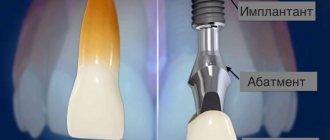
From this article you will learn:
- how a sinus lift is performed – reviews, videos,
- open and closed sinus lifting – price for 2022,
- How can this operation be avoided?
A sinus lift is a surgical operation whose purpose is to increase the volume of bone in the bottom of the maxillary sinuses in the upper jaw. This operation is one of the options for bone grafting, and is sometimes necessary when installing dental implants in the lateral parts of the upper jaw. Most often this is necessary in the area of missing 5-6-7 teeth (i.e. molars and premolars).
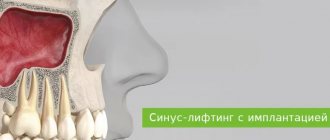
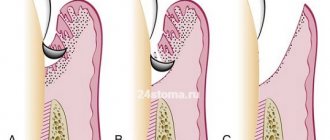
The use of sinus lift during dental implantation is, as a rule, mandatory if the teeth in the lateral parts of the upper jaw were removed a long time ago, because in this case, the bottom of the maxillary sinus subsides in the area of missing teeth (Fig. 1). The implantologist’s task will be to raise the bottom of the maxillary sinus by grafting bone material, which can be done using one of two techniques - open or closed sinus lift.
What does raising the bottom of the maxillary sinus look like (diagram) -
Scheme of sinus lifting and implantation –
This article was written for patients and will allow you to navigate the pros and cons of the 2 main sinus lift techniques. We will also talk about several methods of dental implantation, which in some situations can make it possible to avoid the need for bone grafting altogether.
All about sinus lifting in dentistry – when and why surgery is needed
Article navigation
- What is a sinus lift?
- Why does bone deficiency occur?
- Indications for sinus lift
- Contraindications to the procedure
- Materials for bone grafting
- Diagnosis before surgery
- Types of operations
- 1. Closed sinus lift
- 2. Open sinus lift
- How to Avoid a Sinus Lift
- Recommendations during the rehabilitation period
- Consequences and complications
- Reviews from doctors and patients
- Cost of the operation
Question for a specialist
When preparing for dental implantation, it often turns out that the jaw bone is too small in volume to install an implant into it. In this situation, the patient often requires extension – bone grafting or augmentation – so that the implant can still be fixed. Due to the structural features of the skull, plastic surgery for the upper and lower jaws is performed differently. For the upper jaw, a method called “sinus lift” is used. Next, we will talk about what kind of operation this is and how sinus lifting of teeth is performed in different ways - open and closed, balloon and ultrasound. We will also focus on compatibility with implantation and the nuances of the rehabilitation period.
Features: another name is subantral augmentation, “sinus lift”, “sinus graft”. The procedure takes place exclusively on the upper jaw. It is performed by an experienced maxillofacial surgeon, if necessary, in tandem with an ENT surgeon.
Closed and open sinus lift: reviews
Regarding the sinus lifting operation, reviews from those who have done it boil down to the following... The most traumatic is the open sinus lifting technique, after which during the first 72 hours you need to be prepared for significant swelling of the soft tissues of the face, severe pain, and the occurrence of a hematoma.
You are unlikely to like going through this without a sick leave. The closed sinus lift technique is less traumatic, and there are rarely complications, severe pain or swelling after it. Therefore, whenever possible, preference should be given to a closed sinus lift. In any case, preference should be given only to experienced implantologists who have experience working specifically in inpatient maxillofacial departments of hospitals, and not just experience working in a clinic or private clinic.
Important: most often, infectious complications develop in the first 72 hours after surgery, so it is best to choose for implantation and sinus lift only those clinics where there is a full-time implant surgeon. In most clinics, implant surgeons come only 1-2 working days a week, which threatens that even if you have symptoms of a complication, you will not be able to make an appointment with a doctor for an examination on the same or the next day.
If, with the initial symptoms of a complication, the intervention of a doctor can help avoid its full development, then a missed time of 1-2 days can lead to the development of severe inflammation and, ultimately, simply to an unsuccessful operation. Therefore, choose an implantologist who works in the clinic every working day and who is not going on vacation in the next 2 weeks after the operation.
What is a sinus lift in dentistry?
A sinus lift is an operation to increase the height and volume of bone tissue, which is performed exclusively on the upper jaw. There are accessory air sinuses (or sinuses) around the nose and on the forehead - in this operation they work specifically with the voluminous maxillary sinuses, which are located above the roots of the lateral teeth of the upper jaw. They are lined from the inside with a thin protective film-shell. If you lift it, you can free up some space for filling with bone material, thereby increasing the size of the bone.
The word “lifting” is often used for various procedures in medicine and cosmetology. Therefore, some patients may confuse dental sinus lift surgery and cosmetic augmentation of the angles of the lower jaw or chin with hyaluronic acid fillers. In the first case, it means raising the bottom of the maxillary sinus to increase the height of the alveolar ridge and subsequent high-quality dental implantation. In the second case, the cosmetologist corrects the oval of the face using injections with a special gel. Augmentation of the chin or corners of the lower jaw can be done using implants made of porous polyethylene, but here you should contact a plastic surgeon with skills in performing maxillofacial operations.
%akc54%
Various techniques
One of the most common complications is rupture of the maxillary sinus membrane. It occurs during an open sinus lift, when access to the maxillary sinus is created, or during its membrane peeling. Therefore, burs and cutters have been developed that do not injure the membrane of the maxillary sinus even if they accidentally touch it.
Another option is an endoscopic sinus lift . It is carried out without additional incisions, like a closed one, but with its help you can significantly raise the bottom of the maxillary sinus. With the usual closed version, monitoring the condition of the membrane is carried out only tactilely, therefore, using this method, the bottom of the sinus does not rise more than 2-3 mm. But under the visual control of an endoscope, it is possible to expand the indications and conduct a closed sinus lift even in cases where an open one is indicated.
The main advantages of the endoscopic method are low trauma and an easy postoperative period. Only a few clinics have the necessary expensive equipment to carry out such a procedure.
