In medical practice, subluxation of the jaw is most often observed in the majority of victims who suffer from chronic diseases. To ensure that the injury does not begin to progress and other associated complications do not arise along with it, you must immediately seek help from a qualified doctor who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Timely seeking help will prevent the development of such ailments: gout, arthritis and rheumatism.
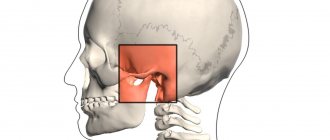
In most cases, subluxation of the lower jaw occurs as a complication associated with a previously received dislocation. Despite the specific similarity of the injury, dislocation and subluxation are two different injuries in structure: with a standard dislocation, the jaw joint completely comes out of the cavity, and with subluxation of the mandibular joint, it only moves a small distance. In both cases, the victim feels piercing pain and cannot open and close his mouth normally.
Causes
For each patient, the intensity of mechanical impact for the development of the problem is different. In some people, subluxation can develop when yawning, while others suffer serious blows to the jaw without consequences.
In general, there are a number of situations that lead to displacement of the bone structure:
- Road accidents, fights, traumatic sports in which the maxillofacial region suffers.
- Yawning with a wide opening of the mouth.
- Shout.
- Trying to bite off a hard or large piece of food.
- Involuntary muscle contraction during epileptic or convulsive seizures.
Jaw displacement is not always associated with traumatic factors. Pathology often manifests itself against the background of internal disorders in the human body:
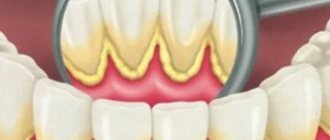
- osteomyelitis;
- arthrosis;
- gout;
- rheumatism.
These diseases gradually lead to joint degeneration and loss of functionality. As a result, the shape of the bones changes and the ligaments are weakened.
Classification
Dislocation and subluxation of the lower jaw differ from each other in symptoms and the degree of damage to the joint. When the TMJ is dislocated, the head flies out of the articular cavity completely. Dislocations are classified by type depending on various criteria. Depending on the time of injury, a distinction is made between chronic and acute dislocation (no more than 10 days have passed since the injury to the joint). Depending on the number of affected bone structures, jaw injury is divided into simple or complicated. In the first case, only the joint is involved in the pathological process. In case of complicated injury, stretching of the ligamentous apparatus is observed.
Depending on the cause of occurrence, a problem of a traumatic and acquired nature is distinguished. In the first case, the jaw shift occurs due to external factors. The chronic type of pathology is associated with the failure of the joint functions and limitation of its mobility.
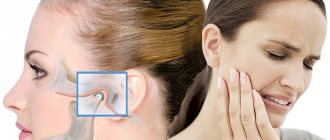
The photo shows the areas of the jaw joint most susceptible to damage.
Structure of the lower jaw
- 1 – mandibular foramen;
- 2 – elevation of the lower jaw;
- 3 – temporal mandibular ridge;
- 4 – lower tongue;
- 5 – large retromolar triangle;
- 6 – retromolar fossa;
- 7 – wing-shaped roughness;
- 8 – sublingual line;
- 9 – radical system;
- 10 – incisors;
- 11 – alveolar edge;
- 12 – submental eminence;
- 13 – main bone of the chin;
- 14 – jaw notch;
- 15 – body of the lower jaw;
- 16 – alveolar tubercles;
- 17 – jaw angle;
- 18 – rough surface for masseter;
- 19 – external oblique line;
- 20 – branch of the lower jaw;
- 21 – joint;
- 22 – articular notch;
- 23 – joint;
- 24 – condylar process;
- 25 – semilunar notch;
- 26 – crown-like process.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a dislocated jaw are in most cases the same for all types of injuries. Characteristic signs of the problem: severe swelling of the soft tissues in the damaged area, increased salivation, limitation of joint mobility and range of motion.
Bilateral anterior dislocation of the temporomandibular joint is supplemented by:
- the inability of a person to close his mouth;
- severe swelling in the ear area;
- the patient's lack of intelligible speech.
With a unilateral lesion, the oral cavity becomes skewed towards the affected joint
Bilateral posterior dislocation is accompanied by its own distinctive signs:
Treatment of the jaw joint
- swelling and pain of the earlobes;
- the patient’s inability to open his mouth slightly;
- displacement of the jaw to the mesial position;
- the occurrence of symptoms of suffocation in a horizontal position;
- difficulty pronouncing words.
Subluxation of the jaw has the same symptoms, but the joint is able to maintain partial mobility. When changing its position, the victim often hears a characteristic click.
Diagnostics
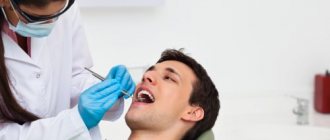
To determine the severity of the injury, the patient is sent for x-rays. It will help to identify the exact clinical picture of a certain type of dislocation (one or two-sided). The image will show how much displacement of the joint has occurred. This will help your orthopedic surgeon prescribe an initial course of treatment (for severe cases). X-rays can also help differentiate a subluxation from a jaw fracture. If the orthopedist still has doubts about the diagnosis, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), axiography and arthroscopy of the joints are additionally prescribed.
In most cases, the subluxation is adjusted by the doctor manually, without applying significant physical force.
In more severe cases, surgical intervention is performed: the head of the joint is narrowed and fixed with staples. A timely visit to the clinic will help to avoid disturbances in chewing functions and prevent the recurrence of injuries.
