth appear as quickly as possible.
You can also use chewing toys (made from special soft fabric) and various nipples for a baby bottle.
Proper nutrition
Cool water is the best option during teething, especially if your baby drinks from a special sippy cup. Drinking a chilled drink will somewhat soothe irritated and inflamed gums in the same way as drinking fruit purees or drinking yoghurt in a cool form.
Creative distraction or special game
Try to distract your child with some creative activities from discomfort and pain in the mouth. Cuddle him, play with him, prepare a warm bath for him. If your baby is still breastfed, feed him.
Gum massage
If you lightly massage your baby's gums with a clean finger, the pain will calm down a little. This may also help the tooth erupt.
Skin protection
You can use baby cream to reduce chin irritation. It is also necessary to change the child’s bedding in a timely manner.
Dental gels
Such drugs are presented by many pharmaceutical companies. They may contain local anesthetic components. Gels give temporary results because they are easily washed off with saliva.
Children's dental gels contain components with a high safety profile, some of which can be used as early as 5 months of age. It is recommended to follow the instructions for use and use only drugs that are registered for children of the appropriate age.
Fever and pain
You should see a doctor if your baby has a high fever or is unusually uncomfortable or painful, which indicates something more serious than teething symptoms.
Finally, don't forget that all children teeth naturally, so don't take your child's painful illnesses too seriously during this difficult time for him (and his family).
How teeth are cut
Teething is a complex process, because at this time tissues are formed, tooth roots grow, and gums are rebuilt. Moreover, teeth begin to form during pregnancy, starting from the 6th week. Around this time, calcium begins to be deposited in the tissues of future teeth.
Next comes the fun part – teething. It is considered normal if teeth begin to cut between 4 and 7 months. But every body is unique, so everyone cuts their teeth differently. It depends on many things, for example:
- From genetics. Often the age at which a child begins to cut teeth depends on when his relatives - mom, dad, grandparents - started cutting teeth.
- From nutrition. If your baby doesn't have enough vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin C or calcium, his teeth will start cutting later.
- From the course of pregnancy. If there was fetal toxicosis during pregnancy, this will also slow down the appearance of teeth.
And normally, teeth are cut in pairs, that is, the lower central incisors appear first, then the upper central incisors, the upper lateral incisors - the lower lateral incisors, the upper first molars - the lower first molars, etc. But even if the order is disrupted, this does not always mean any illness or serious violation.
Eruption of molars
When should I expect my molars to erupt? The replacement of baby teeth begins at the age of five and continues until the age of fourteen. By the time the shift is completed, the child will have erupted all 24 teeth, except the wisdom teeth. This is a separate topic for study that parents can refer to later.
The first to change are the incisors on the lower jaw. Then the “sixes” are cut, and only after that the molar upper central incisors grow. By the age of 8, the upper lateral incisors erupt. After this, at 9–10 years old, the upper and lower “fours” change. At 10–11 years old, “fives” change, at 12–13 years old, fangs, and at 14–15 years old “sevens” erupt.
When talking about molars in children, you need to understand that these teeth will remain for life. That is why it is necessary to create favorable conditions for the formation of a new dentition. This is done by taking care of baby teeth and monitoring the eruption of each new molar.
Timely correction of curvature, mineralization, treatment of caries, sealing of fissures - procedures thanks to which the child does not have to hide his teeth while smiling and wear braces for several years.
Remember: each period of teeth change is characterized by its own characteristics and sensations. For example, before this process begins, the child may experience discomfort and pain due to jaw growth. Another example is the eruption of “sixes”, which grow by the age of 6 and are immediately indigenous. Parents should be aware of this so as not to mistake these teeth for baby teeth.
The process of formation of molars will take place without pain and problems if the child is regularly examined by a dentist. It will correct imperfections in time and help teeth grow straight, strong and beautiful.
Possible complications of molars
The main danger in the process of changing teeth will be insufficient oral hygiene. The child should brush his teeth regularly and properly and eat well. He should know that after eating sweet food he must brush his teeth or at least rinse his mouth.
A common problem after teething is the potentially dangerous pigmentation of fissures - depressions on the chewing surface of the teeth (not counting the canines and incisors). The fact is that the process of mineralization and formation of a strong tooth structure takes about 3 years after eruption. During this period, teeth are vulnerable and, with insufficient hygiene, can become pigmented and subsequently become infected with caries.
Let us remind you: if there were problems with your baby teeth, they will most likely affect the new molars. Also, possible complications of molars are associated with infections that can get inside the gums after baby teeth fall out. Therefore, hygiene during this period of the baby’s life must be strictly monitored.