Why does bone deficiency occur?
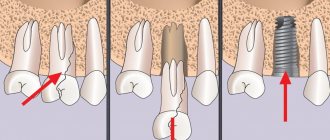
Not all patients have sufficient knowledge about their body, which sometimes leads to misunderstanding of the importance of certain procedures in dentistry. Here it is worth understanding what happens after tooth extraction. When, for some reason, a person loses a permanent tooth, the resorption of the spongy bone around the place (socket) where the roots were previously located begins almost immediately.
In the process of chewing food, the tooth received a load that extended to the jaw bone, forcing the microscopic blood vessels that penetrate the bone substance and nourish it to “work.” No roots equals no load. That is, in the “toothless” area, the bone is removed from work. The capillaries gradually atrophy, and the spongy substance left without nutrition is resorbed, because resolves, and outwardly it looks like bone subsidence. Already in the first 6 months, serious changes are noticeable, and after a year, resorption actually reaches its “peak”. As for the upper jaw, the bone substance here is more porous and light (compared to the lower jaw). It atrophies faster both from the outside and from the maxillary sinus - the latter case is often found in patients of retirement age.
Statistics show that if 70% of respondents (wearing removable or standard bridges) knew about bone atrophy and the discomfort that constantly shifting dentures bring, then dental implantation would be the preferred replacement for lost teeth. The implant uses the bone in which vital processes are restored, so atrophy practically does not occur.
When is bone grafting required?
After a tooth is removed, the area of bone in which it was located is deprived of chewing load. As a result, the bone becomes loose and thins due to gradual resorption. To install an implant, you need sufficient height and width so that the root can be firmly anchored in the jaw. If there is too little hard tissue, traditional implantation becomes impossible without replacing the lost bone volume.
Alternative implantation techniques or fixed dentures on your own teeth can be used. However, these methods are inferior to implantation, so it is worth considering the option of bone grafting.
Indications for sinus lift during implantation
The main indication is a lack of bone substance in the area of future implant installation, and if this area falls into the projection of the maxillary sinus - that is, in the absence of teeth in the lateral (distal) sections. Only an implantologist can understand when a sinus lift or bone augmentation is needed in principle. After all, each clinical case is unique in its own way and requires implants of different lengths. A lack of even 1 mm of bone may be an indication for osteoplasty surgery. Professionals also take on difficult situations when there is a lack of more than 8 mm of volume in the alveolar process. The standard indication is that the bone height is 6-8 mm or less.
In 60-80% of patients, there is a lack of height of the alveolar ridge of the upper jaw. The “risk zone” includes people who have lost teeth more than 6-12 months ago, patients with periodontal disease and dental cysts, as well as patients with certain anatomical features - when the bone septum is thin and short by nature. All these groups can undergo augmentation - of course, in the absence of contraindications.
Sinus lifting under local anesthesia, general anesthesia or sedation
Any bone grafting is in most cases performed under local anesthesia. Sinus lifting is no exception, but in some situations it is necessary to change the type of anesthesia in the direction of increasing the analgesic effect.
For local anesthesia, the most modern and safe painkillers are used. Sometimes sedatives are added to anesthesia if the patient is terrified of the procedure or is prone to strong feelings. The main problem with such medications is the risk of an allergic reaction. Some groups of patients must undergo a small and painless skin test before administering the product, which helps to exclude intolerance. If the reaction to a provocative test is positive or questionable, then the doctor refuses the incompatible anesthetic and selects a compatible one.
Sinus lifting can be performed under general anesthesia, especially for open surgery. Such anesthesia is required for patients with an excessive gag reflex and people with contraindications to local anesthesia. General anesthesia is also performed during operations in hospitals, if hospitalization is required, or at the request of the patient, if he is afraid of surgery.
Contraindications to the procedure
Osteoplasty is not possible in the presence of acute immune diseases of the body (AIDS, HIV). Contraindications also include oncology, bleeding disorders, problems of the cardiovascular system, decompensated diabetes mellitus, too close to the bottom of the maxillary sinus (which makes it impossible to displace the membrane).
The presence of acute ENT diseases, caries or stomatitis are relative contraindications. Before surgery, it is imperative to completely cure a runny nose of any etiology (and constantly relieve allergic/medicinal rhinitis), as well as sanitize the oral cavity to minimize the risk of wound infection and other complications.
Contraindications
In addition to general contraindications (type 1 diabetes, recent radiation therapy, etc.), there are a number of factors that may carry additional risks for the operation. The most common limitation is inflammatory diseases in the maxillary sinus area. It is necessary to identify the source of inflammation. Additional consultation with an ENT specialist may be required. Some difficulties may be due to previous operations in the area of the maxillary sinuses.
Materials for bone grafting
All types of materials used in sinus lifting can be divided into 3 types - autograft, xenograft and synthetic bone. Let us dwell in more detail on the features of each type.
Autograft
The best option for the procedure is the patient’s own bone – an autograft. A small piece is cut from the lower jaw or chin, then the material can be crushed and replanted while raising the floor of the maxillary sinus. The advantages of this approach are complete immune compatibility, i.e. the autograft takes root perfectly. But there are also disadvantages - sometimes a lot of material is required (which becomes traumatic for the patient, because after osteoplasty 2 operated areas will already heal). Disadvantages also include increased resorption of the autograft during the healing period; as a result, the patient sometimes requires repeated augmentation.
Previously, another type of natural material for osteoplasty was used - allograft. This substance is taken from a donor (most often cadaveric material is meant) and goes through several stages of processing and disinfection. The material is outdated due to unstable survival rate and ethical component.
Xenograft
Bone replacement materials of animal origin are obtained from bovine bone. The substance is crushed, sterilized and part of the impurities – collagen (or protein, protein) – are removed. The result is a substance that is sorted according to the diameter and shape of the particles - crumbs with a diameter of 0.25-1 mm, chips - from 1 to 2 mm, granules - from 4 to 6 mm. The crumbs can be pressed into blocks up to 3 cm long.