First aid
Before visiting a doctor, the patient must be given first aid. All measures in this case will be aimed at minimizing the load on the joint and reducing the intensity of pain symptoms.
First of all, the affected joint is immobilized with a bandage or scarf. The jaw is fixed from top to bottom and from front to back using two flaps of fabric. At this time, the patient is prohibited from speaking and opening his mouth wide.
Options for fixing the jaw using a bandage
If a person has dislocated his jaw, his mouth will be slightly open. To prevent dirt and dust from getting into the cavity, cover it with a damp cloth. This will also reduce saliva production. For severe pain, a non-steroidal solution can be administered intramuscularly. An ice container is placed at the site of the suspected injury to reduce the severity of swelling. This event will also reduce the intensity of pain.
Which doctor should I go to if I have a problem? Jaw injuries require consultation with a surgeon. After examining the patient, the doctor decides whether to realign the joint or perform surgery. Jaw subluxations often occur in the dentist’s office, when the patient opens his mouth wide during manipulation. In this case, the specialist provides the person with qualified assistance on the spot.
If bone damage occurs at night, an ambulance is called for the person. The victim is taken to a 24-hour emergency room, where the necessary manipulations are performed. Before determining a treatment regimen, the doctor orders an x-ray to analyze the characteristics of the injury.
Joint reduction method
What to do if the jaw joint is damaged? Treatment of the pathology includes moving the joint to its original position. For this purpose, there are many techniques used by traumatologists. A person can use some of these methods independently, if they have the skills and knowledge.
Hippocrates' method
Before putting the jaw back in place, the doctor gives the patient an X-ray. For reduction, general or local anesthesia is used, as the procedure is accompanied by acute pain.
The specialist wraps the thumbs with a bandage and presses them on the root elements. The doctor fixes the mandibular joint with the remaining fingers. Such manipulations are necessary to relax the masticatory muscles.
After this, the doctor shifts the jaw mesially (towards the teeth) and upward until a characteristic click appears when the head is inserted into the capsule. The person is given a special bandage for a week. During treatment for a dislocated jaw, it is forbidden to open your mouth wide and consume hard foods. The diet during rehabilitation includes vegetable and fruit purees, soups and cereals. All products must be well chopped before consumption. It is also important to avoid situations where there is a risk of injury to the jaw.
Reduction of a dislocated jaw using the Hippocratic method
Popescu method
This method is used for habitual dislocation, since other methods will be ineffective or will lead to a worsening of the situation. The procedure must be performed under local or general anesthesia.
The patient lies in a horizontal position, and the doctor places cotton swabs between the teeth above and below. The movement on the chin is carried out upward and backward. The bolsters prevent injury to teeth and soft tissues as the jaws move into place.
If the Popescu method does not help, then they resort to surgery, which is subsequently supplemented with physiotherapeutic measures and wearing corrective devices.
Blechman–Gershuny method
The method is suitable for straightening the jaw at home. These activities are usually taught to relatives of a patient who suffers from chronic subluxations of the jaw joint. First, the displaced process is felt, and then pressure is applied back and down.
After the procedure, the victim is given a fixing bandage for 5 days. If the condition worsens: accompanied by pain in the temple, increased signs of swelling and the inability to open the mouth, then you should immediately consult a traumatologist.
You can put the joint back in place yourself using special splints on the teeth. The method is used only for chronic forms of the problem. The devices unload the affected jaw, giving it time for rapid regeneration. In parallel, anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out. Hormones (hydrocortisone) are injected into the affected joint. The procedure is performed by a doctor in an outpatient clinic or in a hospital setting.
Treatment of subluxation using the Blechman-Gershuny method
Symptoms and signs
The universal symptoms noted with any form of subluxation include:
- Painful sensations of varying severity, intensifying when trying to move the lower jaw;
- Deterioration of TMJ mobility, interfering with the usual way of life;
- Excessive salivation caused by impaired swallowing function.
Clinical cases characterized by bilateral lesions of the frontal zone are characterized by:
- Severe violation of occlusion, forcing you to keep your mouth open constantly;
- Headaches, swelling of tissues in the ear area, as well as impaired speech function.
With unilateral subluxation, similar symptoms are observed, but the patient has the opportunity to at least partially close the jaws, reducing the level of discomfort. But in the case of a posterior bilateral dislocation, the opposite situation arises - it becomes extremely difficult to open the jaws, since the lower section is pressed into the laryngeal region.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is more often prescribed for old injuries, when the joints have had time to change and become thinner under the influence of negative internal or external factors. Surgeons use several treatment methods.
Lindemann method. The purpose of the operation is to increase the size of the tubercle. Teflon materials are embedded into it and secured in place with metal seams. In addition, the articular notch is deepened. After Dindeman's operation, recurrence of dislocation is rarely observed.
Rauer's method. During the intervention, the articular tubercle is enlarged using grafts. Rib cartilage is used as the implanted material. Additionally, the joint capsule is reduced for better fixation in the jaw apparatus.
Self-reduction of a dislocated jaw is only possible if the victim or his relatives are trained in the technique of inserting the joint. Inept actions lead to fractures of bone structures, damage to soft tissues and nerve endings. The consequences of this require surgical intervention.
Prevention of the problem includes avoiding opening objects with your mouth and minimizing the consumption of hard foods. If you are prone to jaw loss, you should undergo regular dental examinations and diagnostic measures.