A large amount of proteins makes the material less dense, which reduces the fixation ability when installing an implant. It is considered optimal when the material contains at least 75-90% minerals, and the rest is collagen.
Xenografts have good survival rate and relatively low cost, so this type is often used in osteoplasty. After surgery, the material begins to interact with surrounding tissues. Gradually, your own young bone is formed, and the graft is absorbed. The following materials are widely used for augmentation: Swiss Bio-Oss from Geistlich Pharma and Russian Osteomatrix. Similar bone materials can be mixed with autografts.
Synthetic material
Synthetic bone has a complex mineral composition, presented in the form of granulate - medical two-phase calcium phosphate. It contains artificial crystalline hydroxyapatite and beta-3-calcium phosphate (an analogue of natural hydroxyapatite, which is the main building block of bone). The diameter of the granules is about 0.2-2 mm. After replanting, two-phase calcium phosphate is also gradually replaced by living young bone. Popular brands that have confirmed their high quality and biocompatibility are BoneCeramic from Straumann and Maxresorb from Botiss Dental.
Very often, along with augmentation, a PRF membrane (or PRF, PRP) is applied. This is a thick gel-like preparation obtained from the patient's own blood. The membrane contains a huge amount of fibrin protein, platelets and growth factors, which actively stimulate regeneration processes. This method will be a significant addition to osteoplasty, especially if large areas were operated on - this way the patient’s rehabilitation will be much faster and less painful.
What bone replacement materials are used in sinus lifting?
The reference material for sinus lifting is the patient’s own bone. It has maximum regenerative potential and absolute biocompatibility. However, to get your own bone you need to get it from somewhere. This is the disadvantage of this method, because... it is more traumatic. In addition to surgery in the maxillary sinus area, it is necessary to perform a second operation to obtain your own bone tissue. Most often it is obtained from the angle of the lower jaw, or from the chin area.
There are bone replacement materials that give a similar result as the patient’s own bone. They are produced in the form of granules and are obtained from the bones of cattle, or are completely synthesized. These are absolutely safe materials, the most famous of them is called Bio Oss from the Swiss company Geistlich. The mechanism of action of bone replacement materials is that they create the basis for the germination of one’s own blood vessels and cells. Over the course of 6-9 months, bone replacement materials gradually dissolve, being completely replaced by the patient’s own newly formed bone.
Diagnosis before surgery
To properly plan the procedure and select the optimal one, it is necessary to undergo diagnostics. An important step is to refer the patient for a computed tomography (CT) scan - this way the doctor will have a complete picture of the structure of the upper jaw and maxillary sinus, as well as the exact measurements of the thickness of the bone and sinus membrane. Additionally, blood tests are required, at a minimum - general clinical and to determine glucose levels. If certain diseases (endocrine or cardiovascular) are detected or present, you will need to consult a specialized specialist and prescribe therapy.
Restrictions after surgery
- You can't blow your nose;
- It is forbidden to drink through a straw;
- It is worth refraining from air travel;
- Food should be soft or semi-liquid; cold, hot, and spicy foods are prohibited;
- You cannot chew on the side where the operation was performed;
- During the first nights, it is recommended to sleep on high pillows with your head elevated so as not to provoke swelling;
- You cannot visit the bathhouse, swim, dive, you should exclude any physical activity, you need to rest;
- You need to take the medications prescribed by your doctor.
Read more about restrictions and recommendations here.
Types of operations in dentistry
Implantologists around the world have been using augmentation for more than 30 years to create a strong foundation for dental implants in the upper jaw. How is a sinus lift done? There are only 2 main types of procedures:
- closed or soft: if the bone height is more than 5 mm,
- open: if the alveolar ridge bone height is less than 4 mm.
A number of clinics offer a procedure called Bio Sinus Lift. In essence, this is a standard operation, but with a “selling” name. The difference between this method is that only natural materials without synthetics are used for augmentation: auto- or xenografts. Or if during the operation a biological clot is implanted - a PRF membrane.
Osteoplasty is performed without incisions in the skin and muscles of the face; all work is carried out from the oral cavity. Regardless of the type of operation, the procedure is performed under anesthesia. If the patient is very afraid, xenon sedation or general anesthesia is possible. But usually standard anesthesia is sufficient - a sinus lift lasts about 30-60 minutes. When are sutures removed after surgery? After about 5-10 days - depending on the size of the operated area.
Another “advertising variety” is ultrasonic sinus lifting. In fact, this is not a separate procedure, but a companion technique for open and closed types, and for other methods of bone augmentation. The bottom line is that the dentist uses a special ultrasonic device as a bur - a piezotome. Also, instead of a scalpel, a laser beam can be used.
Closed type of procedure
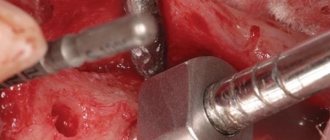
What is a closed sinus lift - this is the name of the procedure with minimal trauma to the gingival and bone tissues, when the bottom of the sinus and bone grafting is carried out through a small vertical hole in the lower part of the alveolar ridge. As a rule, a one-way method is used – i.e. restoration of teeth from only one part of the row. This is the simplest (for the patient) type of operation. This is explained by the fact that when replanting bone material, implants are usually installed immediately, that is, the use of simultaneous dental implantation. How is a closed operation performed? Let's consider all the stages in order:
- Stage 1: one or more holes are created in the gum and then in the bone (according to the number of implants). The doctor acts very carefully so as not to damage the sinus lining (this is why CT data is needed).
- Stage 2: the necessary instruments are inserted through the “passages” formed in the bone, and the bottom of the nasal sinus is carefully shifted,
- Stage 3: the resulting cavity is gradually filled with artificial bone and fibrin clot,
- Stage 4: Immediately after placing the transplant, implants are installed - holes through which osteoplasty is carried out, their dimensions are specially created. Next, plugs are screwed into the implants,
- Stage 5: a collagen membrane is applied (it holds the implanted bone and promotes regeneration), the gum is sutured.
The main condition for a closed-type operation is the presence of the patient’s own bone of 5 mm or more in height (which is required for the primary fixation of titanium implants). Using the procedure, you can install 1-3 implants at the same time.
How does a closed sinus lift work? It can be carried out in two ways:
- balloon method: lifting with air using a special ball, which, when inflated, lifts the bottom of the sinus. Refers to the most gentle and safe technique,
- mechanical: the mucous membrane is carefully lifted with hand instruments.
Open procedure type
What is an open sinus lift and how is it done? The open type is a complex and complete surgical operation, the indication for which is a pronounced lack of bone substance or the absence of more than 3 chewing teeth in a row. To raise the bottom of the maxillary sinus and introduce bone material, several small holes are not enough (as in the previous method). First, a gingival flap is peeled off in the projection of the sinus. Then the doctor performs an osteotomy - cutting out a large “window” on the side of the bone. Then the lining of the maxillary sinus is lifted. As a result of manipulations, a little free space is freed up. The operation can then continue in 2 scenarios:
- with one-stage implantation (installation of implants): if the lack of bone is 5-6 mm, then the implants can be installed immediately - you just have to additionally make vertical holes for them from below. Then the graft is introduced through the side “window”, a membrane is applied (if necessary), and the gum flap is sutured,
- without immediate installation of implants: bone material is inserted and a membrane is applied. Next, the gum flap is placed in place, stitches are applied, and after 3-4 months the implants can be placed. This type of open osteoplasty is used when the initial bone height is 4 mm or less.
During the creation of an opening in the bone, perforation of the sinus lining may occur. The doctor may stitch it up and continue with the sinus lift, or put stitches and postpone surgery until it is completely healed. To avoid the risk of damage to the mucosa, which adheres quite tightly to the bone, the best option would be to choose a piezoelectric tip with diamond coating. Such an instrument creates vibrations rather than rotation, so the osteotomy is performed with greater precision.
Sometimes native bone is not enough
The bone of the upper jaw is more porous and, in the presence of a tooth, is penetrated by a system of capillaries that nourish the bone. If a patient removes a tooth and does not think about installing an implant immediately, then after 6 months thinning of the bone tissue is observed.
This occurs due to the absence of a tooth, which was responsible for the functioning of the bone. The absence of a tooth root leads to a lack of chewing load, the “feeding” of blood stops and the spongy substance becomes thinner. After a year, subsidence reaches its peak and when installing an implant or bridge, a sinus lift of the jaw will absolutely be required.
At the same time, in elderly patients, thinning occurs even from the side of the maxillary sinus - from the inside.
You can avoid the consequences by installing an artificial dental implant in place of the extracted tooth within a period that will not exceed six months after surgery.
Types of surgery
Indications for a sinus lift are a lack of bone tissue, and even if one millimeter is not enough to securely install a new six, for example, the matter cannot be done without surgical intervention.
Additional Information. According to available statistics, 80% of patients suffer from a lack of maxillary ridge height. The risk group includes people who lost their teeth more than six months ago, suffering from periodontal disease and cysts. In addition, thinning bone tissue is sometimes a congenital feature.
The type of manipulation depends on the size of the missing tissue.
Closed operation
A closed sinus lift is a simpler type of surgery that is easier for the patient to tolerate. Includes several steps:
- Creation of several holes in the gum that are drilled into the bone. It is important at this stage to act carefully and not damage the sinus membrane, so specialists use data from computed tomography or 3D images;
- Insertion of instruments through the resulting holes and displacement of the bottom of the sinus;
- Filling the cavity with bone tissue;
- Installation of implants immediately after thickening the bone - they are installed inside the sinus, simulating the roots of the teeth, and plugs are screwed onto them from the outside;
- Suturing of the gums takes up to 10 days, the period depends on the size of the operation area.
The use of this method is possible only if the thickness of the “native” bone is sufficient, from 5 mm. In this case, it is possible to install three root implants at once.
The formation of a pocket for filling is carried out either using a balloon ball, which, when inflated, creates the required volume (the safest method), or with hand tools using a mechanical method.
Open surgery
Open sinus lifting is a complex, full-fledged surgical intervention, which is performed when there is significant thinning of the tissue (more than 6 mm) and in the absence of three or more teeth in the dentition.
Procedure of manipulations:
- Detachment of gingival matter. The doctor carefully pries and lifts the thin gum to get to the bone;
- Osteotomy - drilling out a small section of bone to open access to the maxillary sinus;
- Lifting the sinus membrane from the inside and filling the formed pocket with bone tissue.
Creating a space in the bone can lead to perforation of the meningeal sinus. In this case, the doctor either sews up the holes and continues working, or applies stitches and postpones further actions until after healing.
Next, the dental surgeon decides to immediately place an implant if there is a slight lack of bone, or:
- add bone material;
- apply a membrane;
- cover the bone with gum;
- apply stitches.
After the new materials have implanted, the patient returns after 3-4 months to have implants installed.
Contraindications
Any surgical intervention has contraindications and sinus lift surgery is no exception.
Absolutely prohibited:
- clotting problems and other disorders of the heart and circulatory system (including heart failure);
- various diseases of the immune system, including AIDS and HIV (can lead to implant rejection);
- hormonal diseases (thyroid problems and diabetes);
- recent chemotherapy or radiation therapy;
- oncological diseases in the active phase of treatment;
- any bad habits such as alcoholism, smoking, etc.
There are also relative contraindications that can be addressed before lifting surgery:
- acute viral infections;
- ENT diseases in the acute phase;
- dental caries and stomatitis.
Important! Hold off on manipulations for colds, especially those accompanied by a runny nose. First - health, then - implants.
Thus, before going to the surgeon, it is necessary to sanitize not only the oral cavity, but also the entire body.
If lifting is still contraindicated for the patient, then shorter implants and a conditionally removable prosthesis can be installed.
Materials used
Material for bone tissue augmentation can be:
- Autograft is the patient’s native bone, which is obtained by cutting from the lower jaw or chin. Afterwards, the material is crushed and the pocket formed by raising the sinus is closed. This material prevents rejection by the immune system, engraftment is ideal, however, the downside is the high risk of injury - you need to wait for two surgical sites to heal, especially if a lot of material is required for filling.
Attention! Internal components thin out faster and in this case additional augmentation will be required.
2. Materials of animal origin, which are obtained from samples of bones of cattle. In this case, after grinding, the substance undergoes mandatory sterilization and removal of impurities (collagen) for drying. The resulting crumbs can be adjusted to the required size by pressing into blocks. This material has a good survival rate and low cost, so it is most common among surgeons. The animal components begin to interact with the tissues that surround them, forming new bone and being resorbed when the job is done.
On a note! Often, animal tissue is mixed with autograft to reduce the cost of surgery.
3. Artificial fabric - consists of synthetic fibers - granulate or calcium phosphate. The composition contains a replacement for the building bone substance - hydroxyapatite. The action is similar to the animal component; after bone growth, resorption occurs. Modern materials are high cost, but stimulate an active regeneration process, as well as biocompatibility.
The choice of material depends on several factors:
- the amount of bone tissue to be inserted into the sinus;
- the capabilities of the patient's lower jaw;
- funds available to a person.
What happens after
Complications after a sinus lift are possible, since this manipulation is considered a full-fledged surgical intervention. The only question is how to avoid most of them and prepare for treatment.
Medical errors
They can be avoided if you choose a trusted clinic. Choose carefully who you trust with your jaw to avoid:
- Incorrect choice of augmentation method (this can happen due to illiterate diagnosis and determination of bone tissue thickness), resulting in rapid rejection or destruction of the implant;
- Violation of operation technology and sanitary standards.
The dentist’s inexperience may also manifest itself during the manipulation process:
- perforation of the sinus wall - this requires urgent suturing of the film or application of collagen material, you need to act quickly and accurately;
- in turn, undetected perforation leads to the entry of bone tissue into the maxillary sinuses, which in the future will manifest itself as constant congestion, sinusitis and other complications;
- bleeding is a common situation, but can unsettle you;
- infection in case of non-compliance with epidemiological rules, which leads to tissue suppuration, chronic infectious diseases of the respiratory tract and the formation of cysts.
Reviews from patients and friends will help you avoid “medical” complications after a sinus lift. Approach this with full responsibility.
Patient unconsciousness
Choosing a good clinic is not enough. It is important to follow all the recommendations given by the specialist after the operation, and also not to withhold information at the stage of collecting anamnesis and diagnosis. Violation of these principles will lead to:
- inflammation of the sinuses;
- uncontrolled bleeding during and after manipulations;
- suture infection and bone inflammation;
- rejection or slight mobility of implants;
- pushing artificial materials deep into the jaw (in case of violation of nutritional rules);
- loss of transplanted tissue due to severe sneezing and coughing;
- ENT complications.
Recommendations
The list of tips for maintaining the desired effect is quite extensive, here are the main points:
- take prescribed medications on time, especially antibiotics and anti-allergy drugs;
- follow a certain diet - only soft and warm food in the first weeks before the sutures are removed, chew on the healthy side to avoid unnecessary stress;
- Avoid physical activity until the sutures are removed, then only light exercise for up to a month;
- If possible, avoid air travel;
- to avoid swelling after sinus lifting, it is necessary to avoid visiting the pool and saunas;
- do not create unnecessary tension in the nasal cavity - try to sneeze, cough and blow your nose less.
Inconvenience can be avoided if an implant is placed in time to replace the extracted tooth. But, if there are indications and time has passed, select a reliable specialist and then everything will go well.
Differences between open and closed procedures
What is the difference between open and closed sinus lift? All the features of each variety have been described in detail above. But, in short, with the open type of operation, a large “window” is created on the side of the jawbone, through which the bottom of the sinus is raised and the graft is inserted. This is more traumatic, recovery takes longer - complications arise more often, and there are more dietary restrictions. Unlike the open type, the closed type does not need such a “window” - small round holes at the bottom are enough. Since tissues are injured less, complications occur less frequently, and rehabilitation occurs faster.
Platelet Rich Plasma
To stimulate the growth of the patient's own bone, PRP technology is used - platelet rich plasma - platelet rich plasma. Before the sinus lift begins, a test tube of blood is taken from a vein. It is placed in a centrifuge, in which it is separated into fractions within 12 minutes, one of which is platelet-rich plasma. Using this method, it is possible to obtain bone growth factors. Unlike collecting your own bone, which also contains growth factors, obtaining a tube of venous blood is much easier. By using the patient's own blood, the risks of incompatibility and allergic reactions are eliminated.
How to Avoid a Sinus Lift
Is implantation possible without sinus lift? In general, the ideal option would be a timely visit to the implantologist after tooth extraction (or even before extraction, but when all the prerequisites for this are present), before the bone substance has time to atrophy. How else can you do without raising the sinus floor and building up the bone? If the dentist, after studying the images, still insists on performing osteoplasty of the upper jaw, then it is worth considering alternative approaches - dental implantation with immediate loading, the basal method. But this is only provided that you need to restore from half of the dentition to all the teeth, otherwise there will still not be enough space for the implant (for a vertical, not an inclined installation).
The principle of attaching implants to bone tissue with immediate loading protocols allows complex areas of atrophy to be bypassed in 50% of cases. And the prosthesis can be installed within 3 days after implantation. These techniques often become a panacea for people with bone atrophy, but not always. Therefore, before making a final decision, we recommend visiting an implantologist who practices the Immediate Load method and consulting with him.
Modern drugs for anesthesia in dentistry are completely safe and do not cause complications
Numbness after local anesthesia lasts only a couple of hours, and patients recover from general anesthesia immediately. The risk of an unfavorable outcome is usually not due to side effects of the drug, but to drug inconsistencies and incorrect training of the anesthesiologist, which occur very rarely.
Levin Dmitry Valerievich
Chief physician, Ph.D.
Recommendations during the rehabilitation period
Sinus lifting is considered a traumatic procedure with a long recovery period. And almost all patients are concerned with questions such as how long it will take for the wound to heal, when the swelling will subside, how to eat properly or which side to sleep on, what not to do after treatment, why not to fly on an airplane, go to the bathhouse, play sports, etc. To reduce the number of possible negative consequences after surgery, you should be very careful about all the recommendations of your doctor:
- do not forget about drug therapy: take all prescribed medications in a timely manner - antibiotics, antihistamines, use medicinal dental ointments and gels, make cold compresses, do not heat the cheek. The pain will gradually disappear by day 5-7, and swelling may increase on day 2-3, and then subside within 3-5 days. The wound can heal completely in 7-14 days,
- you need to fully rest and devote enough time to sleep: at work you will have to take sick leave - for at least 3 days,
- follow a certain diet: in the first week before the sutures are removed - only soft or ground food, warm (neither hot nor cold). Too hard foods should be excluded from the diet. Chew on the healthy side without putting pressure on the affected area. Failure to comply with the diet can lead to displacement of implants and a decrease in the volume of implanted materials,
- physical activity should be excluded: any serious physical effort or active sports before the sutures are removed can lead to unpleasant consequences. Also, you should not pick up something from the floor by bending towards the object - any changes in body position are made only with a straight back (that is, you first need to sit down and then straighten up),
- Air travel is prohibited: pressure changes contribute to the narrowing and expansion of blood vessels, bleeding, loss of bone chips,
- postpone visits to the pool and saunas: jumping into water and diving are also not allowed - this is also associated with changes in the lumen of blood vessels (it narrows from cold, expands from heat). Bleeding may begin, swelling or inflammation may increase,
- You should not drink from a straw: low pressure is created in the oral cavity, but in the maxillary sinus it remains normal. This creates a threat to the integrity of the sutures and the extrusion of bone substance into the oral cavity,
- you should not blow your nose: after the procedure, transparent contents may come out of your nose - you should not blow it to avoid pressure changes in the sinuses - it is better to simply wipe your nose with a paper napkin,
- It is better to sleep on the healthy side or on your back (with a high pillow under your head): so as not to stimulate a strong blood flow to the “sick” side.
Bone atrophy – cause or effect?
Atrophic changes in the bone of the upper jaw, depending on the clinical situation, can be both a cause and a consequence of tooth loss. Bone tissue is involved in many pathological processes, for example, with periodontitis, periodontal disease, osteoporosis, tumor development and a number of other diseases. Tooth loss in such cases occurs due to changes in the quantity and quality of the bone mass, which simply cannot fully fix the teeth. However, sometimes bone atrophy is a consequence of prolonged absence of teeth. If a patient has had a tooth removed for medical reasons or has lost a tooth due to injury or aging, then it is necessary to restore the integrity of the dentition as soon as possible.
Prolonged absence of teeth and physiological chewing load leads to atrophic changes and a number of other unpleasant consequences, which include:
- Speech dysfunction;
- Difficulty chewing and, as a result, digestive problems;
- Aesthetic problems associated with changes in the configuration of the facial part of the skull, premature appearance of wrinkles;
- Violation of the location of other teeth;
In addition, prolonged absence of teeth and bone atrophy create favorable conditions for the spread of inflammatory and infectious processes in the oral cavity. Therefore, regardless of the reason for tooth loss or extraction, you must always consult with a dentist about options for restoring it.
Consequences and complications of surgical intervention
Is a sinus lift dangerous and is it worth doing? This is a rather complicated procedure that scares off many people due to the presence of a large list of unpleasant consequences. However, if the surgical intervention is performed by a professional and experienced doctor, and the patient follows all his recommendations before and after, problems should not arise. However, this is an ideal situation when all risks are excluded - therefore, information about possible complications and their symptoms can be very relevant for patients. Let's look at the dangers of subantral augmentation - the most common problems that arise after the procedure.
Complications due to medical error
As mentioned above, osteoplasty is performed by a maxillofacial surgeon - and it is favorable if the clinic has an ENT surgeon (who can help with perforation of the maxillary sinus). But not all institutions have specialized specialists. You should approach the choice of a clinic very carefully and find out in advance about the qualifications and experience of the doctor. Complications arising due to the fault of the doctor are most often associated with the following situations:
- illiterate planning of the procedure: for example, they incorrectly determined the height of the bone and chose the wrong method of operation or implanted substance. As a result, the graft may not take root or be quickly resorbed,
- lack of experience: violation of technology or sanitary standards.
Possible complications during the sinus lift operation itself:
- perforation of the sinus wall: occurs in 25% of clinical situations. The membrane can be damaged during an osteotomy, raising the sinus floor with an instrument, or when installing an implant. Immediate suturing of the membrane (if it is sufficiently dense) or application of a collagen absorbable membrane will be required,
- insertion of a bone graft into the maxillary sinus: if the doctor did not notice the perforation. May manifest as sinusitis, pain, bloody or purulent contents from the nose,
- bleeding at the time of osteotomy: also occurs quite often - the doctor eliminates the problem on the spot,
- infection of the operated area: surrounding tissues may fester, chronic sinusitis may occur after surgery, as well as sinus cysts and sinusitis.
Complications due to violations on the part of the patient
If the patient does not follow the doctor’s recommendations or conceals information about diseases that can negatively affect the quality of maxillary augmentation, the following complications may occur:
- inflammation of the maxillary sinus,
- bleeding and sharp pain in the operated area,
- wound infection, bone inflammation,
- mobility or rejection of implants,
- pushing implants deep into the sinus: due to non-compliance with nutritional rules,
- loss of the graft: with a strong cough or sneeze, the stitches may come apart and the material may spill out,
- development of ENT diseases.
Dental implantation using the Osstem system = 18,500 rubles. until January 15, 2022!
All inclusive, treatment guaranteed!
Premium implants at an affordable price. Free consultation with an implantologist +7 (495) 215-52-31 or write to us
A negative consequence may be non-engraftment of the bone material or its rapid resorption. In general, the percentage of effectiveness of the operation (without simultaneous installation of implants) is in the range of 40-60%. That is, 4-6 patients out of 10 will have to undergo the procedure again - and this also does not always give a good result. It happens that due to constant interventions, your own bone becomes so small that augmentation can no longer be carried out. Therefore, it is better to either immediately choose implantation with immediate loading, or do extensions with simultaneous implantation.
Who is indicated for the operation?
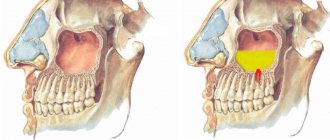
Any type of osteoplasty is used when the quantity or quality of the patient’s own bone tissue is insufficient for dental implantation. Sinus lifting is chosen in cases where implants need to be installed in the lateral parts of the upper jaw. The main anatomical feature of this bone is considered to be the presence of the maxillary sinus, which consists of two paired cavities located in the lateral sections. The maxillary sinus belongs to the paranasal sinuses and plays an important role in maintaining the normal functioning of the upper respiratory tract.
To make room for the introduction of bone replacement material when performing a sinus lift, the surgeon carefully lifts the lower wall of the maxillary sinus. After the introduction of bone replacement material or the installation of an autograft, an implant is implanted, for the engraftment and stabilization of which all conditions have now been created. The general indications for performing this manipulation are the loss of a tooth or teeth, accompanied by a lack of bone tissue. Most often, a similar clinical picture is observed in the following conditions:
- Inflammatory gum diseases. Stomatitis, gingivitis and periodontitis are the most common inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, regardless of gender and age. If these diseases are not treated in a timely manner, bone tissue is involved in the pathological process, which leads to tooth loss.
- Advanced forms of caries. Caries develops quite slowly and with regular visits to the dentist the unpleasant consequences of this disease can be avoided. The development of this pathology is influenced by improper oral hygiene, eating large amounts of foods containing sugar and many other external and internal factors.
- Endocrine pathologies (diabetes mellitus). With decompensated diabetes mellitus, periodontitis often develops, which, without proper treatment and without normalizing blood glucose levels, can lead to premature tooth loss;
- Malocclusion. One of the most severe consequences of malocclusion is tooth loss and bone atrophy. This occurs due to improper distribution of the chewing load and the development of periodontal disease. Therefore, bite correction should be done as early as possible;
- Osteoporosis. This systemic bone disease significantly reduces the quality of life of patients. One of the manifestations of the disease is bone tissue atrophy followed by tooth loss. Treatment should be aimed at normalizing metabolic processes;
- Injuries to the facial part of the skull. To avoid atrophy, it is necessary to restore teeth lost due to injury as quickly as possible. In some cases, due to significant deformations, injuries to the facial part of the skull may become a contraindication to sinus lifting;
- Physiological aging of the body. In old age, teeth fall out due to chronic oral diseases, bad habits, insufficient oral hygiene, concomitant diseases, metabolic disorders;
- Poor oral hygiene. Promotes the development of inflammatory and infectious diseases of the oral cavity and, as a result, tooth loss;
- Bad habits (smoking). Smoking has a bad effect not only on tooth enamel, but also on the blood vessels of the oral cavity, creating favorable conditions for the development of pathological processes;
The presence of any of the above conditions is dangerous for the development of atrophic processes in bone tissue and is a potential indication for sinus lifting. However, prompt treatment of dental and gum disease can prevent or significantly delay tooth loss and related problems.
Reviews from doctors and patients
Sinus lifting is often the only solution for people with bone atrophy - a statement that most doctors agree with. But professionals also consider alternative methods (discussed above) to be an excellent solution. A lot here depends on the individual characteristics of the body. Patient reviews of maxillary augmentation vary greatly - this is mainly due to their well-being during the rehabilitation period. The fastest recovery occurs after a closed sinus lift with the additional use of a membrane.
Open
The first step is to numb the surgical site. Local anesthesia, as for dental treatment. The procedure itself is painless.
At the second stage, an incision is made in the gum in the area of the missing teeth. The gum itself moves upward, exposing the underlying bone tissue. Then access to the maxillary sinus is created. With the help of special instruments, the wall of the maxillary sinus is thinned, limiting it from the oral cavity. The inside is lined with mucous membrane (Schneiderian membrane). During surgery, the mucous membrane peels off and rises.
Bone replacement material is placed in the resulting space, which eventually dissolves and is replaced by its own bone.
Despite the apparent complexity of the procedure, open sinus lift has several advantages. It is possible to significantly increase the volume of bone in the maxillary sinus area, even in cases where the distance to it is only 1 mm. The operation is performed under direct vision control, so the implant surgeon can take into account all anatomically complex areas and avoid complications, for example, rupture of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus.
Open sinus lift with immediate installation of implants.
Cost of the operation
How much does a sinus lift cost? The average price of closed-type augmentation is 25 thousand rubles, and the open type costs higher - about 30 thousand. If a synthetic or animal graft is needed, the cost will increase by approximately 10 thousand rubles. Membrane application – from 15 thousand. The price of preliminary sanitation of the oral cavity is very individual - it may be that it is not needed at all, but most often it is necessary to cure several carious teeth and have professional oral hygiene done. You can also save on treatment. For example, if you go to a regional clinic or choose Russian material for osteoplasty rather than foreign. When implants are installed at the same time, the cost of treatment also increases.
Author: Bespalov R. D. (Thank you for your help in writing the article and the information provided)
Price
The price of a sinus lift consists of the work of the implantologist, as well as the cost of bone replacement materials.
The average cost of a sinus lift is 30-70 thousand rubles.
A closed sinus lift, especially with a slight elevation of the bottom of the maxillary sinus, can be performed without the use of additional bone replacement materials.
| Expert, author of the article: Akhtanin Alexander Pavlovich Orthopedic dentist, implantologist 35 years of implantation experience Material updated: October 11, 2022 |
Preparing for surgery
Sinus lifting is performed only after a thorough examination of the patient. When diagnosing, the doctor chooses the method of performing the procedure based on X-ray data - structure, density, total bone volume, location of the roots of nearby teeth.
A comprehensive examination of the patient is carried out to exclude restrictions to sinus lifting:
- Chronic and acute inflammatory processes of the nasopharynx (sinusitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, etc.)
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding period.
- Coagulopathies of congenital and acquired nature.
- Severe cardiovascular diseases, heart failure.
- Chronic pathologies in the stage of decompensation.
- Mental disorders.
The doctor weighs the pros and cons and decides whether to perform surgery or look for alternative treatment methods.
Recovery period
After biosinus lifting, the patient follows a number of recommendations:
- On the first day, it is forbidden to swim in a hot bath or steam in a sauna, or drink alcoholic beverages.
- Physical activity is excluded (on average for one to two weeks).
- Every 3-4 hours after surgery, cold is applied to the cheek in the wound area to eliminate swelling.
- The doctor prescribes a course of antibiotics, healing ointment, analgesics and a disinfectant rinse solution. The patient must strictly adhere to medication prescriptions.
- A new soft toothbrush is used to brush your teeth (on the 2nd day after surgery). It is recommended to use for two weeks. Then they proceed to the usual cleaning. During the first days after surgery, cotton swabs soaked in an antiseptic solution are used to clean the wound surface.
- Rinsing is carried out with an antiseptic solution for 7 days, after each meal.
If the rules are not followed during the rehabilitation period, there is a risk of complications. After surgery, the patient must carefully evaluate the condition to prevent complications. If suspicious symptoms appear, you should immediately go to the dentist and determine the cause.
Recovery period
Even if the procedure was successful, complications may arise in the first few days, especially if the patient neglects the doctor's advice. Until the soft tissues heal, it is recommended to eat soft or liquid food at a comfortable temperature. Eating hard, rough foods or hot food can damage the wound.
You should not smoke, as nicotine constricts blood vessels and tissues heal worse. In the first week, you should not overheat the body, engage in sports or heavy physical labor, otherwise bleeding may occur. It is better to sleep on the side where no surgical procedures were performed.
The positive aspects of the technique are noted by many scientific and clinical studies
- Bone tissue of animal (or cadaveric) origin is not implanted.
- there is no rejection of the injected drug.
- there is no inflammation in the paranasal sinus.
- there is no introduction into the body and no change in the biological laws of regeneration.
- the body’s own bone cells and active regeneration proteins “deceive” the body’s immune system, which allows almost 100% of the planted substrate to degenerate into bone tissue.
- rapid implantation.
- mini-incision of the mucous membrane.
- bio sinus lift can be performed simultaneously with implantation.
- rare and minimal swelling.
- no pain in the postoperative period.
Bone material and membranes for sinus lift
Own bone
In the first case, the donor of the bone material is the patient himself - bone chips are taken from the chin or lower jaw area. Previously, it was believed that such a graft survives with minimal risk of rejection. However, the 30% risk of proven self-dissolution of the transplanted block forced us to abandon block transplantation many years ago. The second reason why we do not use this is that autogenous transplantation is more traumatic for the patient, since it involves surgical intervention in two places at once; rehabilitation is very memorable, especially in older patients.
Donor and artificial bone
An alternative material is donor bone taken from another person or animal, as well as artificial substances. In this case, the risk of rejection is higher, although the materials are always processed to improve survival rate. There are observations that prove that when using donor blocks it is impossible to guarantee the ideal biological purity of samples. Difficult choice for hygienic and ethical reasons.
Osteoplastic stimulators of bone regeneration
The best option, but the most expensive. There is no need to transplant a bone from a leg, and there is no need to transplant foreign bones either. A very quiet and honest bone growing technology. Genuine American growth stimulants cost from 22,000 rubles per mini bottle. Such stimulants are not found in network clinics or “promotional implantation” clinics. There are a lot of Russian and Asian analogues, I can’t comment on the results of their use, I haven’t tried them.
Membranes
Resorbable membranes during sinus lifting perform an important barrier function - they separate the space in which new bone is formed from the rest of the cavity of the maxillary sinus. Over time, the membrane dissolves. The membrane is necessary to keep the osteoplastic material stationary.
Postoperative period
All patients of our Center receive a set of necessary medications and instructions with recommendations that must be followed to avoid complications.
First days
- For the first few hours, it is recommended not to eat, drink or smoke anything.
- Rinse three times a day with special combined antiseptic agents from the kit.
- Take medications strictly as prescribed by your doctor.
For patients who want to recover faster, an accelerated rehabilitation complex .
Aimed at improving microcirculation, restoring the integrity of soft tissues, reducing swelling and hematomas.
Bioreparation - injections of hyaluronic acid biostimulants with vitamins, amino acids and microelements to improve the condition of facial skin
PRP plasma lifting - injections of blood plasma to improve tissue regeneration, accelerate healing, eliminate bruises and swelling
Microcurrent therapy - exposure to weak pulse currents accelerates recovery processes at the cellular level, relieves micro-spasms and pain
Levin Dmitry Valerievich
Founder and Chief Doctor of the Center
Wound healing period
Over the next 14 days, when eating, you should take care of the operated side, avoid getting pieces of food and liquid, and avoid injury while brushing your teeth.
Period of final bone maturation
After the final healing of the soft tissues, the longest period begins - the formation of new bone structures. It lasts for several months, and dosed loads are allowed on the operated side. Recovery is monitored using x-rays every 1-2 months.
Read more about the postoperative period - After sinus lift
Price in Moscow
The cost of a sinus lift depends on several factors:
- sinus lift techniques;
- type, volume and authenticity of consumables;
- the number of membranes used, reinforcing pins;
- the presence of a special surgical operating unit;
- disposability of instruments
- qualifications of the anesthesiologist performing sedation;
- additional possibilities (probability of immediate implantation).
It is beneficial in a batch calculation, when implantation is immediately included and combined with a sinus lift operation in one visit. Thus, the complex includes all services for preparation for operations and their implementation, in one visit. Prices for sinus lifting in Moscow in all clinics are approximately the same, the work performed on average costs about 50,000 rubles per side, radical differences are determined only in additional consumables.
The main problem of choosing a comfortable price is that the harmony of cost is always regulated by savings on consumables and at the level of the work performer, the doctor’s competence is the main factor in explaining the price, the pretentiousness of the clinic has nothing to do with it.